-
Toilet Challenge, 1: Caltech’s solar-powered toilet wins Reinvent Toilet Challenge
The World Health Organization reports that 2.5 billion people around the globe are without access to sanitary toilets, which results in the spread of deadly diseases; every year, 1.5 million people, mostly those under the age of five, die from diarrhea; Caltech scientist awarded grant to develop solar-powered sanitation system
-
-
Toilet Challenge, 2: Loughborough’s hydrocarbonization design wins second Reinvent the Toilet Challenge prize
Researchers from Loughborough University, located in Leicestershire, United Kingdom , won second prize in the Reinvent the Toilet Challenge; their toilet uses a process called Continuous Thermal Hydrocarbonization which kills all pathogens to create safe to handle, valuable material and uses power from heat generated during processing
-
-
Toilet Challenge, 3: U Toronto wins toilet challenge third place for sand filter and UV-ray design
The U of T solution is novel in its simplicity. It uses a sand filter and UV-ray disinfecting chamber to process liquid waste and a smolder chamber, similar to a charcoal barbeque, to incinerate solid waste that has been flattened and dried in a roller/belt assembly
-
-
Health consequences of the Fukushima disaster
The results of two studies in the 15 August issue of JAMA report on the psychological status of workers at the Fukushima nuclear power plants in Japan several months after the earthquake and tsunami in March 2011, and the amount of internal radiation exposure among residents of a city north of the power plant that experienced a meltdown
-
-
Climatic impacts of megapolitan expansion
Arizona’s Sun Corridor is the most rapidly-growing megapolitan area in the United States. Nestled in a semi-arid environment, it is composed of four metropolitan areas: Phoenix, Tucson, Prescott, and Nogales. With a population projection expected to exceed 9 million people by 2040; a first study of its kind, attempting to quantify the impact of rapidly expanding megapolitan areas on regional climate, showed that local maximum summertime warming resulting from projected expansion of the urban Sun Corridor could approach 4 degrees Celsius
-
-
Researchers move a step closer toward universal flu vaccine and therapies
Researchers describes three human antibodies that provide broad protection against Influenza B virus strains; the same team had previously reported finding broadly neutralizing antibodies against Influenza A strains; the work is a key step toward “universal” vaccine and therapies against flu
-
-
Wastewater key to addressing growing global water shortage

Parched cities and regions across the globe are using sewage effluent and other wastewater in creative ways to augment drinking water, but four billion people still do not have adequate supplies, and that number will rise in coming decades
-
-
Water sustainability flows through complex human-nature interactions
The fate of water in China mirrors problems across the world: water is fouled, pushed far from its natural origins, squandered, and exploited; China’s crisis is daunting, though not unique: two-thirds of China’s 669 cities have water shortages, more than 40 percent of its rivers are severely polluted, 80 percent of its lakes suffer from eutrophication — an over abundance of nutrients — and about 300 million rural residents lack access to safe drinking water
-
-
Immediate, in-the-field identification of hazardous materials

