-
UN chief alarmed at “weakening taboo” after Syrian chemical weapons attacks
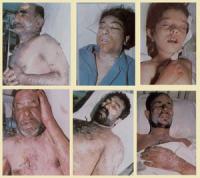
United Nations Secretary-General Ban Ki-Moon expressed his concerned Monday about “the weakening taboo” against chemical weapons attacks, after numerous reports that more such attacks have taken place in Syria in recent weeks. In a letter to the UN Security Council, Ban expressed fears that the use of chemical weapons could become “normalized in this or any conflict, present or future.”
-
-
First large-scale, citywide test of advanced radioactive threat detection system
Field testing of more than 1,000 networked, mobile radiation sensors in Washington, D.C., yields valuable data for implementing enhanced radiation-detection networks in major U.S. cities. By getting volunteers to walk all day looking for clues, the DARPA-sponsored exercise provided the largest test yet of DARPA’s SIGMA program, which is developing networked sensors that can provide dynamic, real-time radiation detection over large urban areas.
-
-
Sensors monitor bridges’ health – and tweet the information they gather
While bridge collapses are rare, there have been enough of them to raise concerns in some parts of the world that their condition is not sufficiently monitored. Sweden is taking a hi-tech approach to its aging infrastructure. Researchers are rigging up the country’s bridges with multiple sensors that allow early detection of wear and tear. The bridges can even tweet throughout the course of a day.
-
-
Nanobionic spinach plants can detect explosives
Spinach is no longer just a superfood: By embedding leaves with carbon nanotubes, MIT engineers have transformed spinach plants into sensors that can detect explosives and wirelessly relay that information to a handheld device similar to a smartphone. This is one of the first demonstrations of engineering electronic systems into plants, an approach that the researchers call “plant nanobionics.”
-
-
Immobilizing radioactive waste in glass for millions of years
How do you handle nuclear waste that will be radioactive for millions of years, keeping it from harming people and the environment? It is not easy, but researchers have discovered ways to immobilize such waste – the offshoot of decades of nuclear weapons production – in glass and ceramics.
-
-
Nuclear CSI: Noninvasive procedure could spot criminal nuclear activity
Determining whether an individual – a terrorist, a smuggler, a criminal — has handled nuclear materials, such as uranium or plutonium, is a challenge national defense agencies currently face. The standard protocol to detect uranium exposure is through a urine sample; however, urine is able only to identify those who have been recently exposed. Scientists have developed a noninvasive procedures that will better identify individuals exposed to uranium within one year.
-
-
Nanomaterials help solve the problem of nuclear waste
In the last decades, nanomaterials have gained broad scientific and technological interest due to their unusual properties compared to micrometer-sized materials. Nuclear fuels production, structural materials, separation techniques, and waste management may all benefit from more knowledge in the nano-nuclear technology.
-
-
Shark antibodies for chemical, biological threat detection, treatment
New research shows that shark antibodies offer new alternatives to chemical and biological threat detection and treatment tools. In an era of Department of Defense belt-tightening, the goal is to find more innovative, cost-effective approaches to protecting our warfighters.
-
-
ISIL uses toxic chemicals in its defense of Mosul
In the run up to the U.S.-led coalition campaign to liberate Mosul, U.S. officials warned that ISIS would likely use chemical weapons to slow down the progress of coalition forces and terrorize the residents. Last Thursday ISIS took the first step in its chemical strategy by setting ablaze the Mishraq Chemical plant and sulphur mine, located thirty km south of Mosul. The toxic cloud includes lethal sulphur dioxide and hydrogen sulphide. When combined with residue from burning oil wells, it is deadly for people caught in the open or without gas masks. Military experts say health effects from the toxic fumes from oil and sulphur will likely subside in about eighteen months, but the toxic clouds could harm much of the plant and animal life in the area and make it difficult for local farmers to return to their fields until then.
-
-
Assad regime used chemical weapons: UN
The White House on Saturday sharply condemned the use of chemical weapons by the government of Bashar al-Assad, after an international inquiry found that Syrian government forces used toxic gas in spring 2015 in attacks on two rebel-held towns. The fourth report from the 13-month-long inquiry by the UN and the Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW), the UN chemical weapons watchdog, blamed Syrian government forces for a toxic gas attack in Qmenas in Idlib governorate on 16 March 2015.
-
-
Suspension of U.S.-Russia plutonium disposal agreement a setback: Expert
Earlier this week the lower house of the Russian parliament approved President Vladimir Putin’s decree on suspending the U.S.-Russian Plutonium Management and Disposition Agreement (PMDA), which requires each nation to dispose of thirty-four metric tons of plutonium from its dismantled nuclear weapons and military stockpiles. Russia has claimed that the United States is violating the agreement by changing its disposition method from irradiating the plutonium as mixed-oxide (MOX) fuel for commercial nuclear reactors to a process called dilute and dispose, but a nuclear expert says that the United States has not violated the terms of the PMDA by proposing that it change its plutonium disposition approach.
-
-
Developing tests for radiation absorbed in nuclear emergency
In a large-scale nuclear or radiological emergency, such as a nuclear detonation, hundreds of thousands of people may need medical care for injuries or illness caused by high doses of radiation. To help save as many people as possible and better prepare the nation for the health impacts of such catastrophic emergencies, HHS will sponsor late-stage development of two tests, known as biodosimetry tests, which can determine how much radiation a person’s body has absorbed.
-
-
HHS bolsters U.S. health preparedness for radiological threats
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services’ (HHS) Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response (ASPR) says that as a part of its mission to help protect Americans’ health following even the most unthinkable of disasters, it is purchasing two medical products to treat injuries to bone marrow in victims of radiological or nuclear incidents. Bone marrow is essential to producing blood.
-
-
Bacteria can help make underground nuclear waste repositories safer
It takes about two hundred thousand years for the radioactivity of spent nuclear fuel to revert to the levels of naturally occurring uranium. As a result, most research into the long-term safety of nuclear waste disposal focuses on processes that tick to a slow geological clock: the mechanics of the rock layers that make up the storage site or the robustness of the protective barriers in place that are engineered to contain the radiation. However, all these studies neglect one key factor: biology. Naturally occurring bacteria could consume pent-up hydrogen gas in nuclear waste repositories to prevent radioactive leaks.
-
-
Terrorism fallout shelters: Is it time to resurrect nuclear civil defense?
Fifty-five years ago, on 6 October 1961, President John F. Kennedy advised Americans to build an underground protective room, commonly known as a “fallout shelter,” in their homes. The American people heeded his advice and began an enormous grassroots effort to construct fallout shelters in every private residence and public building. Today, smaller nations and terrorist groups, such as al-Qaeda, are seeking nuclear weapons. Some nations, like North Korea, already have them. Others may be a decade away. It is not unreasonable to believe that the use of a single nuclear weapon by a rogue nation or a terrorist group now poses a more likely scenario for a nuclear confrontation than a nuclear war between Russia and the United States. We need a strategy to protect ourselves against these adversaries, and right now we don’t have one, except screening cargo. If we don’t find a more effective strategy to thwart nuclear terrorism soon, we may be forced to go back to fallout shelters as our only protective option, whether we like it or not.
-
More headlines
The long view
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
