-
Easing contamination fears in Japan's food industry

With much of Japan’s manufacturing sector, land, and critical infrastructure badly damaged from the March 11 earthquake and tsunami, dairy and rice manufacturers have struggled to produce enough to feed the nation; Japan produces all of its own milk, rice, and yogurt products, but domestic plants are operating far below full capacity; shortages may persist into the summer; as production ramps up, fears of contamination from radiation leaked from the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant may dampen consumption; one analyst suggests that Japan institute a food tracking program that will allow consumers to track the production of food every step of the way to help ease fears
-
-
Release of radioactive water into ocean stopped

Radioactive water stopped flowing from Japan’s damaged nuclear power plant into the Pacific Ocean Wednesday after a special material was used, the utility said; the release, which began Monday, was described as an unavoidable process to avert a much bigger problem resulting from the leakage of the highly contaminated water; in terms of volume, about three million gallons of low-level radioactive water will have been dumped into the seas; the flooded basement of the buildings and their underground trenches at Nos. 1, 2, and 3 reactors are believed to hold about 60,000 tons of the more highly radioactive water; this water, which is also preventing workers from doing other emergency work, eventually will be stored in tanks at the reactors’ nuclear waste disposal sites, the government nuclear safety agency said. Those tanks will be shipped by the end of this month, the agency said
-
-
Modeling shows limited spread of Fukushima's radioactive release in ocean
Daily computer simulations are suggesting that, so far, the hazardous radioactive materials being released into the sea by the Fukushima nuclear plants are still largely restricted to areas near the coast; the powerful Kuroshiro current — the Pacific’s version of the Gulf Stream — tends to block contaminated seawater from flowing southward toward Tokyo Bay while picking up little contamination itself
-
-
IAEA: after Japan, no more nuclear "business as usual"

The world cannot take a “business as usual” approach to nuclear power in the wake of the disaster in Japan, UN atomic watchdog chief Yukiya Amano said; “Thinking retrospectively, the measures taken by the operators as a safety measure (were) not sufficient to prevent this accident,” Amano said; he added that the crisis in Japan caused by the 11 March earthquake and tsunami “has enormous implications for nuclear power and confronts all of us with a major challenge”
-
-
Scientific explanation overturned -- good news for nuclear fusion
A team of Duke University researchers has discovered, much to its surprise, that a long-accepted explanation of how nuclei collide to produce charged particles for electricity — a process receiving intense interest lately from scientists, entrepreneurs, and policy makers in the wake of Japan’s nuclear crisis — is flat out wrong; the discovery of the error makes nuclear reactors based on fusion more realistic
-
-
Subterranean salt beds to keep U.S. nuclear waste

Beds of salt up to one kilometer thick lie within one or two kilometers of the surface across much of the United States; they were deposited hundreds of millions of years ago by evaporating seas; a new study suggests that since President Obama killed the only national nuclear waste burial program — the Yucca mountain site — the United States should look again at the pre-Yucca plan to bury nuclear waste in subterranean salt beds
-
-
Algae might help reduce nuclear waste
The humble algae — Closterium moniliferum — might one day soon be used to help separate strontium from calcium in nuclear waste; if successful, the process could lead to a reduction in the amount of nuclear waste that is left over from nuclear power facilities, and might even help in cleanup when accidents occur such as the one in Chernobyl, Ukraine, that spewed great quantities of strontium into the surrounding environment
-
-
U.S. reactors have weaker back-up batteries than Fukushima Daiichi had
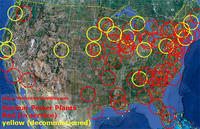
Almost all American nuclear power plants have backup batteries that would last only half as long as those at Japan’s troubled Fukushima Daiichi plant did after a tsunami knocked out power there; just eleven of the U.S. 104 plants had eight-hour batteries, and 93 had four-hour batteries; the batteries are not powerful enough to run pumps that direct cooling water, but they can operate valves and can power instruments that give readings of water levels, flow and temperatures
-
-
Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant lost
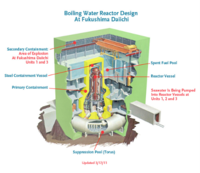
The radioactive core in the Unit 2 reactor at the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant appears to have melted through the bottom of its containment vessel and is now resting on a concrete floor; officials are now struggling with two crucial but contradictory efforts: pumping in water to keep the fuel rods cool and pumping out contaminated water; an investigation found that Tokyo Electric Power Co. officials had dismissed scientific evidence and geological history that indicated that a massive earthquake — and subsequent tsunami — was far more likely than they believed; more than 11,000 bodies have been recovered, but officials say the final death toll is expected to exceed 18,000. Hundreds of thousands of people remain homeless, their homes and livelihoods destroyed. Damage could amount to $310 billion — the most expensive natural disaster on record
-
-
Nuclear power here to stay

