-
A 34-story wooden skyscraper to be built in Stockholm
A Swedish architectural form is building a 34-story wood skyscraper in downtown Stockholm. Solid wood will be the predominant material in the building’s pillars and beams, while inside the apartments, walls, ceilings, fittings and window frames will be also constructed of wood.The firm says that wood is not only cheaper than either steel or concrete, but is also more fire resistant than both. This is due to 15 percent of wood mass being water, which will evaporate before the wood actually burns. In addition, logs get charred which protects the core.
-
-
Assessing the risks of global aftershock
The entire world becomes an aftershock zone after a massive magnitude (M) 7 or larger earthquake — but what hazard does this pose around the planet? Researchers are working to extend their earthquake risk estimates over a global scale, as they become better at forecasting the impact of aftershocks at a local and regional level.
-
-
Making storm warnings more exact, useful
The College of Staten Island (CSI)is the home of one of the most powerful mainframe computer systems in the country, an outgrowth of the City University of New York’s (CUNY) Decade of Science initiative. Following August 2011 Hurricane Irene, CSI scientistsset out to use that computing horsepower to generate scientific data hard enough to make the warnings something more than abstract. They fed millions of data points into the supercomputers, turning an admixture of geology, oceanography, climatology, and land surveys into a set of highly specific projections. Then, on 25 October 2012, Superstorm Sandy hit, and the actual water surges could be measured against the surge projections of the CSI model. On street after street, the computer model predicted flooding to within a foot of the actual surges.
-
-
Firefighting robot creates 3D images of burning buildings’ interiors for rescuers
Researchers develop novel robotic scouts that can help firefighters to assist in residential and commercial blazes. The robots will map and photograph the interior of burning buildings by using stereo vision. Working together both collaboratively and autonomously, a number of such vehicles would quickly develop an accurate augmented virtual reality picture of the building interior. They would then provide it in near real time to rescuers, who could better assess the structure and plan their firefighting and rescue activities.
-
-
Man-induced quakes to help in building safer, sturdier buildings
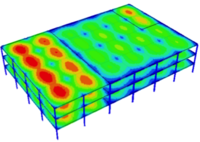
A team led by Johns Hopkins structural engineers is shaking up a building in the name of science and safety. Using massive moving platforms and an array of sensors and cameras, the researchers are trying to find out how well a two-story building made of cold-formed steel can stand up to a lab-generated Southern California quake.
-
-
Ten-fold increase in frequency of Katrina-magnitude storms this century
Tropical cyclones arise over warm ocean surfaces with strong evaporation and warming of the air. Since 1923, there has been a Katrina magnitude storm surge every twenty years. Researchers found that 0.4 degrees Celcius warming of the climate corresponds to a doubling of the frequency of extreme storm surges like the one following Hurricane Katrina. If the temperature rises an additional degree, the frequency will increase by 3-4 times, and if the global climate becomes two degrees warmer, there will be about ten times as many extreme storm surges.
-
-
Climate change threatens world food security
The last few decades have witnessed a substantial decline in the number of hungry people worldwide. Since 2007, however, progress has slowed and world food supply and demand have been precariously balanced — climate change threatens to tip this balance, most dramatically in the poorer areas of the world.
-
-
Climate change may fuel extreme wildfires
Climate change may be fueling the larger and more destructive wildfires which are scorching vast areas of the American West, according to new research. August 2012 saw 3.6 million acres burn in the region, the most of any August since 2000. There were, however, only 6,948 fires in August 2012 — the second fewest in that 12-year timeframe — meaning the fires were much larger.
-
-
Quake Summit 2013: showcasing research on earthquakes, tsunamis
Members of a national earthquake simulation research network next week will gather at the University of Nevada, Reno (UNR), for Quake Summit 2013, a scientific meeting highlighting research on mitigating the impact of devastating earthquakes and tsunamis. Titled “Earthquake & Multi-Hazards Resilience: Progress and Challenges,” the annual summit of the 14-site George E. Brown Network for Earthquake Engineering Simulation (NEES), will run from 6 August through 8 August at UNR’s Joseph Crowley Student Center.
-
-
Online tools accelerate progress in earthquake engineering, science
A new study has found that on-line tools, access to experimental data, and other services provided through “cyberinfrastructure” are helping to accelerate progress in earthquake engineering and science. The cyberinfrastructure includes a centrally maintained, Web-based science gateway called NEEShub, which houses experimental results and makes them available for reuse by researchers, practitioners, and educational communities. NEEShub contains more than 1.6 million project files stored in more than 398,000 project directories and has been shown to have at least 65,000 users over the past year.
-
-
Simulations help in studying earthquake dampers for structures
Researchers have demonstrated the reliability and efficiency of “real-time hybrid simulation” for testing a type of powerful damping system that might be installed in buildings and bridges to reduce structural damage and injuries during earthquakes. The magnetorheological-fluid dampers are shock-absorbing devices containing a liquid that becomes far more viscous when a magnetic field is applied.
-
-
Raw cotton offers new, ecologically friendly way to clean up oil spills

The Deepwater Horizon disaster highlighted the need for better ways of cleaning up oil spills. A new solution addresses this need. It is based on the finding that unprocessed, raw cotton may be an ideal, ecologically friendly answer, with an amazing ability to sop up oil.
-
-
Tornadoes do not take weekends off

Do tornadoes take the weekends off? Some scientists had hypothesized that aerosols, which are more common in the atmosphere during the work week due to increased vehicle and manufacturing pollution levels, were also responsible for increased tornadic activity during Monday-Friday period. New research finds that the numbers of tornadoes that occurred on any given day of the week varied, with no clear pattern showing that weekends had significantly less activity.
-
-
U.K. winter flooding to get more severe, frequent

Winter flooding in the United Kingdom is set to get more severe and more frequent under the influence of climate change as a result of a change in the characteristics of atmospheric rivers (ARs). ARs are narrow regions of intense moisture flows in the lower troposphere of the atmosphere that deliver sustained and heavy rainfall to mid-latitude regions such as the United Kingdom.
-
-
Feds give upstate New York counties $5 million money to repair roads, bridges
The Federal Highway Administration (FHA) has approved $5 million in emergency funding to help fifteen upstate New York counties make repairs to their roads and bridges damaged in a flood late last month.
-
More headlines
The long view
Trump Aims to Shut Down State Climate Policies
By Alex Brown
President Donald Trump has launched an all-out legal attack on states’ authority to set climate change policy. Climate-focused state leaders say his administration has no legal basis to unravel their efforts.
