-
Russia attempted 2018 interference, gearing up to infiltrate election systems in 2020
Defense Department and Homeland Security officials warn Russia did try to interfere in the 2018 election, and the United States is not prepared for what foreign adversaries likely will launch in 2020. One official told lawmakers on the House Appropriations Homeland Security Subcommittee that “what keeps him up at night” is thinking about the new ways adversaries will attempt to infiltrate US election systems in 2020.
-
-
Trapdoor found in SwissVote election system

Researchers have examined the source code published as part of the SwissPost e-voting system, provided by Scytl, and discovered a cryptographic trapdoor. If exploited, researchers say this could allow insiders who ran or implemented the election system to modify votes undetected.
-
-
Fraudulent news, disinformation become “new normal” political tactics

New report warns of the risk of fraudulent news and online disinformation becoming a normalized part of U.S. political discourse. The report sounds an alarm that fraudulent news and online disinformation, which distort public discourse, erode faith in journalism, and skew voting decisions, are becoming part of the toolbox of hotly contested modern campaigns.
-
-
Information literacy must be improved to stop spread of “fake news”
It is not difficult to verify whether a new piece of information is accurate; however, most people do not take that step before sharing it on social media, regardless of age, social class or gender, a new study has found.
-
-
A new world for hackers: Acoustic side-channel attack
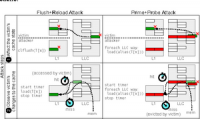
During the DNA synthesis process in a laboratory, recordings can be made of the subtle, telltale noises made by synthesis machines. And those captured sounds can be used to reverse-engineer valuable, custom-designed genetic materials used in pharmaceuticals, agriculture and other bioengineering fields.
-
-
Deterrence in the cyber age: U.K. Foreign Secretary's speech

U.K. foreign secretary Jeremy Hunt last Thursday spoke at Glasgow University on cybersecurity and the U.K. government’s approach to deterring cybercrime. “In the cyber age, an authoritarian regime armed with nothing more ambitious than a laptop computer could try to manipulate our democracy, Hunt said. “For every example of publicly attributed interference [by Russia], there have been others that never saw the light of day.” He added: “The material fact is that the Russian state has tried to subvert democracy,” concluding: “We can no longer afford to wait until an authoritarian regime demonstrably succeeds in changing the outcome of an election and weakening trust in the integrity of democracy itself. The risk is that after just a few cases, a pall of suspicion would descend over a democratic process – and once that happens, the damage would be difficult, perhaps impossible, to repair.”
-
-
U.S. military steps up cyberwarfare effort

The U.S. military has the capability, the willingness and, perhaps for the first time, the official permission to preemptively engage in active cyberwarfare against foreign targets. The first known action happened as the 2018 midterm elections approached: U.S. Cyber Command, the part of the military that oversees cyber operations, waged a covert campaign to deter Russian interference in the democratic process.
-
-
White supremacist propaganda and events soared in 2018

White supremacists dramatically stepped up their propaganda efforts targeting neighborhoods and campuses in 2018, far exceeding any previous annual distribution count for the United States and showing how these extremist groups are finding ways to share hateful messages while hiding the identity of individual members.
-
-
Securing the “internet of things” in the quantum age

Quantum computers can in principle execute calculations that today are practically impossible for classical computers. Bringing quantum computers online and to market could one day enable advances in medical research, drug discovery, and other applications. But there’s a catch: If hackers also have access to quantum computers, they could potentially break through the powerful encryption schemes that currently protect data exchanged between devices.
-
-
Flaws in 4G, 5G networks could allow hackers intercept calls, track location
Newly discovered vulnerabilities in 4G and 5G networks could be used to intercept phone calls and track users’ locations, according to researchers. Not only has 5G promised to be faster than previous generations, but it should also be more secure. That such serious vulnerabilities have been found in the new networks is hardly reassuring, as the 5G standard was specifically developed to better protect against these kind of attacks.
-
-
Protect confidential information from cyberattacks
The NSF is funding research aiming to develop new guidelines for sharing secret information through wireless communication that would improve security for users and minimizes cost.
-
-
Secure information exchange: Quantum communication over fiber-optic networks
Searching for better security during data transmission, governments and other organizations around the world have been investing in and developing technologies related to quantum communication and related encryption methods. Researchers are looking at how these new systems—which, in theory, would provide unhackable communication channels—can be integrated into existing and future fiber-optic networks.
-
-
U.S. Cyber Command cut Russian troll factory’s access to the internet

The U.S. Cyber Command blocked the internet access of the St. Petersburg’s-based Internet Research Agency (IRA), a Russian disinformation and propaganda outfit which was contracted by the Kremlin to orchestrate the social media disinformation campaign to help Donald Trump win the 2016 presidential election. The IRA’s access to the internet was blocked on midterms Election Day, and for a few days following the election.
-
-
Most laptops vulnerable to attacks via peripheral devices

Many modern laptops and an increasing number of desktop computers are much more vulnerable to hacking through common plug-in devices than previously thought, according to new research. The research shows that attackers can compromise an unattended machine in a matter of seconds through devices such as chargers and docking stations.
-
-
Telegram used by ISIS to spread propaganda globally
The Counter Extremism Project (CEP) this week reports about a Telegram channel that called for lone actor terrorist attacks in London, alongside other online websites that host ISIS videos and propaganda online. The encrypted messaging app is the platform of choice for terrorist group to call for violence.
-
More headlines
The long view
Researchers Develop AI Agent That Solves Cybersecurity Challenges Autonomously
New framework called EnIGMA demonstrates improved performance in automated vulnerability detection using interactive tools.
