-
Collaboration with industry leads to improved forensics
Three-dimensional (3D) scanners used at crime scenes for forensic investigations are not just the stuff of prime time television. Investigators and crime laboratories are using 3D laser scanning measurement systems to measure and model, in 3D simulations, the critical aspects of crime scenes. A 2009 National Academy of Sciences (NAS) report, however, questioned the reliability of some forensic sciences, including the use of 3D scanning technique. Furthermore, pressure began building in the forensics community to have crime laboratories and stand-alone crime scene units in the United States adhere to specific standards in their services, which require traceability to the SI [the SI in SI traceability refers to the International System of Units (Système International d’unités)].
-
-
Secure, private Internet and cloud to soldiers, marines at the tactical edge
Squads of soldiers or marines on patrol in remote forward locations often do not have the luxury of quickly sharing current intelligence information and imagery on their mobile devices, because they cannot access a central server. Troops frequently have to wait until they are back at camp to download the latest updates. In the meantime, mission opportunities may erode because the information needed at the tactical edge isn’t immediately available. DARPA’s Content-Based Mobile Edge Networking (CBMEN) program aims to provide an alternative approach to the top down focus of most military networks by starting the content sharing at the individual soldier or marine level.
-
-
Breakthrough fuel cell technology: the future of electricity generation
We currently rely upon an increasingly vulnerable electrical grid to provide the energy we need. The best way to decrease that vulnerability is through distributed energy, that is, by making our own energy on-site. A breakthrough fuel cell technology promises to provide always-on electricity to businesses, homes, and eventually automobiles, at about one-tenth the cost and one-tenth the size of current commercial fuel cell systems. The technology allows people to generate their own electricity with a system nearly impervious to hurricanes, thunderstorms, cyberattacks, derechos, and similar dangers, while simultaneously helping the environment.
-
-
Detecting radioactive material smuggled in containers

Nearly 90 percent of imported and exported goods travel the globe in shipping containers. Roughly 500 million containers travel the sea each year. A Sandia National Laboratories team completed acceptance testing on an enormous mobile scanner — the Mobile Radiation Detection and Identification System (MRDIS) — which makes smuggling radiological materials in containers more difficult.
-
-
New camouflage makeup shields soldiers, firefighters from heat of bomb blasts, fire
Camouflage face makeup for warfare is undergoing one of the most fundamental changes in thousands of years, as scientists today described a new face paint that both hides soldiers from the enemy and shields their faces from the searing heat of bomb blasts. Firefighters also could benefit from the new heat-resistant makeup.
-
-
Top 6 hottest new weapons
Competition spurs innovation and there is nothing more competitive than countries battling in the trenches of war. With billions upon billions in defense budget to spend, research into developing the best and most efficient weapons is on the forefront of investment.
-
-
Teams compete in challenging robotic helicopter competition
A U Michigan student team took part in an autonomous aerial vehicle competition. Their task: build a 3-pound flying machine that can, under its own control, take off, fly through a window into a model building, avoid security lasers, navigate the halls, recognize signs, enter the correct room, find a flash drive in a box on a desk, pick it up, leave a decoy, exit, and land in under ten minutes. Beyond military uses, autonomous vehicle they built could one day be used to survey collapsed buildings or inspect hard-to-get-to parts of bridges and other infrastructure. An offshoot group from a previous U-M team is working to commercialize the U-M technology through a startup called SkySpecs, which inspects windmills.
-
-
Small modular reactors (SMEs) a “poor bet” to revive U.S. nuclear renaissance: report
A shift to small modular reactors (SMRs) is unlikely to breathe new life into the troubled U.S. nuclear power industry, since SMRs will likely require tens of billions of dollars in federal subsidies or government purchase orders, create new reliability vulnerabilities, as well as concerns in relation to both safety and proliferation, according a report issued last week.
