-
WHO calls Zika virus “Public Health Emergency of International Concern”
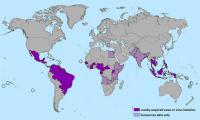
The Emergency Committee of the World Health Organization (WHO), after considering the health threat associated with the continuing spread of Zika virus disease in Latin America and the Caribbean, agreed that the situation meets the conditions for a Public Health Emergency of International Concern. WHO called for a coordinated international response to minimize the threat in affected countries and reduce the risk of further international spread.
-
-
Most vaccine-related posts on Pinterest are anti-vaccine: Study
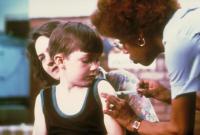
About 75 percent of the vaccine-related posts on Pinterest are negative toward vaccination, according to new research. Messages ranged from simple posts questioning the safety of vaccines to more radical claims that vaccines are being created to kill people. Twenty percent of the posts talked about conspiracy theories, such as pharmaceutical companies out to make money at the expense of children and governments trying to harm children for the purposes of population control. The authors are calling for better communication about vaccination.
-
-
Biodefense Panel concerned as Zika, avian flu expand their reach toward U.S.
The Blue Ribbon Study Panel on Biodefense responded last week with what it described as “serious concerns” over two emerging infectious diseases that now threaten the United States — Zika virus and avian influenza.
-
-
NIST seeks vendors to help secure wireless medical devices

Medical devices such as the infusion pumps that deliver medication intravenously were once standalone instruments that interacted only with the patient. Today, they have operating systems and communications hardware that allow them to connect to other devices and networks. While this technology has created more powerful tools and the potential for improved patient care, it also creates new safety and security risks.
-
-
Mosquito species carrying Zika virus found in Washington, D.C.
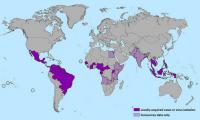
On Monday (25 January), the World Health Organization (WHO) announced that Zika virus, a mosquito-borne illness that in the past year has swept quickly throughout equatorial countries, is expected to spread across the Americas and into the United States. Zika virus is transmitted by the mosquito species Aedes aegypti, also a carrier of dengue fever and chikungunya, two other tropical diseases. Though Aedes aegypti is not native to North America, researchers who study the species have reported a discovery of a population of the mosquitoes in a Capitol Hill neighborhood in Washington, D.C.
-
-
Mercury levels in rainfall are rising in parts of U.S.
An analysis of long-term trends in the amount of mercury in rainfall and other forms of precipitation in North America found recent increases at many sites, mostly in the center of the continent. At other sites, including those along the East Coast, mercury levels in rainfall have been trending steadily downward over the past twenty years.
-
-
Theranos blood-testing lab poses “immediate jeopardy” to the public: U.S. government

Theranos is facing another major setback after the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) described the company’s blood-testing technology as posing “immediate jeopardy” to the public. The Silicon Valley firm has been valued at $10 billion, raising $400 million from investors for what it described as “breakthrough” technology which allowed it to do blood tests using a pinprick, rather than a full blood draw.
-
-
Zika virus spreads in Colombia
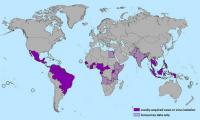
In October 2015, a team of researchers ran the first tests confirming the presence of Zika virus transmission in Colombia. In their study, the researchers document a disease trajectory that started with nine positive patients and has now spread to more than 13,000 infected individuals in the South American country. Colombia is now only second to Brazil in the number of known Zika infections.
-
-
Flint Water Study research team to present findings on Thursday

Virginia Tech’s Marc Edwards and his team of research scientists and students will give a presentation on Thursday, 28 January, in Blacksburg to outline their work — done in collaboration with Flint, Michigan, residents — which exposed widespread lead-in-water contamination. The presentation will provide an overview of the Flint Water Study team’s efforts combining ethics engineering, citizen science, laboratory experiments, investigative science, and social media to confirm the high lead levels in Flint’s water.
-
-
Piping as poison: the Flint water crisis and America’s toxic infrastructure

