-
Anti-surveillance clothing blocks security cameras’ facial-recognition software
New anti-surveillance clothing has been developed, allowing wearers to prevent security cameras which use facial recognition technology from recognizing them. The clothing uses complex colored patterns of digitalized faces, and parts of faces, to overload and trick facial recognition software.
-
-
Robotic lie detector for border, aviation security
When you engage in international travel, you may one day find yourself face-to-face with border security that is polite, bilingual and responsive — and robotic. The Automated Virtual Agent for Truth Assessments in Real Time (AVATAR) is currently being tested in conjunction with the Canadian Border Services Agency (CBSA) to help border security agents determine whether travelers coming into Canada may have undisclosed motives for entering the country.
-
-
Images that fool computer vision raise security concerns
Computers are learning to recognize objects with near-human ability. But Cornell researchers have found that computers, like humans, can be fooled by optical illusions, which raises security concerns and opens new avenues for research in computer vision.
-
-
Half of American adults are in a little regulated police face recognition database
Half of American adults — more than 117 million people — are in a law enforcement face recognition network, according to a report. Of the fifty-two government agencies that acknowledged using face recognition, only one obtained legislative approval for its use and only one agency provided evidence that it audited officers’ face recognition searches for misuse. Not one agency required warrants, and many agencies did not even require an officer to suspect someone of committing a crime before using face recognition to identify her.
-
-
More than 800 ineligible individuals granted U.S. citizenship owing to incomplete fingerprint records
U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) granted U.S. citizenship to at least 858 individuals from special interest countries — individuals who had been ordered deported or removed under another name. DHS IG says that this happened because neither the digital fingerprint repository at DHS nor the repository at the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) contains all old fingerprint records of individuals previously deported. Currently, about 148,000 fingerprint records of aliens from special interest countries who had final deportation orders or who are criminals or fugitives have yet to be digitized.
-
-
Protecting privacy in genomic databases
Genome-wide association studies, which try to find correlations between particular genetic variations and disease diagnoses, are a staple of modern medical research. But because they depend on databases that contain people’s medical histories, they carry privacy risks. An attacker armed with genetic information about someone — from, say, a skin sample — could query a database for that person’s medical data. Researchers describe a new system that permits database queries for genome-wide association studies but reduces the chances of privacy compromises to almost zero.
-
-
Accessing a murder victim’s fingerprint-protected smartphone to help solve a crime
Last month, when the Michigan State University Police Department approached professor Anil Jain to see if he could access a fingerprint-locked deceased man’s smartphone to aid in a police investigation, Jain accepted the scientific challenge. On Monday, 25vJuly, it was mission accomplished – Jain and his team unlocked the phone.
-
-
Separating the DNA of identical twins
Since its first use in the 1980s — a breakthrough dramatized in recent ITV series “Code of a Killer” — DNA profiling has been a vital tool for forensic investigators. Now researchers at the University of Huddersfield have solved one of its few limitations by successfully testing a technique for distinguishing between the DNA — or genetic fingerprint — of identical twins.
-
-
How well do facial recognition algorithms cope with a million faces?
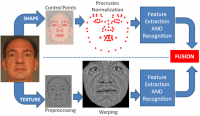
In the last few years, several groups have announced that their facial recognition systems have achieved near-perfect accuracy rates, performing better than humans at picking the same face out of the crowd. But those tests were performed on a dataset with only 13,000 images — fewer people than attend an average professional U.S. soccer game. What happens to their performance as those crowds grow to the size of a major U.S. city? Researchers answered that question with the MegaFace Challenge, the world’s first competition aimed at evaluating and improving the performance of face recognition algorithms at the million person scale.
-
-
CBP issues long-anticipated Biometric Exit Program RFI
Last Monday, the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) issued its highly-anticipated call to industry to share solutions for the Biometric Exit Program. The Request for Information (RFI), issued by U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP), explains that CBP intends to add biometrics to confirm when foreign nationals are departing the United States, in order to deter visa overstays, to identify criminals, and to defeat imposters.
-
-
The accuracy of the FBI’s face-recognition technology may be improved: GAO
The Department of Justice’s (DOJ) Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) operates the Next Generation Identification-Interstate Photo System (NGI-IPS) — a face recognition service that allows law enforcement agencies to search a database of over thirty million photos to support criminal investigations. The GAO examined the FBI’s face recognition capabilities, and the extent to which the FBI’s use of face recognition adhered to privacy laws and policies, and the accuracy of these capabilities.
-
-
Terrorist or criminal? New software uses face analysis to find out

Pulling a poker face means betraying no visible emotion, so that opponents cannot tell what you are really thinking. But a Tel Aviv startup’s face-profiling technology recently proved fairly accurate at predicting which four players were most likely to beat out forty-six other contenders in an amateur poker tournament. The company say that its technology, which analyzes faces shown in photos and videos and classifies them according to fifteen parameters predictive of personality traits and types, can help identify terrorists.
-
-
U.K. to destroy biometric information of 45 terror suspects due to botched paperwork
British security agencies will have to destroy fingerprints and DNA of forty-five terror suspects because the police retained the biometric samples longer than the law allows. The law does allow the police to keep biometric information of terrorism suspects indefinitely, but certain paperwork must be completed within a certain period of time to allow that, and if the paperwork is not completed, the samples must be destroyed. A new report reveals that Britain holds biometric information and materials on nearly 8,000 suspects.
-
-
Selfies could replace security passwords – but only with an upgrade
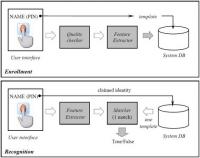
The next time you do some online shopping or call your bank, you may find you no longer have to scrabble around to remember your security password. Banks are increasingly turning to voice recognition technology as their preferred way of ensuring customers are who they say they are when they use telephone banking services. But does this kind of technology really mean that you’ll soon be able to just forget your passwords? The short answer right now is “no.”
-
-
Forensics close in on footwear analysis

First it was your fingerprint that gave the game away and then DNA analysis transformed forensic science. But “watch your step” because experts have developed a new technique which could lead to a step change in forensic footwear imaging. The experts have been able to extract additional information and create a digital picture of the personal footprint we leave behind when we stand or walk on a hard surface.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
