-
Fukushima disaster “a profoundly man-made disaster”: investigative commission
The commission investigating the Fukushima disaster of March 2011 concluded that although the combination of the tsunami and earthquake was unprecedented in its ferocity, the disaster was largely man-made because it was amplified by what came before it and what followed it; the disaster itself, the commission said, was sandwiched by practices and conduct which were the result of government-industry collusion and the worst conformist conventions of Japanese culture; the government, nuclear regulators, and Tepco, the plant operator, “betrayed the nation’s right to safety from nuclear accidents”
-
-
A third Bell 412 helicopter delivered to NYPD for counterterrorism missions

The NYPD dedicated many hours to designing the specifications of the department’s third Bell 412 to meet the diverse needs of the police department; one of the counterterrorism additions to the Bell 412 is a radiation detection system that can identify radiation signatures from an altitude of 200 feet in an effort to protect the city from nuclear bomb threats
-
-
Even a limited India-Pakistan nuclear war would substantially reduce global crop yields

Worries about nuclear winter have faded since the end of the cold war, but existing stockpiles of nuclear weapons still hold the potential for devastating global impacts; researchers have found that the climate effects of a hypothetical nuclear war between India and Pakistan would greatly reduce yields of staple crops, even in distant countries
-
-
A third Bell 412 helicopter delivered to NYPD for counterterrorism missions
The NYPD dedicated many hours to designing the specifications of the department’s third Bell 412 to meet the diverse needs of the police department; one of the counterterrorism additions to the Bell 412 is a radiation detection system that can identify radiation signatures from an altitude of 200 feet in an effort to protect the city from nuclear bomb threats
-
-
Bomb threat? There’s an app for that
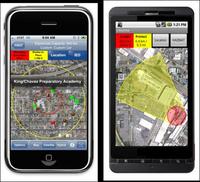
In the first chaotic moments after suspicion of a bomb threat, first responders have a myriad of questions, assessments, and decisions to make, all at once, and all the while the scene could be changing rapidly: Is the bomb real? How large is the potential blast radius? Where will we evacuate people? Are there any critical infrastructure or special-needs population centers in the vicinity? Any schools, hospitals nearby? What roads should be closed? Which roads should stay open for evacuees? There are many more questions, many more uncertainties; DHS Science and Technology Directorate (S&T) and its private sector partners have now developed a must-have app: the First Responder Support Tools (FiRST) for computers and smartphones
-
-
Radiation-resistant circuits from mechanical parts

Engineers designed microscopic mechanical devices that withstand intense radiation and heat, so they can be used in circuits for robots and computers exposed to radiation in space, damaged nuclear power plants, or nuclear attack; the devices can also survive work in space
-
-
More effective radiation detection of cargo, baggage
A new technique for radiation detection that could make radiation detection in cargo and baggage more effective and less costly for homeland security inspectors; the novel detection method relies on spectral shape discrimination (SSD), taking advantage of a new class of nanoporous materials known as metal-organic frameworks (MOFs)
-
-
Seismic sensors seek source of Spokane quakes
It has been a decade since a swarm of relatively mild earthquakes shook up parts of Spokane, Washington; now, armed with the right tools, scientists want to find out what was at fault
-
-
New method uses gunshot residue to determine caliber, type of weapon used in crime
Researchers have developed a method to determine the caliber and type of weapon used in a crime by analyzing gunshot residue (GSR); using near-infrared (NIR) Raman microspectroscopy and advanced statistics, the new technique may play a pivotal role in law enforcement cases and forensic investigations
-
-
Airport security screening technology market to grow
In 2011, TSA distributed approximately $437.1 million in contract obligations toward airport screening technologies; this amount is likely to grow in coming years as airport security authorities look for technology which would allow them to balance the requirements of tight security, on the one hand, and demands from the public for faster and less intrusive screening measures
-
-
Saab shows new CBRN detection system
Saab introduces a new concept in CBRN detection: a CBRN detection and warning system designed for use by non-specialists in the field
-
-
Experts: stronger regulation of military, civilian nuclear programs required

All nuclear energy and weapons programs should be independently regulated and subject to rigorous peer review, according to three experts on nuclear policy who held high office in different U.S. administrations; they note that despite international diplomatic efforts to prevent the proliferation of nuclear weapons and ensure that nuclear material is protected against theft, there is growing apprehension about terrorists acquiring weapons or nuclear material
-
-
Nuclear weapon simulations show performance in molecular detail
U.S. researchers are perfecting simulations that show a nuclear weapon’s performance in precise molecular detail, tools that are becoming critical for national defense because international treaties forbid the detonation of nuclear test weapons
-
-
Silkmoth inspires novel explosive detector
Scientists, imitating the antennas of the silkmoth, Bombyx mori, designed a system for detecting explosives with unparalleled performance; made up of a silicon microcantilever bearing nearly 500,000 aligned titanium dioxide nanotubes, the device is capable of detecting concentrations of trinitrotoluene (TNT) of around 800 ppq 1 (that is, 800 molecules of explosive per 1015 molecules of air), thus improving one thousand-fold the detection limit attainable until now
-
-
NIST releases new standard reference material for detecting PETN and TATP
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has released a new standard reference material (SRM) to aid in the detection of two explosive compounds that are known to be used by terrorists; researchers designed the new test samples to simulate the size and behavior of residues that remain after handling the explosives PETN (pentaerythritol tetranitrate) and TATP (triacetone triperoxide)
-
More headlines
The long view
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
