-
Explosives dumped into Gulf of Mexico pose big problems
Millions of pounds of unexploded bombs and other military ordnance that were dumped decades ago in the Gulf of Mexico, as well as off the coasts of both the Atlantic and Pacific oceans, could now pose serious threats to shipping lanes and the 4,000 oil and gas rigs in the Gulf, warns two oceanographers
-
-
Helping improve microbes’ ability to remediate toxic metal contamination
Naturally occurring bacteria in the Gulf of Mexico did a great job helping to clean up 2010’s huge Deepwater Horizon oil spill, but bacteria can do even heavier lifting; routinely used to help clean up toxic metals at contaminated sites, bacteria and other soil microbes are fed to boost their ability to turn soluble metals into solids that will not leech into streams or aquifers
-
-
Keystone XL pipeline: reliability of remote oil-spill sensors questioned
The oil industry plans to build thousands of miles of pipelines in the next five years, making leak detection a growing issue; many of the new pipelines will cross aquifers and rivers which are used for drinking water and irrigation; the Keystone XL pipeline has already experienced its share of controversies, and now there is a debate over the quality and reliability of the pipeline’s sensor system for remote detection of oil spills
-
-
Why common explosive sometimes fails

The explosive PETN has been around for a century and is used by everyone from miners to the military, but it took new research by Sandia National Laboratories to begin to discover key mechanisms behind what causes it to fail at small scales
-
-
Removing toxins from the environment

A Florida State University chemist’s work could lead to big improvements in our ability to detect and eliminate specific toxic substances in our environment; the novel approach is based on stripping electrons from the toxic chemical known as fluoride; in addition to toxin removal, the approach has many other applications
-
-
U.S. urgently needs better bioterrorism, disease tracking system
Nearly eleven years have passed since the fall 2001 bioterrorism-related anthrax attacks that shook the United States, killing five people and injuring seventeen, a leading bioterrorism expert says the country has still not learned its lesson; he says that current data mining approaches are passive and do not provide immediate solutions to the emergencies at hand, proposing instead an electronic, clinician-based reporting system which would have the capacity to limit the impact of a bioterrorism attack
-
-
Thorium to play limited role in U.K. future power supply
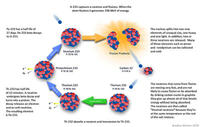
Worldwide, there has for a long time been a sustained interest in the thorium fuel cycle and presently there are several major research initiatives which are either focused specifically on the thorium fuel cycle or on systems which use thorium as the fertile seed instead of U-238; the U.K. National Nuclear Laboratory examined the topic and concluded that thorium has theoretical advantages but that these benefits are often overstated; as a result, thorium fuel cycle at best has only limited relevance to the United Kingdom as a possible alternative plutonium disposition strategy and as a possible strategic option
-
-
Nuclear waste-burning technology to make nuclear energy more appealing
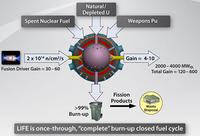
Toxic nuclear waste is stored at sites around the United States, and the need to store nuclear waste is widely considered to be a major disadvantage associated with nuclear energy; physicists have been granted a U.S. for patent for a novel fusion-fission hybrid nuclear reactor which would use nuclear fusion and fission together; the invention could drastically decrease the need for any additional or expanded geological repositories, making nuclear power cleaner and more viable
-
-
Radiation-enabled computer chips allow low-cost security imaging systems
With homeland security on high alert, screening systems to search for concealed weapons are crucial pieces of equipment; these systems, however, are often prohibitively expensive, putting them out of reach for public spaces such as train and bus stations, stadiums, or malls, where they could be beneficial; until now
-
-
Many Americans exposed to drinking water-related gastrointestinal illness
More than 100 million people in the United States rely on water piped into homes, schools, and businesses from public water systems that get their water from wells, rather than lakes, rivers, and other above-ground sources; much of that water either is not disinfected at all or is not adequately disinfected to kill disease-causing viruses
-
-
DHS submersible Pluto mimics the real narco-subs
In the early 1990s, South American drug cartels came up with a new tactic to transport narcotics destined for the United States: small, radar-dodging, self-propelled, semi-submersibles (SPSSs); better to address the submersible problem, DHS Science and Technology Directorate created its own submersible and called it Pluto, after the planet which is difficult to spot
-
-
Questions raised about cost, reliability of BioWatch upgrade

One year ago, DHS said a new contract for Biowatch, a system for detecting biological attacks on the United States, would be awarded in May 2012 and would cost an estimated $3.1 billion during its initial five years of operation; now DHS has decided to postpone the plans due to concerns about cost and reliability
-
-
Netanyahu cancels security cabinet meeting on Iran after leaks

Israel’s prime minister, Benjamin Netanyahu, scheduled a 2-day marathon meeting of Israel’s security cabinet for Tuesday and Wednesday, with an 8-hour session planned for each day; the 2-day meeting was called for a thorough and comprehensive – and probably decisive — discussion of Iran’s nuclear weapons program and what should Israel do about it; the speakers on Tuesday included the directors of Israel’s military and civilian intelligence agencies; early Wednesday, Netanyahu abruptly canceled the meeting’s second session because of leaks from Tuesday top-secret meeting session appeared in the Israeli press
-
-
As shoe-scanning devices fail, passengers continue to remove their shoes

In the last five years the U.S. government has tested several scanning devices for detecting explosives and other weapons concealed in the shoes of airline passengers; after spending millions of dollars on these devices, TSA has concluded that the detection systems are ineffective; the result: removing shoes at security check points is going to be a part of air travel for the foreseeable future
-
-
The costs, benefits, and efficiency of aviation security measures
The threat of terrorist attack on American aviation has made the system the focus of intense security efforts, but it is difficult to determine if the benefits outweigh their cost; efficient security policy — a focus on getting the most security for the least cost — should be the priority in an era of fiscal austerity, says a new RAND report
-
More headlines
The long view
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
