-
Radioactive material, leaked from a Russian nuclear complex, detected over Europe
The Russian state meteorological agency Roshydromet today released data which show exceedingly high atmospheric concentration of ruthenium-106 in the area where the Rosatom Mayak nuclear complex, located in the Southern Urals. The late-September leak, initially denied by Roasatom, the operator of the complex, caused the radioactive material to spread over northern Europe, where it was detected by IRSN and BfS, the French and German nuclear safety agencies, respectively.
-
-
Plague outbreak: where does it still exist, and could it spread?

An outbreak of plague has been occurring in Madagascar, with more than 2,000 cases and 170 deaths reported since August 2017. This island nation is one of the few remaining hotspots for plague in the world, with cases usually reported between September and April each year. It’s not possible to eradicate plague, as it is widespread in wildlife rodents outside the sphere of human influence. Outbreaks generally are managed reactively by “firefighting teams” deployed to clear houses of fleas, identify and treat cases and give pre-emptive treatment to contacts at risk. A more preventative approach, such as the identification of areas at risk using climate models and animal surveys to focus flea and rat control efforts would be better. But this requires a better understanding of transmission pathways in each region where disease persists.
-
-
Permissive concealed-carry laws tied to higher homicide rates
Easier access to concealed firearms is associated with significantly higher rates of handgun-related homicide, according to a new study. The study suggests that current trends towards more permissive concealed-carry laws are inconsistent with the promotion of public safety. “Some have argued that the more armed citizens there are, the lower the firearm homicide rate will be, because the feared or actual presence of armed citizens may deter violent crime,” said one of the authors. “Our study findings suggest that this is not the case.”
-
-
Severity of firearm injuries increased over the past 20 years
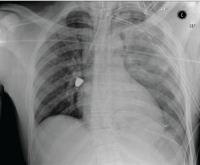
New research presented today at American Public Health Association’s (APHA) 2017 Annual Meeting and Expo revealed that the severity of firearm injuries has increased over the past twenty years, among those hospitalized for their injuries. Researchers noted that their findings have broad implications for public health beyond increased suffering on the individual level.
-
-
Improving public safety during severe weather, other disasters
Our ability to observe and predict severe weather events and other disasters has improved markedly over recent decades, yet this progress does not always translate into similar advances in the systems used in such circumstances to protect lives. A more cohesive alert and warning system that integrates public and private communications mechanisms and adopts new technologies quickly is needed to deliver critical information during emergency situations. At the same time, better understanding of social and behavioral factors would improve the ways we communicate about hazards, inform response decisions such as evacuations, develop more resilient urban infrastructure, and take other steps to improve weather readiness.
-
-
WannaCry report shows NHS chiefs knew of security danger, but management took no action
A report from the parliamentary National Audit Office into the WannaCry ransomware attack that brought down significant parts of Britain’s National Health Service in May 2017 has predictably been reported as blaming NHS trusts and smaller organizations within the care system for failing to ensure that appropriate computer security measures such as software updates and secure firewalls were in place. But the central NHS IT organization, NHS Digital, provided security alerts and the correct patches that would have protected vulnerable systems well before WannaCry hit. This is not a cybersecurity failure in the practicalities, but a failure of cybersecurity management at the top level.
-
-
North Korea behind May 2017 WannaCry attack on British health services: U.K.
The British government has said it was all but certain North Korea carried out the “WannaCry” malware attack which hobbled the IT systems of the NHS, Britain’s national health service, in May. The National Audit Office (NAO) released a report on Friday which found that hospitals and clinics were left exposed to cyberattack because they failed to follow basic cybersecurity recommendations. WannaCry attacks were not limited to the United Kingdom: More than 300,000 computers in 150 countries were also infected with the WannaCry ransomware. The malware crippled organizations — government agencies, global companies, small firms — by targeting computers with outdated security.
-
-
Acoustic gunshot sensor technology may benefit shooting victims
A number of U.S. cities have installed acoustic gunshot sensor technology to accurately locate shooting scenes and potential gunshot victims, but the effectiveness of this technology for saving lives had not been studied until now. A new study shows that the technology contributes to quicker hospital arrival times and equal survival rates despite more severe injuries.
-
-
Simulation technology to predict refugee destinations, improving aid efforts
A computer simulation of refugees’ journeys as they flee major conflicts can correctly predict more than 75 percent of their destinations, and may become a vital tool for governments and NGOs to help better allocate humanitarian resources.
-
-
S&T funds training of the next generation of animal health experts
Transboundary Animal Diseases (TADs) are highly contagious with high morbidity and mortality. These diseases quickly cross-national borders, negatively impacting a country’s economic stability and public health by reducing exports, food quality and quantity, and the availability of livestock products and animal power. They pose serious threats to a country’s well-being, and scientists around the world are continuously investigating new methods to prevent their spread. This past summer, DHS S&T funded two programs — Texas A&M University’s Bench to Shop program and Kansas State University’s Transboundary Animal Disease Fellowship — to train the next generation of animal health experts.
-
-
About 2.1 million Americans using wells high in arsenic
About 44 million people in the U.S. get their drinking water from private wells. A new study by the U.S. Geological Survey and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that about 2.1 million of them may be getting their drinking water from private wells considered to have high concentrations of arsenic, presumed to be from natural sources.
-
-
Heading off the post-antibiotic age
Worldwide deaths from antibiotic-resistant bugs could rise more than tenfold by 2050 if steps aren’t taken to head off their spread. Anthony Fauci, the director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, warned of the danger of a “post-antibiotic age,” tracing the spread of antibiotic resistance to rampant overprescribing, to the widespread use of the drugs to promote livestock growth, and to the relative trickle of new drugs being developed as possible replacements.
-
-
Battling fires increases firefighters’ exposure to carcinogens
The threat of getting burned by roaring flames is an obvious danger of firefighting, but other health risks are more subtle. For example, firefighters have been found to develop cancer at higher rates than the general population. Now researchers have measured how much firefighters’ exposure to carcinogens and other harmful compounds increases when fighting fires.
-
-
Homicide the largest contributor to years of lost life among African Americans
Homicide is the largest contributor to potential years of life lost among black Americans, according to a new study. Homicide was the 12th highest contributor to potential years of life lost for white Americas. Black Americans are disproportionately affected by homicide, but the amount invested in homicide research is dramatically underrepresented in public health. Research on heart disease, white Americans’ No. 1 cause of potential years of life lost, received 341 grants and almost 600 publications during 2015; research on homicide received just a handful of federal grants and publications.
-
-
More than half of police killings in U.S. not officially documented on death certificates

Official death certificates in the United States failed to count more than half of the people killed by police in 2015 — and the problem of undercounting is especially pronounced in lower-income counties and for deaths that are due to Tasers, according to a new Harvard study. In contrast, a database from the London-based Guardian newspaper captured a large majority of these deaths, the study found.
-
More headlines
The long view
We Ran the C.D.C.: Kennedy Is Endangering Every American’s Health
Nine former leaders of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), who served as directors or acting directors under Republican and Democratic administrations, serving under presidents from Jimmy Carter to Donald Trrump, argue that HHS Secretary Roert F. Kennedy Jr. poses a clear and present danger to the health of Americans. He has placed anti-vaxxers and conspiracy theorists at top HHS positions, and he appears to be guided by a hostility to science and a belief in bizarre, unscientific approaches to public health.