-
-
Firefighting robot creates 3D images of burning buildings’ interiors for rescuers
Researchers develop novel robotic scouts that can help firefighters to assist in residential and commercial blazes. The robots will map and photograph the interior of burning buildings by using stereo vision. Working together both collaboratively and autonomously, a number of such vehicles would quickly develop an accurate augmented virtual reality picture of the building interior. They would then provide it in near real time to rescuers, who could better assess the structure and plan their firefighting and rescue activities.
-
-
SkySweeper robot inspects power lines easily, cheaply
Mechanical engineers invented a robot designed to scoot along utility lines, searching for damage and other problems that require repairs. Made of off-the-shelf electronics and plastic parts printed on an inexpensive 3D printer, the SkySweeper prototype could be scaled up for less than $1,000, making it significantly more economical than the two models of robots currently used to inspect power lines.
-
-
Molecule “scanner” uses terahertz radiation to identify single molecules
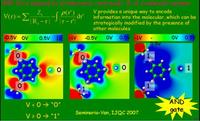
Molecules could soon be “scanned” in a fashion similar to imaging screenings at airports, thanks to the world’s smallest terahertz detector, developed by University of Pittsburgh physicists. The scanner has the ability chemically to identify single molecules using terahertz radiation — a range of light far below what the eye can detect.
-
-
Eighty-six collegiate teams compete for the best car design and build
Eighty-six teams competed in the Baja Society of Automotive Engineers competition in Bellingham, Washington to determine the Baja car with the best design and build. Every year, collegiate automotive clubs enter to compete in any of the three national competitions that test the design, speed, maneuverability, and endurance of a student-manufactured Baja car — a frame-only vehicle used for off-roading and high adventure activity. Arizona State University’s Sun Devil Motorsports Team improved its ranking from 37th last year to 17th this year.
-
-
Locating criminals by tracking their cell phones’ digital fingerprints
To keep from being tracked and getting caught, criminals use evasion tactics such as modifying the built-in ID code in their cell phone or swapping out SIM cards, making it impossible for law enforcement to track the criminals down by relying solely on cell phone signals. German engineers found, however, that the radio hardware in a cellphone — a collection of components like power amplifiers, oscillators, and signal mixers — all introduce radio signal inaccuracies. When these inaccuracies, or errors, are taken together, as seen in the digital signal sent to a cell tower, the result can be read as a unique digital signal –a digital fingerprint. These digital fingerprints do not change even if the built-in ID code has been modified, or the SIM card has been swapped out.
-
-
New technology enables crops to take nitrogen directly from the air
Nitrogen fixation, the process by which nitrogen is converted to ammonia, is vital for plants to survive and grow. Only a very small number of plants, however, most notably legumes (such as peas, beans, and lentils) have the ability to fix nitrogen from the atmosphere with the help of nitrogen fixing bacteria. The vast majority of plants have to obtain nitrogen from the soil, and for most crops currently being grown across the world, this also means a reliance on synthetic nitrogen fertilizer. Nitrogen pollution is a major problem however, and efforts to deal with it are costly. Researchers have developed a method of putting nitrogen-fixing bacteria into the cells of plant roots. The implications for food production are enormous.
-
-
Harnessing energy from wind whipping through urban concrete canyons
Two Drexel University students developed a wind-harvesting concept which would exploit the wind whipping through “concrete canyons” between buildings and skyscrapers in large urban centers. Their concept involves a system of wind turbines that could be installed in streets and spaces between buildings, using flexible sails to divert otherwise turbulent winds into a more useful stream.
-
More headlines
The long view
New Technology is Keeping the Skies Safe
DHS S&T Baggage, Cargo, and People Screening (BCP) Program develops state-of-the-art screening solutions to help secure airspace, communities, and borders
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
How Artificial General Intelligence Could Affect the Rise and Fall of Nations
By Barry Pavel et al.
Visions for potential AGI futures: A new report from RAND aims to stimulate thinking among policymakers about possible impacts of the development of artificial general intelligence (AGI) on geopolitics and the world order.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
By John Domol
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
By Zach Winn
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
