-
How mobile ads leak personal data
The personal information of millions of smartphone users is at risk due to in-app advertising that can leak potentially sensitive user information between ad networks and mobile app developers, according to a new study.
-
-
Detecting hidden malicious ads hidden in apps
The danger of acquiring a computer virus or spyware used to come with the risk of visiting the dark, sketchy corners of the Internet. But now trusted and harmless smartphone apps like MyFitnessPal and Candy Crush carry their own risks. As more and more people own smartphones, the number of malicious ads hidden in apps is growing — tripling in just the past year.
-
-
Asia, Middle East lead rise in 2015 arms imports
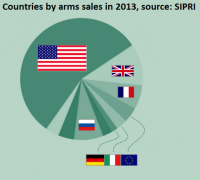
The volume of international transfers of major weapons has grown continuously since 2004 and rose by 14 percent between 2006 and 2010 and 2011–2015, according to new data. Six of the top ten largest arms importers in the 5-year period 2011–15 are in Asia and Oceania. Arms imports by states in the Middle East rose by 61 percent between 2006 and 2010 and 2011 and 2015.
-
-
Integrating markets to offset climate-related food insecurity
Global market integration is key to buffering future commodity prices and food security from the negative effects of climate change on agriculture. Rising temperatures and an increase in extreme weather events will likely have adverse impacts on global crop production, leading to higher food prices and food scarcity. But global markets that have the ability to deliver food where it is needed most could help offset these consequences.
-
-
Sanctions boost foreign military more than they hurt economy
The available evidence indicates that economic sanctions are not effective tools for achieving specific policy goals in foreign nations, according to new research. The researchers argue that increased military spending caused by economic sanctions counterbalances the adverse impact of the sanctions – and points to Iran as a case study in how this can happen.
-
-
Apple refuses to comply with court order to help FBI investigate San Bernardino terrorists
Apple’s encryption technology has placed the company at the heart t of the privacy vs national security debate, as the company said it would defy a court order which requires to company to help investigate the San Bernardino attack by helping the FBI crack the code of an iPhone , Syed Rizwan Farook, one of terrorists, used. The U.S. government, stunned by Apple’s refusal to help in investigating a terrorist attack on U.S. soil, persuaded a court to issue on order compelling Apple to cooperate in the investigation.
-
-
Cybercrime’s true toll

Cyber thieves who steal credit and debit card numbers are making millions of dollars in profits, fueling a global criminal enterprise marked by the high-profile data breaches of major companies such as Target and Home Depot. A criminologist offers one of the first scientific studies to estimate cybercrime profits, saying the findings should be a wakeup call for consumers and law enforcement officials alike.
-
-
Securityhunter receives $200 million Blanket Purchase Agreement (BPA) from SSA

Baltimore, Maryland-based Securityhunter, Inc., a government security solutions integrator, has just received a $200 million Blanket Purchase Agreement (BPA) to provide security systems and support services for 1,500 Social Security Administration (SSA) locations around the country.
-
-
Extracting rare-earth elements from coal could soon be economical in U.S.

The United States could soon decrease its dependence on importing valuable rare-earth elements (REEs) which are widely used in many industries, according to a team of researchers. who found a cost-effective and environmentally friendly way to extract these metals from coal byproducts.
-
-
Hyperion cyber security technology receives commercialization award
The commercial licensing of a cybersecurity technology developed at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory has been recognized by the Federal Laboratory Consortium for Technology Transfer (FLC) as a good example of moving technology to the marketplace. Hyperion, which has the capability automatically to analyze executable programs and recognize behaviors that signal malicious intent and vulnerabilities, was licensed to Virginia-based R&K Cyber Solutions, LLC, in late 2014.
-
-
DEA, European authorities uncover massive Hezbollah drug, money-laundering operation
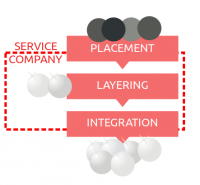
The U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) yesterday announced what the agency described as a “significant enforcement activity,” including arrests targeting Lebanese Hezbollah’s External Security Organization Business Affairs Component (BAC), which is involved in international criminal activities such as drug trafficking and drug proceeds money laundering. These proceeds are used to purchase weapons for Hezbollah for its activities in Syria.
-
-
Aussie stationery chain pulls world globe which names Palestine, omits Israel
The Australian stationery chain Typo has stumbled into one of the world’s most contentious issues – and had to pull a line of globes which named Palestine but omitted the label “Israel.” Israel’s name was not omitted altogether: The globe was designed so that Israel and twelve other small countries were represented by a number on the map, corresponding to a number in a legend at the base of the globe. The globe sparked charges of anti-Semitism, but the company’s decision to halt production of the globes has led to boycott threats by Palestine advocates.
-
-
Rapid, affordable energy transformation in U.S. possible
The United States could slash greenhouse gas emissions from power production by up to 78 percent below 1990 levels within fifteen years while meeting increased demand, according to a new study. The study used a sophisticated mathematical model to evaluate future cost, demand, generation, and transmission scenarios. It found that with improvements in transmission infrastructure, weather-driven renewable resources could supply most of the nation’s electricity at costs similar to today’s.
-
-
New regulations improve opportunities for certain highly skilled workers

DHS’ U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services on Friday announced changes to the programs serving the H-1B1, E-3, and CW-1 nonimmigrant classifications, and the EB-1 immigrant classification. The purpose of the changes was to remove the obstacles and disadvantages workers in these categories faced compared to workers in other visa classifications.
-
-
World leaders urged to oppose encryption back doors
In an open letter made public on Monday, nearly 200 Internet and digital rights leaders and experts, companies, and organizations are calling on the Obama administration and other world leaders to reject efforts to create “back doors” to encryption. “Encryption tools, technologies, and services are essential to protect against harm and to shield our digital infrastructure and personal communications from unauthorized access,” the letter states.
-
More headlines
The long view
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
Trump Is Fast-Tracking New Coal Mines — Even When They Don’t Make Economic Sense
In Appalachian Tennessee, mines shut down and couldn’t pay their debts. Now a new one is opening under the guise of an “energy emergency.”
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
