-
Detecting suicide bombers from a safe distance
Suicide bombings have now spread to Syria; a Florida company produces equipment designed to aid in the detection of a suicide bomber at standoff distances, before a terrorist can reach his intended target
-
-
Novel radiation detection technology to thwart nuclear terrorism
Researchers at the Georgia Tech Research Institute (GTRI) are developing ways to enhance the radiation-detection devices used at ports, border crossings, airports, and elsewhere; the aim is to create technologies that will increase the effectiveness and reliability of detectors in the field, while also reducing cost
-
-
New DNA-based chemical sensor acts as an all-electronic nose
Chemical sensors are very good at detecting a single substance or a class of chemicals, even at highly rarified concentrations; biological noses, however, are vastly more versatile and capable of discriminating subtle cues that would confound their engineered counterparts; even highly trained noses, however, do leave a certain ambiguity when relaying a signal
-
-
Bomb-sniffing dogs used in Everglades python invasion

Burmese pythons have invaded the Florida Everglades, adapting well to the Everglades environment; they have also been wreaking havoc with the delicate ecosystem of the area; now, there is a new weapon in the fight against the Burmese python: dogs, trained to sniff out explosives, are being re-trained to locate the Burmese python
-
-
Concerns raised about body-cavities explosives attack on aviation

Security services raised the possibility that al Qaeda affiliates may decide to mark the anniversary of the killing of Osama Bin Laden by sending suicide bombers with explosives inside their bodies to bring down airplanes; these experts point to an August 2009 attempt by a suicide body-bomber on a Saudi prince, and to the fact that U.S. drones earlier this year killed a Yemeni doctor who had devised medical procedures which could be used surgically to plant explosive devices in humans
-
-
Smart gas sensors offer better chemical detection

Smart chemical sensors can detect chemical weapon vapors or indicators of disease better than the current generation of detectors; they also consume less power, crucial for stretching battery life on the battlefield, down a mineshaft, or in isolated clinics
-
-
Android app for radioactivity detection

Just-release Android app uses software and the smartphone’s camera to measure radioactivity levels, allowing users to find out whether their environments are safe; the software is the civilian version of technology developed under contracts with the U.S. Department of Defense and with DHS
-
-
Rapid test strips detect swimming water contamination
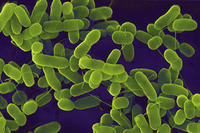
Water-testing technology has never been fast enough to keep up with changing conditions, nor accessible enough to check all waters; researchers have developed a rapid testing method using a simple paper strip that can detect E. coli in water within minutes; the new tool can close the gap between outbreak and detection, improving public safety
-
-
Cost of a dirty bomb attack in L.A. would reach $16 billion

A dirty bomb attack on downtown Los Angeles’ financial district could severely affect the region’s economy at a cost nearly $16 billion, fueled primarily by psychological effects which could persist for a decade
-
-
Naturally occurring enzyme to defend against chemical terrorism
Today, protection against nerve agents relies primarily on physical barriers such as gas masks and protective suits that can easily be breached; following exposure, people are treated with drugs that help with the symptoms but do not eliminate the nerve agent; researchers hope to change this, relying on the principles of evolution to produce a more efficient version of an enzyme that occurs naturally in all of us
-
-
INCOM to commercialize Argonne’s detection technology
Microchannel plate (MCP) detectors are used for detection of particles (electrons or ions) and impinging radiation (ultraviolet radiation and X-rays); this is an important technology for a variety of imaging applications ranging from medicine and physics to national security
-
-
More efficient bioterrorism response plan
In the event of a bioterror attack on a building (think: the 2011 anthrax attack on the offices of two Democratic Senators, Tom Daschle of South Dakota and Patrick Leahy of Vermont), the current approach to decontamination is to clean up the building until no pathogens can be detected; researchers suggest, however, that whether or not pathogens are found depends greatly upon how extensively the buildings are tested
-
-
Identifying ammunition, gun used to commit a crime
New, Raman spectroscopy-based gun-shot residue (GSR) analysis technique would make it possible for forensic investigators to match minute amounts of GSR to the exact type of ammunition, and the caliber of the gun, used to commit a crime
-
-
U.S. nuclear industry strong safety performance in 2011
Studies show that the U.S. nuclear power industry achieved strong safety performance in 2011; U.S. nuclear energy facilities in 2011 recorded the lowest number of unplanned shutdowns in more than a decade
-
-
Miniature sensors to advance climate studies, battlefield detection
Self-sealing valves are not only better for collecting reliable climate information – they also increase data reliability for airborne industrial and battlefield gas detection and point-of-contact medicine
-
More headlines
The long view
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
