-
The world likely to face more frequent, and more severe, blackouts
U.S. household electricity usage increased by 1,300 percent between 1940 and 2001. In the last few decades, air conditioning has been the greatest factor in increased electrical consumption, and one of the greatest sources of systematic strain, with considerably more blackouts occurring in the summer months than during winter. The electricity used to fuel America’s air conditioning is currently of a similar volume to the U.S. entire energy consumption in the 1950s. A new study reveals that today’s occasional blackouts are dress rehearsals for the future, when they will occur with greater frequency and increased severity. Power cuts will become more regular around the globe as electrical supply becomes increasingly vulnerable and demand for technology continues to grow at an unprecedented rate.
-
-
Natural flood management as a solution against future flooding

Natural Flood Management (NFM) aims to reduce the downstream maximum water height of a flood — the peak — or delay the arrival of the flood peak downstream, increasing the time available to prepare. Back-to-nature flood schemes which use the land’s natural defenses to slow river flow and reduce flooding could be a cost-effective way of tackling one of the biggest problems facing the United Kingdom today.
-
-
Deepwater Horizon: Identifying harmful elements of persisting oil

Scientists are unraveling the composition of persisting oil residues collected from Gulf of Mexico beaches following the Deepwater Horizon disaster, insisting on further assessment of the toxic impact of these chemical remnants on the marine ecosystem. A new study targeted the most abundant compounds in the residual oil, dissecting their composition with unprecedented accuracy. This is important for understanding the environmental impact of persisting oil remnants, because ecotoxicologists have demonstrated that all three chemical groups can be harmful to living organisms. More worrisome, relatively little is known about the broader toxicity of saturates and oxygenated hydrocarbons in the marine ecosystem, like the Gulf of Mexico —where there are 223 offshore oil rigs — even though these compounds constitute most of the persisting oil.
-
-
ExxonMobil to pay fines for violations at its Baton Rouge chemical facilities
In a settlement with Louisiana’s Department of Environmental Quality (DEQ), ExxonMobil is ordered to pay $2.329 million to address violations from 2008 to 2013 at its greater Baton Rouge facilities. ExxonMobil was cited for a series of problems at its refinery and resin-finishing and chemical plants in East Baton Rouge Parish, and its tank-farm facility in West Baton Rouge.
-
-
Halting bugs’ crop destruction in India saves up to $309 million
Researchers who first discovered a devastating pest in India and devised a natural way to combat it have now put an economic value on their counterattack: up to $309 million the first year and more than $1 billion over five years. This is the amount of damage the papaya mealybug would have wreaked on farmers and consumers in India without scientists’ intervention. The winning intervention centered on three natural enemies of the mealybug — three parasitic wasps from Mexico— which the U.S. government first employed in Florida after the pest spread there in the late 1990s.
-
-
Israel considering earthquake-proofing important Biblical-period structures
Israel is located in one of the world’s earthquake-prone areas, along the friction point of the African and Arabian tectonic plates.Officials in Israel are taking preventative measures to protect the country’s most important ancient sites from earthquake damage. Engineers from the University of Padua in Italy have installed sensors throughout the Tower of David, one of Jerusalem most important historical sites, to determine what sort of earthquake-proofing may be needed. Some experts opined that in the event of an earthquake, Jerusalem’s most ancient structures might actually be the city’s most dependable. “If they still stand after so many earthquakes during the last 2,000 years, they must be good structures,” one of them said.
-
-
USAF nuclear-missile officers alleged to have regularly cheated on readiness tests

