-
Wastewater treatment plants spread antibiotic resistance
The products of wastewater treatment have been found to contain trace amounts of antibiotic resistant DNA. These products are often reintroduced to the environment and water supply, potentially resulting in the spread of antibiotic resistance.
-
-
Potential impacts of future heat waves on humans and wildlife
Climate change is often talked about in terms of averages — like the goal set by the Paris Agreement to limit the Earth’s temperature increase to 2 degrees Celsius. What such numbers fail to convey is that climate change will not only increase the world’s average temperature, it will also intensify extreme heat waves that even now are harming people and wildlife.
-
-
Feeling the heat: Recognizing the risks of extreme weather
Heat waves are more dangerous than tornadoes, statistically. They kill more people than sharks, and put more human lives at risk than blizzards, floods or lightning storms. But they lack a certain dramatic flair, making it surprisingly difficult for many people to grasp and evaluate the real danger lurking behind their devastating effects. Recognizing those risks could be a matter of life or death – especially as a changing climate is making dangerous extreme heat events more and more likely every year in the United States.
-
-
Could a booster shot of truth help scientists fight the anti-vaccine crisis?
The recent outbreak of measles cases in Clark County, Washington – which has been linked to a plummeting vaccination rate in this hotbed of anti-vaccination activism – makes clear that conspiracy theories, fear, and misinformation know no partisan bounds. One of the first lessons to be learned from this “metastasis” of science denial is how dangerous it is not to fight back. Science denial isn’t limited to fringe groups – if it isn’t fought in the trenches of corporate interest and ideology, it can spread not only to the general population, but to government too, with horrible policy consequences. What is the best way to fight back against such rank ignorance? What we need most to fight science denial is a better understanding of how science works, and we should point out that scientific claims are based on evidence. We should not pretend that vaccines are 100 percent safe. There have been isolated cases of negative reactions, sometimes even leading to death. These, however, represent such a small risk – as compared to the much larger one of dying from childhood diseases like measles or whooping cough – that unless a child is immuno-compromised, it doesn’t make sense to forego vaccines. Indeed, because there are immuno-suppressed children out there, one might say that it is the obligation of the rest of us whose children are not in such a risk group to make sure that our own children are vaccinated.
-
-
Rise of European populism linked to vaccine hesitancy

There is a significant association between the rise of populism across Europe and the level of mistrust around vaccines, according to a new study. “It seems likely that scientific populism is driven by similar feelings to political populism, for example, a profound distrust of elites and experts by disenfranchised and marginalized parts of the population,” says the study’s lead author. “Even where programs objectively improve the health of targeted populations, they can be viewed with suspicion by communities that do not trust elites and experts.”
-
-
Doctor-affiliated PACs fund candidates opposing gun safety policies
Researchers found that physician-affiliated political action committees provided more financial support to candidates who opposed increased background checks, contrary to many societies’ recommendations for evidence-based policies to reduce firearm injuries.
-
-
Reducing Illinois gun violence
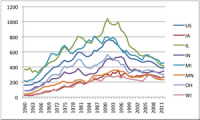
Illinois could reduce the number of people killed each year by gun violence by implementing ten policies supported by available research, according to a new report. The Johns Hopkins report identifies weaknesses or gaps in current Illinois law and offers recommendations to reduce gun violence.
-
-
Antimicrobial resistance: A neglected biodefense vulnerability
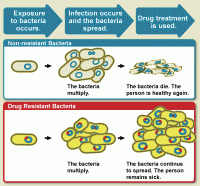
We typically think that biodefense is about defending against bioterrorism or the next pandemic – or, in extreme cases, about some laboratory accident. Biodefense is mostly about all these things, but also about much more. Antimicrobial resistance is not a headline-grabbing topic and it certainly is not getting its own apocalyptic outbreak movie anytime soon, but the microbial threat has been growing since antibiotics were first discovered.
-
-
Measles spreading in U.S., mostly among unvaccinated children

Measles is spreading in the U.S. As of 5 February, there were 50 cases in Washington state and five in Houston. New cases are being added daily. Health officials, including the U.S. surgeon general, are urging parents to get their children vaccinated.
-
-
A global wave of measles cases fed by conspiracies and misinformation has health officials worried

The number of people infected with measles keeps rising in the Washington State and neighboring Oregon. Rick Noack writes that “complacency over vaccinations has been accompanied by outright rejection of the scientific evidence on measles vaccines that has saved over 21 million lives since 2000, according to the WHO. Unsubstantiated conspiracy theories on supposedly negative side effects of vaccinations, either against measles or in a broader context, have gained momentum in some communities, in the United States and other countries.” He notes that deliberately spreading misinformation on vaccines to suggest that citizens are being lied to by their leaders has become a go-to recipe of some populist politicians. Thus, after years of railing against vaccines and even proposing a law against them in 2015, Italy’s Kremlin-supported Five Star Movement is now part of the country’s government.
-
-
Comparing technologies to remove arsenic from groundwater
At least 140 million people in 50 countries have been drinking water containing arsenic at levels above WHO guideline. A new study compares for the first time the effectiveness and costs of many different technologies designed to remove arsenic from groundwater.
-
-
Increasing murder rate is erasing gains in life expectancy among Mexican men
The murder rate in Mexico increased so dramatically between 2005 and 2015 that it partially offset expected gains in life expectancy among men there, according to a new study. “It’s common to see news reports about the toll that drug- and gang-related murders are taking in Mexico,” says UCLA’s professor Hiram Beltrán-Sánchez. “This study confirms that homicide is so widespread that even when considering all causes of death, it stands out as a factor in slowing growth in men’s life expectancy.”
-
-
Review of the “Digitization of WMD” symposium
The digitization of biological and medical science is providing exciting and promising new pathways for improving health and daily life for mankind and our environment. The possibilities for new treatments, better fitness, and less prevalence of genetic diseases are numerous. However, these technologies and the information associated with emerging techniques carry certain risks and vulnerabilities. It is through understanding these risks and continuing to develop mitigation strategies for them, especially during the technology conceptualization and development phases, that we can continue to build promising new tools to improve life with confidence while addressing how they should be properly used.
-
-
Denmark starts building anti-swine border fence
In a controversial move, Denmark, hoping to stop the crossing of disease-carrying German swine into the hog farming region on Denmark, has begun building a border fence along its 40-mile border with Germany. Denmark says the fence is essential for saving the Danish hog farming industry from collapsing. Denmark is the only European country where pigs outnumber people. The country exports about €4 billion of pork each year.
-
-
Death in the air: Revisiting the 2001 anthrax mailings and the Amerithrax investigation
Time may have dimmed the memory of the 2001 anthrax attacks and the sense of urgency surrounding the efforts to identify the attacker. The attacks, which involved mailings of five anthrax-laced letters to prominent senators and media outlets, killed five individuals and made seventeen others ill. The anthrax mailings played a crucial role in raising concerns over possible terrorist use of biological agents in attacks against the homeland. As a result of the anthrax scare, Americans’ perceptions of terrorism came to include an existential fear of biological terrorism.
-
More headlines
The long view
We Ran the C.D.C.: Kennedy Is Endangering Every American’s Health
Nine former leaders of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), who served as directors or acting directors under Republican and Democratic administrations, serving under presidents from Jimmy Carter to Donald Trrump, argue that HHS Secretary Roert F. Kennedy Jr. poses a clear and present danger to the health of Americans. He has placed anti-vaxxers and conspiracy theorists at top HHS positions, and he appears to be guided by a hostility to science and a belief in bizarre, unscientific approaches to public health.
