-
WWII-like message encryption now available for e-mail security
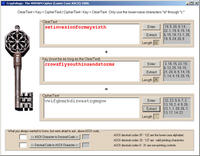
A Singapore-based company offers an e-mail encryption system based on the Verman cipher, or one-time pad, which was invented in 1917 and used by spies in the Second World War; the Vernam cipher is unbreakable because it produces completely random cipher-text that secures data so that even the most powerful super computers can not break the encryption when it is used properly
-
-
U.S. severe weather insurance losses breach $1.2 billion in March

The estimated economic loss of a series of natural disasters in the United States in March reached approximately $2.0 billion, while insured losses are expected to breach $1.1 billion amid more than 170,000 insurance claims
-
-
Combat veterans are risk-averse investors
Veterans who have faced combat are more risk-averse when it comes to investing than noncombatants; as a result, they may struggle to build wealth through long-term investments, the authors say
-
-
Industry insiders: insufficient security controls for smart meters
False data injection attacks exploit the configuration of power grids by introducing arbitrary errors into state variables while bypassing existing techniques for bad measurement detection; experts say current generation of smart meters are not secure enough against false data injection attacks
-
-
India's demand for CCTVs growing fast
Since the Mumbai terrorist attacks in 2008, city surveillance has become a high priority for India; India has twenty-eight states, most with a capital city and a number of other large cities, and video surveillance is being planned for many of them
-
-
U.S. students need new way of learning science

The United States used to lead the world in science education, but now U.S. students are ranked a mediocre 23rd in their science knowledge; a group of prominent scientists says that American students need a dramatically new approach to improve how they learn science
-
-
U.S. power and water utilities face daily cyberattacks
American water and energy companies deal with a constant barrage of cyberattacks on a daily basis; these incidents usually take the form of cyber espionage or denial-of-service attacks against the utilities’ industrial-control systems
-
-
Isotec Security receives Safety Act designation
Isotec Security’s Automated Weapons Control Portals has been awarded SAFETY Act designation by DHS; the company notes that no strategic, public facility, or bank using the solution has suffered an armed incursion or successful armed robbery
-
-
Missouri announces additional funding for Disaster Recovery Jobs Program
Missourigovernor announces an investment of $16.5 million in federal National Emergency Grant (NEG) funding to create temporary jobs for workers in twenty-nine Missouri counties affected by tornadoes, floods, and severe storms last year
-
-
DHS brings military technology to border surveillance
The long list of products and equipment developed for the military but which were adapted to and adopted by civilian and law enforcement agencies has a new entry. Add to the list the Kestrel: a L-3 Wescam MX 360-degree camera mounted to a Raven Aerostar aerostat
-
-
International collaborative effort to develop better radiation detection tool
In mid-February, the Flash Portal Project was launched with the aim of furthering the development and testing of a new technology to detect shielded nuclear materials
-
-
Alternative to Keystone XL pipeline planned

The Obama administration rejected of the Keystone XL pipeline to carry Canadian oil to refineries on the U.S. Gulf coast, and now two companies are collaborating to develop an alternative plan to achieve the same end
-
-
Beef Industry Safety Summit notes successes, challenges
The U.S. beef industry says that beef is increasingly safe and that consumers have more confidence in beef safety, but challenges remain
-
-
2011 disasters: $116 billion in insured losses, record economic losses of $370 billion
Figures confirm that 2011 was the second-highest catastrophe loss year ever for the insurance industry: 2011 saw the highest economic losses in history, at $370 billion; the insurance industry experienced the second-largest insured losses ever, at $116 billion; 2011 also brought the highest insured earthquake losses, at $49 billion; flooding in Thailand resulted in the highest insured losses ever for a single flood event, at $12 billion
-
-
New laws help cut metal thefts

Metal thefts have become a plague to businesses throughout the country; some states pass laws which require licenses and permits to buy and sell non-ferrous metals; Spartanburg, South Carolina, also requires that buyers pay for the purchases with checks rather than cash, in order to create a paper trail to the seller of the metal
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