As the crisis over the water in Flint, Michigan, rolls on, we’re learning more and more about the irresponsibility and callousness of officials and politicians in charge. The mix of austerity politics, environmental racism, and sheer ineptitude makes for a shocking brew, yet the physical conditions that have made it literally toxic for Flint residents are neither as exceptional nor as recent as much of the media coverage suggests. An estimated three to six million miles of lead pipes across the United States still carry water, and most all of them are vulnerable to similar dangers, whether at the hands of short-sighted and prejudicial bureaucrats or politicians whose ideology or opportunism leads them to blithely dismiss well-established science. The best solution would be to replace our lead lines systematically and proactively, not just one crisis-beset city at a time. Until we do so, it’s a safe bet that more Flints lie on our horizon.
-
-
Brazil “badly losing” battle against Zika virus: Health minister
Marcelo Castro, Brazil’s health minister, said Brazil is “badly losing” the battle against the Aedes aegypti mosquito which spreads the Zika virus. Brazil will deploy nearly 220,000 members of Brazil’s armed forces to go door-to-door as part of the mosquito eradication campaign. The government would distribute mosquito repellent to some 400,000 pregnant women who receive cash-transfer benefits. The authorities in Brazil are worried that the Carnival events, scheduled for next month, and the Olympic Games, due to be held in August, may both serve to cause an even more rapid spread of the virus.
-
-
Most Americans support smart guns: Survey

In 2014, the most recent year for which final data are available, 33,599 people died in the United States from gun violence. The majority were suicides (more than 21,000 deaths), and firearm homicides accounted for more than 11,000 deaths. Unintentional shootings, in which children are often the shooter or the victim, comprised more than 500 deaths that year. Survey finds that nearly 60 percent of Americans, if they buy a new handgun, are willing to purchase a smart or childproof gun — a weapon that is only operable in the hands of an authorized user.
-
-
How dangerous people get their guns
The San Bernardino massacre is unique in several respects, but it does bring into focus an important issue with broad relevance: how do dangerous people obtain guns, and what should the police and courts be doing to make those transactions more difficult? Criminal assaults with guns kill thirty Americans every day, and injure another 170. The guns carried and misused by youths, gang members, and active criminals are more likely than not obtained by transactions that violate federal or state law. Unlike in the case of Enrique Marquez, a friend and neighbor of the terrorist couple who purchased two military-style rifles for them, it is rare for the people who provide these guns to the eventual shooters to face any legal consequences. Currently it is rare for those who provide guns to offenders to face any legal consequences, and changing that situation will require additional resources directed to a proactive enforcement directed at penetrating the social networks of gun offenders.
-
-
Protecting drinking water
We place high demands on the quality of our drinking water. If pathogens or toxic substances found their way into the piping system, many people could become infected or injured very quickly. This is why this risk must be kept low. To do this, experts have developed technologies for a comprehensive monitoring, early warning and emergency management system.
-
-
Manmade mercury emissions decline 30 percent between 1990 and 2010
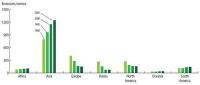
Mercury is a metallic element that poses environmental health risks to both wildlife and humans when converted to methylmercury in ecosystems. It can be converted into gaseous emissions during various industrial activities, as well as natural processes like volcanic eruptions. Between 1990 and 2010, global mercury emissions from manmade sources declined 30 percent. New research finds.
-
More headlines
The long view
We Ran the C.D.C.: Kennedy Is Endangering Every American’s Health
Nine former leaders of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), who served as directors or acting directors under Republican and Democratic administrations, serving under presidents from Jimmy Carter to Donald Trrump, argue that HHS Secretary Roert F. Kennedy Jr. poses a clear and present danger to the health of Americans. He has placed anti-vaxxers and conspiracy theorists at top HHS positions, and he appears to be guided by a hostility to science and a belief in bizarre, unscientific approaches to public health.
