-
Simulating forest and fire dynamics to understand area burn of future wildfires

Climate change and wildfire – it’s a combustible mix with costly devastation and deadly consequences. With a goal of understanding the link between the two variables, researchers over the years have studied the effects of climate and wildfire interactions in the Sierra Nevada mountain range. That research has evolved into learning about the distribution of trees, the extent of forest cover and carbon dynamics.
-
-
Robots help in the demanding Fukushima cleanup efforts
In 2011, a tsunami triggered by a magnitude 9.0 earthquake all but decimated the Pacific Coast of Tohoku, Japan, including the Fukushima Daiichi power plant. A catastrophic meltdown ensued. Many tons of nuclear fuel, boiled down to a radioactive lava, corroded the steel surrounding the facility’s three reactors. Today, the cleanup effort is still projected to take several decades. S&T and NIST developed standard test methods for robots, which the Japanese government is now beginning to apply directly to their Fukushima cleanup efforts.
-
-
Long-distance earthquake detection
In traditional seismology, researchers studying how the earth moves in the moments before, during, and after an earthquake rely on sensors that cost tens of thousands of dollars to make and install underground. Now researchers have figured out a way to overcome these hurdles by turning parts of a 13,000-mile-long testbed of “dark fiber,” unused fiber-optic cable, owned by the DOE Energy Sciences Network (ESnet), into a highly sensitive seismic activity sensor that could potentially augment the performance of earthquake early warning systems currently being developed in the western United States.
-
-
“It eats everything” – the new breed of wildfire that’s impossible to predict

Climate change and negligent forest management are causing higher-intensity, faster-moving fires that can generate enough energy to evolve into erratic firestorms, known as pyroCbs, in the face of which first responders can do little.
-
-
L.A. showcases quake alert system
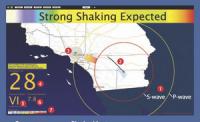
California is earthquake country, and residents of Los Angeles can now get some critical warning, when conditions are right, after a quake has started and seismic waves are heading their way. The long-delayed system, called ShakeAlertLA, is the first of its kind in the United States.
-
-
Which U.S. volcanoes pose a threat?
The United States is one of Earth’s most volcanically active countries. Since 1980, there have been 120 eruptions and 52 episodes of notable volcanic unrest at 44 U.S. volcanoes. An updated USGS assessment finds that 161 U.S. volcanoes pose potential threats to American lives and property, eight fewer than in 2005. The eighteen very highest threat volcanoes are in Alaska, California, Hawaii, Oregon and Washington. Thirty-nine other volcanoes are high threat, 49 are moderate, 34 are low, and 21 are very low threat.
-
-
Climate change increases potential for conflict, violence

Images of extensive flooding or fire-ravaged communities help us see how climate change is accelerating the severity of natural disasters. The devastation is obvious, but what is not as clear is the indirect effect of these disasters, or more generally of rapid climate change, on violence and aggression.
-
-
And now, land may be sinking
In the coming decades, cities and towns up and down the eastern seaboard will have to come to terms with the impact of rising sea level due to climate change. A new study, however, is suggesting that rising sea levels may be only part of the picture — because the land along the coast is also sinking.
-
-
Rising seas disrupt local economies
Impacts from climate change are not always easy to see. But for many local businesses in coastal communities across the United States, the evidence is right outside their doors – or in their parking lots. High-tide flooding resulting from climate change is already disrupting the economy of Annapolis, Maryland. As sea levels rise, the impacts are expected to get worse for coastal communities.
-
-
Keeping the lights on during and after a disaster

The threat of an inevitable earthquake is the uncomfortable truth we all face in the Cascadia Subduction Zone, which stretches from Alaska to California. Because the last major earthquake in the area was in the 1700s, our infrastructure developed without an appreciation and understanding of earthquake resilience. That means the next major earthquake will likely devastate our buildings, roads, bridges, and utility providers, posing immediate risks for the health and safety of those who live in the region. And later, there will be long-term economic aftershocks.
-
-
Using data utilization to augment community resilience, disaster response
A civil engineering who researches resilience against extreme events and natural hazards is responding to lessons learned from California’s deadly Camp Fire by outlining how to utilize the power of data to improve disaster response and minimize economic loss and human harm in similar events.
-
-
Paradigm shift needed for making bridges tsunami-resistant

Over the past fifteen years, big earthquakes whose epicenters were in the ocean off the coasts of Japan and Indonesia have caused tsunamis that killed more than 250,000 people and caused more than $200 billion in damage. The damage includes washing away or otherwise dislodging hundreds of bridges, emphasizing the need to better understand the wave impacts’ underlying physics. Researchers argue in a new study that a paradigm shift is needed for assessing bridges’ tsunami risk.
-
-
In one generation, climate of North American cities will shift hundreds of miles
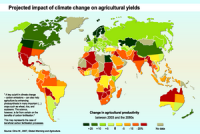
In one generation, the climate experienced in many North American cities is projected to change to that of locations hundreds of miles away—or to a new climate unlike any found in North America today. New web application helps visualize climate changes in 540 North American cities.
-
-
2018 fourth warmest year in continued warming trend
Earth’s global surface temperatures in 2018 were the fourth warmest since 1880, according to independent analyses by NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). Global temperatures in 2018 were 1.5 degrees Fahrenheit (0.83 degrees Celsius) warmer than the 1951 to 1980 mean. Globally, 2018’s temperatures rank behind those of 2016, 2017 and 2015. The past five years are, collectively, the warmest years in the modern record.
-
-
Lawmakers tell Pentagon to redo climate change report
Earlier this month, the Pentagon, in compliance with a congressional mandate, released a landmark report which identified the 79 American military installations most vulnerable to the “effects of a changing climate.” Several Democrats on the House Armed Services Committee welcomed the report – but at the same time harshly criticized it for failing to include details requested by Congress, among them the estimates by each of the armed services of the cost of protecting or replacing the ten most vulnerable military bases.
-
More headlines
The long view
The Surprising Reasons Floods and Other Disasters Are Deadlier at Night
It’s not just that it’s dark and people are asleep. Urban sprawl, confirmation bias, and other factors can play a role.
Why Flash Flood Warnings Will Continue to Go Unheeded
Experts say local education and community support are key to conveying risk.
