-
Forecasters use Iron Dome science to handle disasters

Typhoons, floods, droughts, earthquakes, hurricanes, wildfires — the frequency and intensity of natural disasters across the globe are worsening, and these deadly events could continue plaguing the planet as a result of climate change. Iron Dome tech firm uses rocket science to enable utilities to plan for and manage effects of wildfires, storms, hurricanes and earthquakes.
-
-
Laying groundwork for off-world colonies

Space economy is estimated to reach $1.1 trillion by 2040, but before civilization can move off world it must make sure its structures work on the extraterrestrial foundations upon which they will be built. Researchers are already laying the groundwork for the off-world jump by creating standards for extraterrestrial surfaces.
-
-
Using concrete for space colonies
“Be prepared.” This famous mantra isn’t just for the Boy Scouts of America. The need to build durable infrastructure on other planets is coming, and we must be ready. To prepare, researchers have been exploring how cement solidifies in microgravity environments.
-
-
Wildfire risk in California no longer linked to winter precipitation
From 1600 to 1903, the position of the North Pacific jet stream over California was linked to the amount of winter precipitation and the severity of the subsequent wildfire season, the team found. Wet winters brought by the jet stream were followed by low wildfire activity, and dry winters were generally followed by higher wildfire activity. Wet winters no longer predict possible relief from severe wildfires for California, according to a new study.
-
-
Fast, simple new method for assessing earthquake hazard
Geophysicists have created a new method for determining earthquake hazards by measuring how fast energy is building up on faults in a specific region, and then comparing that to how much is being released through fault creep and earthquakes.
-
-
Asteroids are harder to destroy than previously thought
A popular theme in the movies is that of an incoming asteroid that could extinguish life on the planet, and our heroes are launched into space to blow it up. But incoming asteroids may be harder to break than scientists previously thought, finds a new study that used a new understanding of rock fracture and a new computer modeling method to simulate asteroid collisions.
-
-
Emission regulatory rollback: 200M metric tons of additional green house gasses annually
Following the release of the Fourth National Climate Assessment, the Trump administration is proposing to give four top climate-polluting industries a pass. A new report says that six specific regulatory rollbacks will cause an annual increase of more than 200 million metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent, resulting in the loss of hundreds of billions of dollars in forgone benefits, and lead to tens of thousands of premature deaths.
-
-
Rise of European populism linked to vaccine hesitancy

There is a significant association between the rise of populism across Europe and the level of mistrust around vaccines, according to a new study. “It seems likely that scientific populism is driven by similar feelings to political populism, for example, a profound distrust of elites and experts by disenfranchised and marginalized parts of the population,” says the study’s lead author. “Even where programs objectively improve the health of targeted populations, they can be viewed with suspicion by communities that do not trust elites and experts.”
-
-
“Clustering” land buyouts could improve flood resiliency after Hurricane Harvey
A new study analyzes flood loss claims and estimates from over 74,000 properties impacted by Hurricane Harvey in Houston’s Harris County. The study finds that a strategic land buyout approach that prioritizes the purchase of land parcels in ‘clusters,’ as well as proximity to existing open space, is just as cost-effective as the traditional, piecemeal approach but with major added ecological and social benefits.
-
-
Resilience and adaptation strategies can address the impacts of climate change
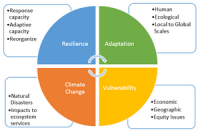
By the end of this century, Chicago could face the kind of searing summer heat that Las Vegas sees now. Phoenix could hit 110 degrees, 60 or more days a year. That’s not wild speculation. It’s the official position of 13 federal agencies on climate change, released late last year with a warning: Local governments need to do more to prepare. Every road they build, every storm drain they put in, will have to hold up under conditions that modern civilization has never seen. How do you plan for that? Researchers at RAND have been working on that problem for a while now.
-
-
Protect confidential information from cyberattacks
The NSF is funding research aiming to develop new guidelines for sharing secret information through wireless communication that would improve security for users and minimizes cost.
-
-
Population increases, climate change will cause future U.S. water shortages
Climate change plus population growth are setting the stage for water shortages in parts of the U.S. long before the end of the century, according to a new study. Even efforts to use water more efficiently in municipal and industrial sectors won’t be enough to stave off shortages, say the authors of the new study. The results suggest that reductions in agricultural water use will probably play the biggest role in limiting future water shortages.
-
-
New periodic table of droplets could help in solving crimes
Liquid droplets assume complex shapes and behave in different ways, each with a distinct resonance – like a drum head or a violin string – depending on the intricate interrelationship of the liquid, the solid it lands on and the gas surrounding it. Researchers have created a periodic table of droplet motions, inspired in part by parallels between the symmetries of atomic orbitals. Better understanding of droplets behavior may help solve crimes.
-
-
Robots help in the demanding Fukushima cleanup efforts
In 2011, a tsunami triggered by a magnitude 9.0 earthquake all but decimated the Pacific Coast of Tohoku, Japan, including the Fukushima Daiichi power plant. A catastrophic meltdown ensued. Many tons of nuclear fuel, boiled down to a radioactive lava, corroded the steel surrounding the facility’s three reactors. Today, the cleanup effort is still projected to take several decades. S&T and NIST developed standard test methods for robots, which the Japanese government is now beginning to apply directly to their Fukushima cleanup efforts.
-
-
Better monitoring of nuclear power plants, nuclear proliferation
The United Kingdom is investing nearly £10 million (about $12.7 million) in a joint project with the United States to harness existing particle physics research techniques to remotely monitor nuclear reactors. Expected to be operational in 2024, the Advanced Instrumentation Testbed (AIT) project’s 6,500-ton detector will measure the harmless subatomic particles called antineutrinos that are emitted by an existing nuclear power plant 25 kilometers, or about 15.5 miles, away.
-
More headlines
The long view
The Future of Open Data in the Age of AI: Safeguarding Public Assets Amid Growing Private Sector Demands
AI offers immense potential, but that potential must be realized within a framework that protects the public’s right to its own information. The open data movement must evolve to meet this new challenge—not retreat from it.
Horses for Courses: Where Quantum Computing Is, and Isn’t, the Answer
Despite the impressive and undeniable strides quantum computing has made in recent years, it’s important to remain cautious about sweeping claims regarding its transformative potential.
Federal R&D Funding Boosts Productivity for the Whole Economy − Making Big Cuts to Such Government Spending Unwise
Large cuts to government-funded research and development can endanger American innovation – and the vital productivity gains it supports. If the government were to abandon its long-standing practice of investing in R&D, it would significantly slow the pace of U.S. innovation and economic growth.
Why Ukraine’s AI Drones Aren’t a Breakthrough Yet
Machine vision, a form of AI, allows drones to identify and strike targets autonomously. The drones can’t be jammed, and they don’t need continuous monitoring by operators. Despite early hopes, the technology has not yet become a game-changing feature of Ukraine’s battlefield drones. But its time will come.
New Tech Will Make Our Airplanes Safer
Odysight.ai’s technology allows for constant monitoring of aircraft, sending alerts in case of malfunctions that could lead to accidents.
New Technology is Keeping the Skies Safe
DHS S&T Baggage, Cargo, and People Screening (BCP) Program develops state-of-the-art screening solutions to help secure airspace, communities, and borders
