-
Pacemakers, other implanted devices, vulnerable to lethal attacks
IT experts reported that security flaws in pacemakers and defibrillators could be putting lives at risk; the experts say that many of these devices are not properly secured and therefore are vulnerable to hackers who may want to commit an act that could lead to multiple deaths
-
-
World public health authorities alarmed about a new coronavirus related to viruses from bats
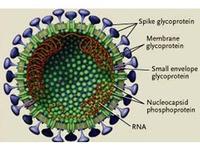
The virus which is causing alarm among global public health authorities after it killed a man in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia earlier this year and is now linked to two other cases of disease, is a novel type of coronavirus most closely related to viruses found in bats, according to a genetic analysis
-
-
Protecting U.S. troops against sand flies
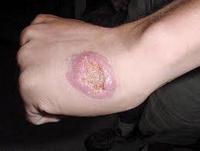
Sand flies are vectors of Leishmania parasites that cause leishmaniasis, a devastating disease for which there is no vaccine or medication; people who are bitten by infected sand flies do not know whether they have the disease until it becomes apparent three or four months later; U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientists are helping deployed American troops protect themselves against sand flies, which are major pests in Afghanistan, Africa, and the Middle East
-
-
The Coca-Cola model for delivering malaria meds is a success, should be continued
A controversial program that uses the private market to provide affordable malaria treatments to people in Africa has dramatically increased access to care and should be continued; The private-market approach — sometimes called the Coca-Cola model in reference to the soda’s apparent ability to reach remote areas of the world — aims to deliver drugs in regions where the majority of people obtain medicines from shops rather than from district hospitals or clinics
-
-
Cleanup of most contaminated U.S. groundwater sites unlikely for many decades

At least 126,000 sites across the United States have contaminated groundwater that requires remediation, and about 10 percent of these sites are considered “complex,” meaning restoration is unlikely to be achieved in the next 50 to 100 years due to technological limitations; the estimated cost of complete cleanup at these sites ranges from $110 billion to $127 billion, but the figures for both the number of sites and costs are likely underestimates
-
-
USGS sampling water in Hurricane Sandy’s aftermath to ensure public health
Excessive nutrients in U.S. rivers, streams, and coastal areas are a major issue for water managers, because they cause algal blooms that increase costs to treat drinking water, limit recreational activities, and threaten valuable commercial and recreational fisheries; U.S. Geological Survey crews are sampling water for nutrients, sediment, and pesticides to document water quality in areas affected by the hurricane
-
-
A coal economy has multiple health, social risks, says major review
A major review of evidence on the impact of coal mining has highlighted serious, ongoing health and social problems, and an urgent need for improvements in government coal mining policy
-
-
New approach to a rapid treatment of malaria
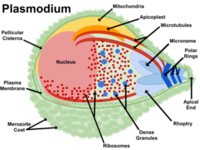
Malaria causes up to three million deaths each year, predominantly afflicting vulnerable people such as children under five and pregnant women, in tropical regions of Africa, Asia, and Latin America; treatments are available for this disease, but the Plasmodium parasite is fast becoming resistant to the most common drugs; researchers have identified a new means to eradicate malaria infections by rapidly killing the blood-borne Plasmodium parasites that cause the disease
-
-
Thriving in toxic environments
Not long ago, a group claimed that these microorganisms, which live in an environment that is rich in the arsenic-based compound arsenate, could take up that arsenate and use it — instead of the phosphate on which all known life on Earth depends; the claim, since disproved, raised another question: How do organisms living with arsenate pick and choose the right substance? Scientists reveal how bacteria living in toxic environments identify and expel the poison
-
-
Removing toxins from the environment

A Florida State University chemist’s work could lead to big improvements in our ability to detect and eliminate specific toxic substances in our environment; the novel approach is based on stripping electrons from the toxic chemical known as fluoride; in addition to toxin removal, the approach has many other applications
-
-
U.S. models underestimates costs of carbon pollution
Model used by government all but ignores economic damages that climate change will inflict on future generations; two economists argue that when these costs are factored in, the real benefits of carbon reduction range from 2.6 to more than 12 times higher than the government’s estimate
-
-
Tasered youth fare as well as adults: study

Adolescents who are tasered by law enforcement officers do not appear to be at higher risk for serious injury than adults, according to new a new study; the conclusions are based on a retrospective study of Taser use from law enforcement data collected by the largest, independent multicenter database established in 2005
-
-
U.S. schools not ready for next pandemic
Many U.S. schools are not prepared for bioterrorism attacks, outbreaks of emerging infectious diseases, or pandemics, despite the recent 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic which resulted in more than 18,000 deaths worldwide
-
-
World-wide alert for Yosemite hantavirus risk
U.S. health officials have alerted thirty-none countries that their citizens, who, as tourists, have stayed in Yosemite National Park tent cabins this summer, may have been exposed to a deadly mouse-borne hantavirus
-
-
Heat waves move toward California coasts, become more humid, imperiling health
Scientists detected a trend toward more humid heat waves which are expressed very strongly in elevated nighttime temperatures, a trend consistent with climate change projections; moreover, relative to local warming, the mid-summer heat waves are getting stronger in generally cooler coastal areas; this carries strong public health implications for the twenty-one million Californians living near the ocean whose everyday lives are acclimated to moderate temperatures
-
More headlines
The long view
A Shining Star in a Contentious Legacy: Could Marty Makary Be the Saving Grace of a Divisive Presidency?
While much of the Trump administration has sparked controversy, the FDA’s consumer-first reforms may be remembered as its brightest legacy. From AI-driven drug reviews to bans on artificial dyes, the FDA’s agenda resonates with the public in ways few Trump-era policies have.