Three former U.S. Air Force officers have alleged that USAF officers responsible for operating nuclear-armed missiles at Malmstrom Air Base in Montana have, for many years, been cheating on monthly readiness tests, and were never punished for it. The former officers claim that cheating is the norm and that officers who did otherwise are the exception.The officers who made the allegations added, though, that misconduct on tests did not impair the safety of the nuclear weapons or the Air Force’s ability to launch missiles if ordered.
-
-
Using pencil and paper to detect hazardous chemicals
Three students from Northwestern University have proven that pencils and regular office paper can be used to create functional devices that can measure strain and detect hazardous chemical vapors. The project originated during a discussion about the conductive properties of graphene, a one-atom thick layer of carbon that can be parsed from regular pencil lead.
-
-
Thumbnail-sized quantum cascade laser, tuning forks detect greenhouse gases
Human activities such as agriculture, fossil fuel combustion, wastewater management, and industrial processes are increasing the amount of nitrous oxide in the atmosphere. The warming impact of methane and nitrous oxide is more than 20 and 300 times, respectively, greater compared to the most prevalent greenhouse gas, carbon dioxide, over a 100-year period. Methane and nitrous oxide detection is crucial to environmental considerations. Scientists use a thumbnail-sized quantum cascade laser (QCL) as well as tuning forks that cost no more than a dime to detect very small amounts of nitrous oxide and methane.
-
-
Botwall: New Web security solution uses real-time polymorphism to ward off attacks
Malware has long used polymorphism — that is, rewriting its code — every time a new machine was infected in order easily to evade antivirus detection systems. Shape Security says its new product, the ShapeShifter, is reversing this advantage which malware has so far enjoyed: the new product uses polymorphic code as a new foundational tool for Web site defense. The patent-pending technology implements real-time polymorphism, or dynamically changing code, on any Web site, to remove the static elements that botnets and malware depend on for their attacks.
-
-
“Virtual earthquakes” used to forecast Los Angeles quake risk
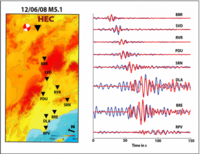
Stanford scientists have developed a new “virtual earthquake” technique and used it to confirm a prediction that Los Angeles would experience stronger-than-expected ground motion if a major quake occurred along the southern San Andreas Fault. The new technique capitalizes on the fact that earthquakes are not the only sources of seismic waves – rather, there is also an ambient seismic field consisting of much weaker seismic waves. The scientists devised a way to make these ambient seismic waves function as proxies for seismic waves generated by real earthquakes. By studying how the ambient waves moved underground, the researchers were able to predict the actions of much stronger waves from powerful earthquakes.
-
-
Texas wants to know whether fracking causes earthquakes
Texas has about 35,000 active injection wells. About 7,000 of Texas’s injection wells are used for disposing wastewater deep underground, and some experts say these wells can cause earthquakes. In response to the several minor earthquakes which occurred in late 2013 around the Azle, Texas area, local officials are investigating whether oil and gas drilling in North Texas and the injection wells that follow after, are responsible for the quakes.
-
-
U.S. power plant emissions down

Power plants that use natural gas and a new technology to squeeze more energy from the fuel release far less of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide than coal-fired power plants do, according to a new analysis. The so-called “combined cycle” natural gas power plants also release significantly less nitrogen oxides and sulfur dioxide, which can worsen air quality.
-
-
New York mulling first U.S. college dedicated to homeland security studies
Political, educational, and law enforcement leaders in New York are actively exploring the idea of creating pro the U.S. first college focused on emergency management and homeland security on the Syracuse University (SU) campus. “Believe it or not, there is no such college,” Governor Andrew Cuomo said during his fourth State of the State address two weeks ago. “I believe this is a field that is only going to grow. Unfortunately, it’s only going to get worse. And we want this college right here in the state of New York, training our people and training others from around the country.”
-
-
Restrictive concealed weapons laws correlated with an increase in gun-related murders

It may make sense to assume that states in which there are tight laws on weapons would make that state a safer place and one with less gun crime, but recent research argues that the very opposite is true. Research shows that in states with more restrictive concealed carry weapons (CCW) laws there is actually an increase in gun related crime. The author notes that his study looks solely at gun crime, rather than violent crime, which is the case in similar research.
-
More headlines
The long view
New Technology is Keeping the Skies Safe
DHS S&T Baggage, Cargo, and People Screening (BCP) Program develops state-of-the-art screening solutions to help secure airspace, communities, and borders
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
How Artificial General Intelligence Could Affect the Rise and Fall of Nations
Visions for potential AGI futures: A new report from RAND aims to stimulate thinking among policymakers about possible impacts of the development of artificial general intelligence (AGI) on geopolitics and the world order.
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
