-
Using building “belt” cheaply, quickly to repair of earthquake damage
Four years after the January 2010 earthquake, 145,000 people still remain homeless in Haiti. Researchers developed a cheap and simple technology to repair earthquake damaged buildings to help to reduce these delays by quickly making buildings safe and habitable. The technology involves wrapping metal straps around each floor of the building, which are then tensioned either by hand or using compressed air tools. Unlike other repair methods, it does not require expensive materials or a high level of technical knowledge, making it ideal for use in the developing world.
-
-
The Philippines is victim of geography, poor infrastructure, poverty
Owing to its location and geography, the Philippines is one of the most natural disaster-prone countries in the world. On average the country experiences nine major typhoons and 900 earthquakes annually, and it has twenty-five active volcanoes. Poor infrastructure and pervasive poverty exacerbate the impact of disasters, making them even more deadly and destructive. “In a cruel cycle, poverty and underdevelopment make disasters worse, and disasters make poverty and underdevelopment worse,” one observer notes.
-
-
Past as prologue: Insights from past natural disasters relevant today
The increasing frequency and intensity of natural disasters constitute a daunting challenge to modern society, which is characterized by a heavy infrastructure and increasing population density. Until now, coping with natural disasters has involved expensive state intervention and technology-aided approaches, but researchers believes that the past contains a wealth of unexploited resources which could also provide solutions to the problems communities face when dealing with need to cope with, and recover from, natural disasters.
-
-
Philippines prepares for worse disasters to come
On average, the Philippines experiences about twenty typhoons a year, including three super-typhoons and many incidents of flooding, drought, earthquakes, tremors, and occasional volcanic eruptions, making the country one of the most naturally disaster-prone areas in the world. Filipino government agencies, with the help of international disaster and relief agencies, have created new strategies for disaster preparedness, response, and mitigation which may well have potential applications in other parts of the world. As the impact of climate change grows more pronounced, the Philippines is becoming a hothouse for developing new methods and systems in the growing business of disaster relief.
-
-
Making cybersecurity a political issue
U.S. federal agencies have reported a dramatic rise in the number of cyberattacks over the past few years, with reported cyber incidents rising from 5,503 in 2006 to 48,562 in 2012. Since cyber incidents pose such a threat to national security and infrastructure, could cybersecurity become a political campaign issue? Experts say that if politicians were to focus their attention, and their constituents’ attention, on cybersecurity, the United States could be made safer from cyberattacks before a “cyber Pearl Harbor” – or a “cyber 9/11” – occurs.
-
-
Resources on disaster preparedness, resilience

One year after Superstorm Sandy hit the eastern United States, local, state, and federal agencies as well as community groups and businesses are working to strengthen the U.S.s resilience to future disasters. A National Research Council (NRC) has issues a series of studies and reports, and has put together workshops and study groups, which should advance the national conversation on preparedness and resilience.
-
-
New method to help coastal communities adapt to sea-level rise
Future sea-level rise seems inevitable, although the rates and geographical patterns of change remain uncertain. Given the large and growing populations and economic activity in coastal zones, as well as the importance of coastal ecosystems, the potential impacts of sea-level change are far-reaching. Current methods to assess the potential impact of sea-level rise have varied significantly and hindered the development of useful scenarios and, in turn, suitable adaption policies and planning.
-
-
Raw cotton offers new, ecologically friendly way to clean up oil spills

The Deepwater Horizon disaster highlighted the need for better ways of cleaning up oil spills. A new solution addresses this need. It is based on the finding that unprocessed, raw cotton may be an ideal, ecologically friendly answer, with an amazing ability to sop up oil.
-
-
Motivating businesses to adopt building resiliency standards
Increased resilience for buildings in the face of hurricanes, earthquakes, terrorism, or cyberattacks has been a major national security focus over the past decade. Such resilient buildings not only would be less susceptible to damage and work interruption but could become community gathering places in a general crisis. It will not be easy, however, to secure voluntary adoption of resiliency standards by industry and builders without adequate justification.
-
-
Oil-devouring microbe communities a mile deep in the Gulf
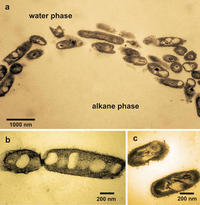
The Deepwater Horizon explosion on 20 April 2010, caused the largest marine oil spill in history, with several million barrels of crude oil released into the Gulf of Mexico over the course of three months. Soon after the spill began, a massive oil slick was visible from orbiting satellites, yet once the underwater gusher was sealed, obvious traces of the crude oil disappeared much sooner than nearly all observers predicted. Some of the oil evaporated; some was skimmed off. Microbes “ate” much of the oil as well.
-
-
Treating oil spills with chemical dispersants may do more damage than good
Treating oil spills at sea with chemical dispersants is detrimental to European fisheries. Post-spill chemical dispersants may reduce problems for surface animals, but the increased contamination under the water reduces the ability for fish and other organisms to cope with subsequent environmental challenges.
-
-
Texas to appeal FEMA decision not to declare West, Texas a disaster area
The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) said President Obama would not declare West, Texas a disaster area in the wake of the massive fertilizer plant explosion there two months ago, and Texas governor Rick Perry is not happy. FEMA said Texas did not make the case the state lacked funds for cleanup and recovery efforts.
-
-
Making buildings more tsunamis-resilient
Often in disasters such as tsunamis, people escape the on-rushing wall of water by climbing to higher ground, called vertical evacuation. As people race to the third or fourth floor of a building, however, how do they know whether the building will hold up? Walls of water often carry with them cars, trucks, and 60,000-pound fully loaded cargo containers, transforming them into projectiles which slam into buildings with tremendous force. Most structural systems are designed to defy gravity, not a side kick from a shipping container. Engineers are now studying the impact of tsunami-carried debris in order to make buildings and other structures more disaster-resilient.
-
-
Improved disaster resilience is imperative for U.S: report
A new report from the National Academies says that it is essential for the United States to bolster resilience to natural and human-caused disasters, and that this will require complementary federal policies and locally driven actions that center on a national vision – a culture of resilience; improving resilience should be seen as a long-term process, but it can be coordinated around measurable short-term goals that will allow communities better to prepare and plan for, withstand, recover from, and adapt to adverse events
-
-
UAVs with dexterous arms to help in infrastructure repair and disaster recovery
With current technology, most UAVs perform passive tasks such as surveillance and reconnaissance missions, tasks which are performed well above ground; researchers are interested in how UAVs might interact with objects at or near ground level; a UAV with dexterous arms could perform a wide range of active near-ground missions, from infrastructure repair and disaster recovery to border inspection and agricultural handling
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
