-
New phone alerts for extreme weather events may prevent casualties in India
India has a mobile phone subscriber base exceeding 929 million people and this is expected to touch 1.15 billion by the end of 2014. An alert system developed for mobiles could reach an estimated 97 percent of the population. Computer science undergraduates have created image-based mobile phone alerts, connected to the Weather Research and Forecasting system.
-
-
U.S. educational system does not help gifted children reach their full potential
Gifted children are likely to be the next generation’s innovators and leaders — yet the exceptionally smart are often invisible in the classroom, lacking the curricula, teacher input, and external motivation to reach full potential. This conclusion comes as the result of the largest scientific study of the profoundly gifted to date, a 30-year study conducted by Vanderbilt University researchers. The researchers tracked 300 gifted children from age 13 until age 38, logging their accomplishments in academia, business, culture, health care, science, and technology.
-
-
Military technology outpaces laws of war

Today’s emerging military technologies — including unmanned aerial vehicles, directed-energy weapons, lethal autonomous robots, and cyber weapons like Stuxnet — raise the prospect of upheavals in military practices so fundamental that they challenge long-established laws of war. Weapons that make their own decisions about targeting and killing humans, for example, have ethical and legal implications obvious and frightening enough to have entered popular culture (for example, in the Terminator films). The current international laws of war were developed over many centuries and long before the current era of fast-paced technological change.
-
-
The benefits, challenges of self-driving cars
Self-driving vehicles offer the promise of significant benefits to society, but raise several policy challenges, including the need to update insurance liability regulations and privacy concerns such as who will control the data generated by this technology, according to a new RAND Corporation study. Researchers suggest that a guiding principle for policymaking is to encourage the technology when the facts indicate clear societal advantages over the capabilities of the average human driver.
-
-
Supercomputers help in search for “cheapium”
In the search for cheaper materials that mimic their purer, more expensive counterparts, researchers are abandoning hunches and intuition for theoretical models and pure computing power. In a new study, researchers used computational methods to identify dozens of platinum-group alloys that were previously unknown to science but could prove beneficial in a wide range of applications.
-
-
“Power to gas”: Synthetic natural gas from excess electricity
“Power to gas” is a key concept when it comes to storing alternative energy. This process converts short-term excess electricity from photovoltaic systems and wind turbines into hydrogen. Combined with the greenhouse gas CO2, renewable hydrogen can be used to produce methane, which can be stored and distributed in the natural gas network. Researchers have now succeeded in further optimizing this process.
-
-
Abandoned mine offers clues about permanent CO2 sequestration
Power plants and other industries are responsible for more than 60 percent of global CO2 emissions, according to the International Energy Agency. Sequestering the CO2 in magnesite deposits would prevent the gas from entering the atmosphere and warming the planet. Stanford University researchers, studyingveins of pure magnesium carbonate, or magnesite — a chalky mineral made of carbon dioxide (CO2) and magnesium – in an abandoned mine in the Red Mountain, propose a novel technique for converting CO2 into solid magnesite, making CO2 sequestration feasible.
-
-
Narrow view of science deters 10-14 year old students from considering science careers
Careers in science rarely appeal to 10-14 year old students unless the student has a family connection to science, new research finds. Researchers, using more than 19,000 survey results and a series of longitudinal interviews at three intervals over five years with students and parents, conclude that students are turned off pursuing science by a narrow view of where studying science leads and lofty conceptions of who is capable of it.
-
-
Eight teams heading to DARPA Robotics Challenge finals

Two weeks ago, on 20-21 December 2013, sixteen teams were the main attraction at the DARPA Robotics Challenge (DRC) Trials, where they demonstrated their prototype robots’ ability to perform a number of critical real-world disaster-response skills. After two days of competition, the agency selected eight teams to receive up to $1 million in funding to continue their work and prepare for upcoming DARPA Robotics Challenge (DRC) Finals.
-
-
New system uses low-power Wi-Fi signal to track moving humans -- even behind walls
The comic-book hero Superman uses his X-ray vision to spot bad guys lurking behind walls and other objects. Now we could all have X-ray vision, thanks to a new system developed by researchers at MIT. The system, called “Wi-Vi,” is based on a concept similar to radar and sonar imaging. But in contrast to radar and sonar, it transmits a low-power Wi-Fi signal and uses its reflections to track moving humans. It can do so even if the humans are in closed rooms or hiding behind a wall.
-
-
U.S. global share of biomedical research spending declines

The U.S. global share of biomedical research spending fell from 51 percent in 2007 to 45 percent in 2012, while Japan and China saw dramatic increases in research spending. The research and development spending in the United States dropped from $131 billion to $119 billion, when adjusted for inflation, from 2007 to 2012, while Japan increased spending by $9 billion and China increased by $6.4 billion. Overall, Asia’s share of spending grew from 18 percent to 24 percent. Europe held steady at 29 percent.
-
-
Relying on geoengineering to reduce climate change unlikely to succeed
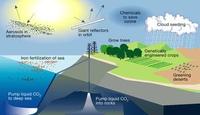
Reducing the amount of sunlight reaching the planet’s surface by geoengineering may not undo climate change after all. Researchers used a simple energy balance analysis to explain how the Earth’s water cycle responds differently to heating by sunlight than it does to warming due to a stronger atmospheric greenhouse effect. Further, they show that this difference implies that reflecting sunlight to reduce temperatures may have unwanted effects on the Earth’s rainfall patterns.
-
-
Urgent action needed to save the Great Plains water supply
Significant portions of the Ogallala Aquifer, one of the largest bodies of water in the United States, are at risk of drying up if it continues to be drained at its current rate.The body of water, also known as the High Plains Aquifer, spans from Texas to South Dakota and drives much of the region’s economy. Scientists are proposing alternatives that will halt and hopefully reverse the unsustainable use of water drawdown in the aquifer.
-
-
Who learns in math classes depends on how math is taught
As debates rage about education and equity in primary and secondary schools, are we ignoring the potential inequities in higher education math classrooms? Most students in university math classes will not become mathematicians and are not intrinsically interested in math. Experts say that a strong case can be made for moving away from passive “sage on the stage” lecturing approaches, in favor of actively engaging students in doing math in class. This “inquiry based learning” approach sees students actively engaging in problem-solving and discussion with peers.
-
-
Risk of earthquake/tsunami in Caribbean higher than previously thought
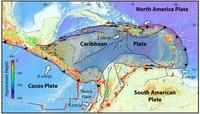
Enough strain may be currently stored in an earthquake zone near the island of Guadeloupe to cause a magnitude 8 or larger earthquake and subsequent tsunami in the Caribbean, according to a new U.S. Geological Survey study.
-
More headlines
The long view
New Technology is Keeping the Skies Safe
DHS S&T Baggage, Cargo, and People Screening (BCP) Program develops state-of-the-art screening solutions to help secure airspace, communities, and borders
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
How Artificial General Intelligence Could Affect the Rise and Fall of Nations
Visions for potential AGI futures: A new report from RAND aims to stimulate thinking among policymakers about possible impacts of the development of artificial general intelligence (AGI) on geopolitics and the world order.
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
