-
Melting Arctic sea ice increases summer rainfall in northwest Europe
A new study offers an explanation for the extraordinary run of wet summers experienced by Britain and northwest Europe between 2007 and 2012. The study found that loss of Arctic sea ice shifts the jet stream further south than normal resulting in increased rain during the summer in northwest Europe. The annual average extent of Arctic sea ice is currently declining at about half a million square kilometers per decade — equivalent to about twice the area of the United Kingdom.
-
-
Urban underground water can be used for sustainable energy
Vast energy sources are slumbering below big cities. Sustainable energies for heating in winter and cooling in summer may be extracted from heated groundwater aquifers. Researchers developed an analytical heat flux model and found that increasing heat in the underground is mainly caused by an increase in surface temperatures and heat release from buildings.
-
-
Helping first responders identify chemical, biological, and radiological agents
The U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) has expanded the reach and capabilities of its rapid urban plume modeling and hazard assessment system, CT-Analyst, by providing a commercial license to Valencia, California-based Safe Environment Engineering (SEE) for the fields of use of public safety, industrial safety and monitoring, and environmental monitoring. CT Analyst is a tool designed to provide first responders with fast and accurate predictions of chemical, biological, and radiological agent airborne transport in urban environments. CT Analyst will be integrated into the existing product line of SEE’s Lifeline MultiMeterViewer software suite.
-
-
Video imaging system for remote detection of hidden threats
By adapting superconducting technology used in advanced telescope cameras, researchers have built a prototype video imaging system for detecting hidden weapons and other threats at distances up to twenty-eight meters away.
-
-
Death of Muslims used by extremists for recruitment, propaganda
In the last thirty years, conflicts in Afghanistan, Iraq, Bosnia, Chechnya, Somalia, and other countries have caused the death of four million Muslims. The theme of innocent Muslims dying as result of conflicts initiated by Western powers and their allies is a central motif used by Islamic militants to recruit new members. It is a theme which fuels anti-American sentiments in the Middle East and North Africa. Historians and Islamic scholars note that the notion that the West is orchestrating a “genocide” of Muslim is patently false, and that beginning with the Iran-Iraq War (1980-88) and continuing to the present day, more and more casualties are inflicted by Muslims against Muslims. Still, the myth of a non-Muslim genocidal “crusade” against Muslims is powerful, and is one which is effectively used by al Qaeda and other Islamic terrorist groups.
-
-
Peru reopens UFO investigation office
The Peruvian air force, saying it was responding to an “increased sightings of anomalous aerial phenomena” in the country’s skies,” has reopened its Departamento de Investigación de Fenómenos Aéreos Anómalos (DIFAA). The investigative office was established in 2001 but closed in 2008. DIFAA will bring together sociologists, archaeologists, astronomers, meteorologists, and air force personnel to analyze these anomalous events. Peru is not the only Latin American country showing renewed interest in UFOs.
-
-
Dolphin-inspired radar system detects hidden surveillance, explosive devices

Scientists, inspired by the way dolphins hunt using bubble nets, have developed a new kind of radar that can detect hidden surveillance equipment and explosives. The twin inverted pulse radar (TWIPR) is able to distinguish true targets, such as certain types of electronic circuits that may be used in explosive or espionage devices, from clutter (for example, other metallic items like pipes, drinks cans, or nails) which may be mistaken for a genuine target by traditional radar and metal detectors.
-
-
New spectrometry standard for handheld chemical detectors
When it comes to detectors for dangerous chemicals, toxins, or nefarious germs, smaller and faster is better. Size and speed, however, must still allow for accuracy, especially when measurements by different instruments must give the same result. The recent publication of a new standard provides confidence that results from handheld chemical detectors can be compared, apples-to-apples.
-
-
Squeezing light improves performance of MEMS sensors
Microelectromechanical systems, known as MEMS, are ubiquitous in modern military systems such as gyroscopes for navigation, tiny microphones for lightweight radios, and medical biosensors for assessing the wounded. Such applications benefit from the portability, low power, and low cost of MEMS devices. The use of MEMS sensors is now commonplace, but they still operate many orders of magnitude below their theoretical performance limits, due to two obstacles: thermal fluctuations and random quantum fluctuations, a barrier known as the standard quantum limit.
-
-
New method to help coastal communities adapt to sea-level rise
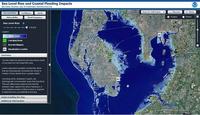
Future sea-level rise seems inevitable, although the rates and geographical patterns of change remain uncertain. Given the large and growing populations and economic activity in coastal zones, as well as the importance of coastal ecosystems, the potential impacts of sea-level change are far-reaching. Current methods to assess the potential impact of sea-level rise have varied significantly and hindered the development of useful scenarios and, in turn, suitable adaption policies and planning.
-
-
Acoustic detection identifies IEDs – and their explosive yield
A number of different tools are currently used for explosives detection. These range from dogs and honeybees to mass spectrometry, gas chromatography, and specially designed X-ray machines.A new acoustic detection system, consisting of a phased acoustic array that focuses an intense sonic beam at a suspected improvised explosive device, can determine the difference between those that contain low-yield and high-yield explosives.
-
-
Innovative technique to detect fingerprints
Researchers have developed an innovative product that uses fluorescence to detect fingerprints. This new product, Lumicyano, will make it possible to highlight fingerprints directly, more rapidly, and at a lower cost, avoiding the cumbersome processes required until now.
-
-
Burping for power: Tapping cow burps for natural gas
Scientists in Argentina have developed a method to transform the gas created by cows’ digestive systems into fuel. The technique channels the digestive gases from bovine stomach cavities through a tube and into a tank, where the gases, called eruptos (burps) in Spanish, are processed to separate methane from other gases such as carbon dioxide.
-
-
U.S. math instruction less effective than Chinese math teaching
International comparisons of students in mathematics have shown higher performance by several nations than by students in the United States. A $200,000 grant from the National Science Foundation will enable a team of U.S. and Chinese researchers to identify instructional supports that lead to higher levels of mathematics achievement. “Even though cultural differences such as the value of education in society are major contributors to the achievement gap between China and the United States, there are also fundamental differences in the ways in which the profession of teaching is organized and supported that may be leading to differences in teaching quality as well,” one of the researchers says.
-
-
$32 million NSF grants for improving prediction of, response to natural disasters
With Sandy’s one-year anniversary – 29 October – next week, how do scientists better predict and respond to natural hazards such as hurricanes, tornadoes, floods, earthquakes, tsunamis, and wildfires? To find answers, the National Science Foundation (NSF) recently awarded twelve new research grants totaling $32 million. The awards will advance understanding of natural hazards and of technological hazards linked with natural phenomena, as scientists study ways of predicting and responding to hurricanes, tornadoes, floods, earthquakes, tsunamis, wildfires.
-
More headlines
The long view
New Technology is Keeping the Skies Safe
DHS S&T Baggage, Cargo, and People Screening (BCP) Program develops state-of-the-art screening solutions to help secure airspace, communities, and borders
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
How Artificial General Intelligence Could Affect the Rise and Fall of Nations
Visions for potential AGI futures: A new report from RAND aims to stimulate thinking among policymakers about possible impacts of the development of artificial general intelligence (AGI) on geopolitics and the world order.
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