There are currently 441 large nuclear power reactors in 35 countries, 120 of which date from the 1970s and early 1980s; collectively the 400-odd reactors supply about 15 percent of the world’s electricity (the average in OECD countries being more than 22 percent); the United States has the greatest number operating, with 104 units providing 20 percent of its electricity supply; this is followed by France with 57 (producing nearly 80 percent of its supply), and Japan, with 54 (providing about 30 percent); so far, the world’s 441 reactors have racked up more than 14,000 reactor-years of operation; to generate electricity for a city of a million people, coal-fired power stations have to burn about three million tons of coals a year, releasing about ten million tons of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere in the process; to generate the same power, nuclear reactors consume only one ton of the fissile uranium isotope, U-235 — and release no carbon dioxide
-
-
Japan's disaster draws attention to little-known U.S. nuclear insurance plan
A little-known insurance pool in the United States that would provide insurance coverage for victims of nuclear reactor accidents occurring in the United States; the pool has been around for decades; Created under the Price-Anderson Nuclear Industries Indemnity Act of 1957 (Price-Anderson), the pool provides general liability insurance
-
-
Fifteen U.S. nuclear reactors are located in an active seismic zone
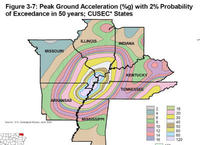
There are 104 nuclear plants in the United States, and fifteen of them are located in what is known as the New Madrid Seismic Zone, a region defined by a fault line of the same name; the New Madrid Seismic Zone involves eight states, and it is an active earthquake area in the central United States that follows the Mississippi River between Missouri, Kentucky, Arkansas, and Tennessee; while the U.S. earthquake zone is active, scientists say the ingredients do not exist there for a Japan-style nuclear disaster; should a large seismic event strike this part of the country, seismologists offer Christchurch, New Zealand, rather than Japan as an example of what to expect. In February, Christchurch suffered a 6.3 magnitude quake and billions of dollars in losses
-
-
Germany's drive to end nuclear power serves as model for others

Germany’s ambitious plan to wean itself from nuclear power and transition to renewable energy can serve as a valuable model for other countries seeking to do the same; nuclear power provides Germany with 23 percent of its energy; seven of its seventeen nuclear reactors will be taken offline; experts warn that the shutdowns could cause instability in the power grid and even blackouts; economists also say that the transition will be costly and result in higher energy prices for consumers; the government remains optimistic; renewable energy provides 17 percent of Germany’s energy needs and the Environment Ministry says that in ten years renewable energy will constitute 40 percent of all production
-
-
Zion's nuclear dry-cask storage solution
In Illinois, 28,588 fuel assemblies, each containing a bundle of 200 rods and weighing about 600 pounds, are cooling in pools on the ground or above reactors — as in Japan; experts say they are “very inviting targets for terrorists”; moreover, “No one has come up with a solution to safely store this waste for 10,000 years into the future”
-
-
NRC: Not all equipment failures at U.S. nuclear plants are reported
Companies that operate U.S. nuclear power plants are not reporting some equipment defects that could create safety risks, according to a new report; the Nuclear Regulatory Commission’s (NRC) inspectors found at least twenty-four instances where possible equipment defects were identified but not reported to the agency from December 2009 through September 2010; the NRC inspector general also raised questions in the report about the agency’s oversight, saying reporting guidelines for the nuclear industry are “contradictory and unclear”; unless the NRC takes steps to improve its reporting guidelines, “the margin of safety for operating reactors could be reduced” the report said
-
More headlines
The long view
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
