-
Using building “belt” cheaply, quickly to repair of earthquake damage
Four years after the January 2010 earthquake, 145,000 people still remain homeless in Haiti. Researchers developed a cheap and simple technology to repair earthquake damaged buildings to help to reduce these delays by quickly making buildings safe and habitable. The technology involves wrapping metal straps around each floor of the building, which are then tensioned either by hand or using compressed air tools. Unlike other repair methods, it does not require expensive materials or a high level of technical knowledge, making it ideal for use in the developing world.
-
-
NIST: Joplin tornado highlights need for building design, construction standards
Nationally accepted standards for building design and construction, public shelters, and emergency communications can significantly reduce deaths and the steep economic costs of property damage caused by tornadoes. That is the key conclusion of a two-year technical NIST investigation into the impacts of the 22 May 2011 tornado that struck Joplin, Missouri. Report and recommendations released for public comment.
-
-
List of most-at-risk L.A. buildings to be released
Scientists have compiled a list of concrete buildings in Los Angeles which could be at risk of collapsing in a major earthquake. The list identifies about 1,500 concrete structures built before 1980 which need further study to determine their risk level. Structural engineers insist that hundreds could die if any of the buildings collapsed.
-
-
A 34-story wooden skyscraper to be built in Stockholm
A Swedish architectural form is building a 34-story wood skyscraper in downtown Stockholm. Solid wood will be the predominant material in the building’s pillars and beams, while inside the apartments, walls, ceilings, fittings and window frames will be also constructed of wood.The firm says that wood is not only cheaper than either steel or concrete, but is also more fire resistant than both. This is due to 15 percent of wood mass being water, which will evaporate before the wood actually burns. In addition, logs get charred which protects the core.
-
-
Man-induced quakes to help in building safer, sturdier buildings
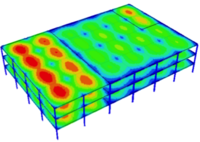
A team led by Johns Hopkins structural engineers is shaking up a building in the name of science and safety. Using massive moving platforms and an array of sensors and cameras, the researchers are trying to find out how well a two-story building made of cold-formed steel can stand up to a lab-generated Southern California quake.
-
-
Motivating businesses to adopt building resiliency standards
Increased resilience for buildings in the face of hurricanes, earthquakes, terrorism, or cyberattacks has been a major national security focus over the past decade. Such resilient buildings not only would be less susceptible to damage and work interruption but could become community gathering places in a general crisis. It will not be easy, however, to secure voluntary adoption of resiliency standards by industry and builders without adequate justification.
-
-
Concrete recycling robot disassembles concrete structures for recycling, reuse

Current concrete-demolition techniques require a lot of power crushing, separation, and machinery, not to mention the fact that they waste a lot of water in order to prevent dust blooms during operation. A new concrete recycling robot is designed efficiently to disassemble concrete structures without any waste, dust, or separation and enable reclaimed building materials to be reused for new prefabricated concrete buildings. It does so by using a water jet to crack the concrete surface, separate the waste, and package the cleaned, dust-free material.
-
-
Earthquake-proofing precast buildings
Precast or ready-made building structures offer a number of advantages when compared to more traditional construction techniques in terms of time and cost savings. The vulnerability of joints and connections between assembled precast elements, however, is widely recognized as a potential safety issue, especially in earthquake-prone areas. An EU-funded project has set out to develop new procedures and guidelines for designing precast structure joints and connections that can stand up to seismic forces.
-
-
U California, Berkeley students win National Student Steel Bridge Competition

The weekend of 31 May residents of Washington State watched as engineers began erecting a temporary steel bridge over the Skagit River, to replace the 160-foot span of a 4-lane bridge that had collapsed a week earlier, after being struck by an over-height truck. Just sixty miles away, on the campus of the University of Washington in Seattle, 620 civil engineering students erected their own temporary steel bridges in a competition to demonstrate their engineering skills. For the second consecutive year and for the second time in the past seven years, a team of students from the University of California, Berkeley captured the title as champions of the ASCE/AISC National Student Steel Bridge Competition (NSSBC).
-
-
Ash from olive residue biomass leads to more effective, cheaper concrete
Researchers have produced self-compacting concrete with ash from boiler combustion of olive pruning residue pellets. The plasticity and cohesion of this type of concrete mean no compaction is needed when used in construction and, moreover, it has other advantages with respect to conventional concrete.
-
-
Making concrete “greener”

Many factors determine the overall energy and environmental impact of concrete. Reducing the amount of portland cement, which reacts with water to bind all the sand, stone, and the other constituents of concrete as it hardens, provides the biggest opportunity. Portland cement manufacturing accounts for more than 5 percent of U.S. industrial carbon-dioxide emissions. In addition, the U.S. cement industry consumes 400 gigajoules of energy annually.
-
-
U.S. infrastructure grade raised from D to a D+, but problems loom
The American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE), in its just-released 2013 Report Card for America’s Infrastructure, gave the U.S. infrastructure an overall grade of D+, showing slight progress from the D in the last Report Card issued in 2009. The Report Card concludes that to raise the grades and get U.S. infrastructure to an acceptable level, a total investment of $3.6 trillion is needed by 2020. Currently, only about $2 trillion in infrastructure spending is projected, leaving a shortfall of approximately $1.6 trillion.
-
-
Improving high-speed rail ties against freezing, thawing conditions
Research project is helping high-speed rail systems handle the stress of freezing and thawing weather conditions; the 3-year study looks at the freeze-thaw durability of concrete railroad ties; the research is essential to developing safe and durable high-speed rail systems
-
-
Safety glass – cut to any shape
If an object slams into the glass façade of a high-rise building, the glass must not shatter and fall down, because it could harm pedestrians below; in addition, the window panes must hold if a person were to fall against it from the inside; architects and builders must therefore use something stronger than laminated safety glass on the façades of high rise buildings; scientists develop a method which offers more flexibility with the design and handling of safety glass
-
-
Rehabilitating historical structures using laser scanning technology
The Carmel Mission Basilica in California is undergoing a restoration using cutting-edge laser scanning technology; earlier this year, engineers the from Blach Construction Company teamed up with CyArk, a non-profit foundation that digitally preserves historical sites, to shoot laser beams at and within the basilica to create precise digital maps of the building from different angles
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
