-
New insights into terrorist threats to ground transportation
A new analysis of terrorist attacks, and attempted attacks, on ground transportation shows that from the late 1980s to the mid-1990s, terrorist groups used chemicals to attack surface transportation; from the mid-1990s on, multiple bombs became the new prototype for terrorist attacks
-
-
£5 million investment in U.K. rail technology, business innovation
The U.K. government is leading on an investment of £5 million to accelerate business innovation and growth in the U.K. rail industry, using the funds to support the development of technologies to address technological and business challenges
-
-
Simulations helps overcome design challenges
Simulation software can pull volumes of complex data beyond simple measurements (think comparative load or stress tolerances) and layer that information into images; simulation can show how a bridge will perform based on how it is used, the conditions around it, its design, materials, and even variables such as the position of a joint — before a single component is manufactured or ground is broken
-
-
New report analyzes the airport security equipment sector
A new report offers a detailed business analysis of the leading 125 companies in the airport security equipment sector
-
-
Formation of hate groups associated with presence of big-box stores
In a new research, economists say that the presence of big-box retailers, such as Wal-Mart, K-Mart, and Target, may alter a community’s social and economic fabric enough to promote the creation of hate groups; the researchers say that the number of Wal-Mart stores in a county is more significant statistically than factors commonly regarded as important to hate group participation, such as the unemployment rate, high crime rates, and low education
-
-
Worldwide UAV market to reach more than $94 billion in ten years
UAV spending will almost double over the next decade from current worldwide UAV expenditures of $5.9 billion annually to $11.3 billion, totaling just over $94 billion in the next ten years; the UAV payload market, worth $2.6 billion in Fiscal Year 2011, is forecast to increase to $5.6 billion in Fiscal Year 2020
-
-
Security industry helps develop DOJ/DHS Suspicious Activity training video
The National Association of Security Companies says it endorses the DOJ/DHS Suspicious Activity Reporting (SAR) training video for private sector security personnel
-
-
WWII-like message encryption now available for e-mail security
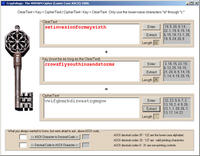
A Singapore-based company offers an e-mail encryption system based on the Verman cipher, or one-time pad, which was invented in 1917 and used by spies in the Second World War; the Vernam cipher is unbreakable because it produces completely random cipher-text that secures data so that even the most powerful super computers can not break the encryption when it is used properly
-
-
U.S. severe weather insurance losses breach $1.2 billion in March

The estimated economic loss of a series of natural disasters in the United States in March reached approximately $2.0 billion, while insured losses are expected to breach $1.1 billion amid more than 170,000 insurance claims
-
-
Combat veterans are risk-averse investors
Veterans who have faced combat are more risk-averse when it comes to investing than noncombatants; as a result, they may struggle to build wealth through long-term investments, the authors say
-
-
Industry insiders: insufficient security controls for smart meters
False data injection attacks exploit the configuration of power grids by introducing arbitrary errors into state variables while bypassing existing techniques for bad measurement detection; experts say current generation of smart meters are not secure enough against false data injection attacks
-
-
India's demand for CCTVs growing fast
Since the Mumbai terrorist attacks in 2008, city surveillance has become a high priority for India; India has twenty-eight states, most with a capital city and a number of other large cities, and video surveillance is being planned for many of them
-
-
U.S. students need new way of learning science

The United States used to lead the world in science education, but now U.S. students are ranked a mediocre 23rd in their science knowledge; a group of prominent scientists says that American students need a dramatically new approach to improve how they learn science
-
-
U.S. power and water utilities face daily cyberattacks
American water and energy companies deal with a constant barrage of cyberattacks on a daily basis; these incidents usually take the form of cyber espionage or denial-of-service attacks against the utilities’ industrial-control systems
-
-
Isotec Security receives Safety Act designation
Isotec Security’s Automated Weapons Control Portals has been awarded SAFETY Act designation by DHS; the company notes that no strategic, public facility, or bank using the solution has suffered an armed incursion or successful armed robbery
-
More headlines
The long view
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
Trump Is Fast-Tracking New Coal Mines — Even When They Don’t Make Economic Sense
In Appalachian Tennessee, mines shut down and couldn’t pay their debts. Now a new one is opening under the guise of an “energy emergency.”
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
