-
Experts trying to determine cause of a giant Louisiana sinkhole

The earth near Bayou Corne, Louisiana opened on 2 August: a 300-foot-wide sinkhole, with depth varying between 50 and 300 feet, suddenly opened up in an area, and the authorities have been trying to determine whether the sinkhole was caused by the collapse of an abandoned brine mining cavern along the margin of the Napoleonville Salt Dome or by something else
-
-
Microstructural improvements enhance material properties
DARPA merges structural engineering principles with new fabrication technologies to demonstrate microstructural control of materials at the micron level; the ultimate objective of the agency’s Materials with Controlled Microstructural Architecture (MCMA) program is to be able to develop materials in the future with properties tailored to meet specific mission requirements
-
-
Decline and fall: all built structures are destined to break down or fail
A series of infrastructure-related accidents in Ontario this summer has caused people to ask: Just how safe are the structures that we build? The answer a materials science and engineering professor offers may not be reassuring: “Nature always looks for ways to use energy in a favorable state — gravity always pushing things downwards is an example. Any built structure naturally goes against nature. Therefore, all structures will eventually be broken or destroyed — given the right amount of time, they will break down or fail.”
-
-
Aerospace materials for on-site building of pipes of infinite length

Concrete and steel pipes are built in short sections to fit on standard 18-wheel trucks; the heavy industrial manufacturing processes, long-distance trucking, and leak-prone joints used in steel and concrete pipe construction exact a heavy toll on the environment, not to mention bottom line; the solution: a new pipe design, consisting of a central layer of lightweight plastic honeycomb, which can be built onsite as a single section of virtually infinite length
-
-
New method for detecting, measuring bridge damage
Researchers have created a bridge health index, which is a rating system that more accurately describes the amount of damage in a bridge; the health index can extend beyond bridges and apply to other structures, such as gas pipelines, dams, buildings, and airplanes
-
-
Automated pavement crack detection and sealing system to extend roadways life

Researchers from the Georgia Tech Research Institute developed a prototype automated pavement crack detection and sealing system; in road tests, the system was able to detect cracks smaller than one-eighth-inch wide and efficiently fill cracks from a vehicle moving at a speed of three miles per hour
-
-
Quick-curing concrete for infrastructure, mining disaster recovery
A quick-curing concrete can be sprayed to reinforce structures — buildings, runways, tunnels, bridges, dams – damaged by an act of terror or natural disaster; the spraying can be done almost immediately, before the structure fails catastrophically, providing safety for rescue workers who risk their lives minutes after disasters hit, and for still stranded in or near the damaged structure
-
-
Hurricane Ike damage analysis point to vulnerable Texas bridges
Preliminary results from a new research show more than a dozen Gulf Coast bridges on or near Galveston Island would likely suffer severe damage if subjected to a hurricane with a similar landfall as Hurricane Ike but with 30 percent stronger winds
-
-
Ancient design concept leads to new ideas for building durable bridges

Engineers combine an ancient concrete arch form, dating back to the Roman empire, with a composite shell to create bridge beams which are designed to last 100 years
-
-
Humble bacteria help create self-healing concrete
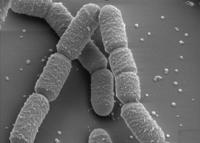
Scientists use a ground-borne bacteria — bacilli megaterium — to create calcite, a crystalline form of natural calcium carbonate; this can then be used to block the concrete’s pores, keeping out water and other damaging substances to prolong the life of the concrete
-
-
Sensing technology helps prevent construction accidents
Researchers have developed a system that employs remote sensing technology to improve safety on construction sites by using tracking tags to monitor movements in real-time
-
-
New Iowa bridge equipped with damage-detection gauges
A new Iowa bridge is equipped with sensors which provide a large amount of quantitative information about the bridge’s performance and condition; these gauges take 100 readings a second for corrosion, strain, surface conditions, moisture within the steel arch, and structure movements over time; the bridge is also equipped to monitor the security of the structure and to record surveillance video; it is a structure monitoring model that could be used for other new bridges, including much larger ones
-
-
U.S. aging bridges in critical condition

There are an estimated 18,000 bridges in the United States that are classed as fracture-critical bridges, requiring continual inspections; the need for increased inspection and maintenance runs against shrinking state and federal budgets for infrastructure improvements; bridges must also be closed for maintenance – but at least for that there is now a solution: instant bridges
-
-
Bridges get a quick check-up with new imaging technique

EPFL engineers have developed a new imaging technique which allows engineers to see the insides of massive concrete bridges; much like a sonogram, this technique provides quick, easy-to-interpret images, so that the health of these expensive structures can be assessed and monitored
-
-
California quake test shows promise of new building code

Researchers place a model hospital on a shake table to assess the structure’s ability to withstand earthquake; in accordance with California latest building code, base isolators, which are rubber bearings intended to absorb the shock of the motion, were installed underneath the structure; the hospital passed the 6.7-magnitude and 8.8-magnitude tests with flying colors
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