Soldiers in war zones, and law enforcement and first responders on the scene will soon have the ability to collect and immediately analyze trace amounts of potentially dangerous chemical, explosive, or biological agents with the help of a surface swabbing device developed and prototyped by a Maine-based technology company with the help of the University of Maine researchers
-
-
New detection device for forensic and security applications
A new biological sampling and detection device could soon be used by first responders in the forensic and security sectors; the patented technology allows for rapid sampling of up to eight targets simultaneously, testing powder, liquids, or surfaces directly and has applications across the forensic and security areas
-
-
USDA’s proposed chicken safety inspection policy could mean trouble for consumers
The federal government has come up with a new proposal to examine chickens for contaminates and diseases, and the proposal has some people concerned and others outright scared; the proposal would reduce the number USDA food safety inspectors at poultry plants from four to one – and rely on plant’s employees to do safety inspections instead
-
-
Dropping lake levels in Michigan are a cause for concern
In a state that boasts 11,000 lakes, Michigan is going through a year long drought that has residents and businesses scrambling as water levels continue to decrease; the low waters is the result of low snowpack last winter and a hot dry summer this year
-
-
Improved disaster resilience is imperative for U.S: report
A new report from the National Academies says that it is essential for the United States to bolster resilience to natural and human-caused disasters, and that this will require complementary federal policies and locally driven actions that center on a national vision – a culture of resilience; improving resilience should be seen as a long-term process, but it can be coordinated around measurable short-term goals that will allow communities better to prepare and plan for, withstand, recover from, and adapt to adverse events
-
-
Extreme summer heat events, global warming linked: research
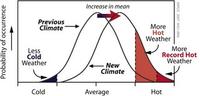
Since the late 1980s researches have been asserting that global warming would reach a point in the coming decades when its connection to extreme events would become more apparent; while some warming should coincide with a noticeable boost in extreme events, the natural variability in climate and weather can be so large as to disguise the trend; to distinguish the trend from natural variability, NASA researchers turned to statistics; the researchers did not focus on the causes of temperature change, analyzing instead surface temperature data
-
-
Canadian company offers the first treatment to neutralize red mud

Red mud is the most significant waste product of the traditional Bayer process for aluminum production; the industry produces more than 100 million tons of red mud a year, of which less than 5 percent is be reused; the rest is stored in ponds and reservoirs, posing serious environmental and economic risk; on 4 October 2010, for example, a flood of toxic red mud devastated Hungary after a retaining dyke ruptured, causing an ecological disaster; Canadian company Orbite Aluminae offers a technology to tackle the aluminum industry’s most serious problem
-
More headlines
The long view
What We’ve Learned from Survivors of the Atomic Bombs
Q&A with Dr. Preetha Rajaraman, New Vice Chair for the Radiation Effects Research Foundation in Hiroshima and Nagasaki, Japan.
Combatting the Measles Threat Means Examining the Reasons for Declining Vaccination Rates
Measles was supposedly eradicated in Canada more than a quarter century ago. But today, measles is surging. The cause of this resurgence is declining vaccination rates.
Social Networks Are Not Effective at Mobilizing Vaccination Uptake
The persuasive power of social networks is immense, but not limitless. Vaccine preferences, based on the COVID experience in the United States, proved quite insensitive to persuasion, even through friendship networks.
Vaccine Integrity Project Says New FDA Rules on COVID-19 Vaccines Show Lack of Consensus, Clarity
Sidestepping both the FDA’s own Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee and the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), two Trump-appointed FDA leaders penned an opinion piece in the New England Journal of Medicine to announce new, more restrictive, COVID-19 vaccine recommendations. Critics say that not seeking broad input into the new policy, which would help FDA to understand its implications, feasibility, and the potential for unintended consequences, amounts to policy by proclamation.
Are We Ready for a ‘DeepSeek for Bioweapons’?
Anthropic’s Claude 4 is a warning sign: AI that can help build bioweapons is coming, and could be widely available soon. Steven Adler writes that we need to be prepared for the consequences: “like a freely downloadable ‘DeepSeek for bioweapons,’ available across the internet, loadable to the computer of any amateur scientist who wishes to cause mass harm. With Anthropic’s Claude Opus 4 having finally triggered this level of safety risk, the clock is now ticking.”
“Tulsi Gabbard as US Intelligence Chief Would Undermine Efforts Against the Spread of Chemical and Biological Weapons”: Expert
The Senate, along party lines, last week confirmed Tulsi Gabbard as Director of National intelligence. One expert on biological and chemical weapons says that Gabbard’s “longstanding history of parroting Russian propaganda talking points, unfounded claims about Syria’s use of chemical weapons, and conspiracy theories all in efforts to undermine the quality of the community she now leads” make her confirmation a “national security malpractice.”
