-
Bolstering water security in a crowded world
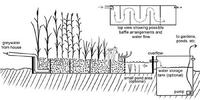
With limited water and the increasing number of people depending on it – there will be more than nine billion people on the planet by 2050 — water security is tenuous. Integrated water management plans using “blue,” “green,” and “gray” water, however, can increase water security by allowing agriculture to rise to the challenge of feeding a growing world population while leaving enough water for other uses.
-
-
Government shutdown stymies U.S. science agencies
A U.S. Government furloughs affecting virtually all National Science Foundation (NSF) employees and three-fourths of those at the National Institutes of Health could impact American competitiveness, the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) warned. “If the government shutdown continues for a week or more, it is going to make the United States less desirable as an international research collaborator,” said an AAAS representative. “When funding is no longer reliable, many of our research partners may be unable to continue collaborating with us. That could eventually have longer-term impacts on American innovation and competitiveness.”
-
-
Reducing security threats from explosives
Researchers, as part of the Awareness and Localization of Explosives-Related Threats center (ALERT), a DHS Center of Excellence, are working on ways to detect explosives and neutralize their impact. The researchers are developing portable detectors as well as larger systems to scan for explosives. Some technologies will analyze the spectrum of light shining through vaporized samples; others will analyze solid residues.
-
-
Delaware prepares for sea-level rise

Benjamin Franklin said that that an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure, and Governor Jack Markell of Delaware agrees. Two weeks ago he unveiled an initiative aiming to prepare his state for the effects of climate change and sea-level rise. Markell has signed an executive order requiring all state agencies to take sea-level rise into account when designing and locating state projects. The order also requires development of strategies to make state facilities and operations better prepared to deal with climate change and sea-level rise.
-
-
Radioactive shale gas contaminants seep into a Pennsylvania creek

Researchers examined the quality of shale gas wastewater from hydraulic fracturing and the stream water above and below the disposal site in western Pennsylvania. Elevated levels of radioactivity, salts, and metals have been found in river water and sediments at a site where treated water from oil and gas operations is discharged into a creek.
-
-
Making clean drinking water universally available “achievable”
More than 780 million people around the world still do not have safe and reliable drinking water. The problem of providing clean water is most acute in developing countries, particularly in Africa, where creaking infrastructures struggle to keep pace with fast-growing urban populations; in rural areas, millions of water pumps stand unused waiting to be repaired.
-
-
Societies with rigid cultural values produce more terrorists

Examining more than 80,000 terrorist attacks which occurred between 1970 and 2007, researchers find that cultural values and norms which promote rigid thinking are related to a greater number of terrorist attacks or fatalities. Societies that have the belief that one’s destiny and life events are predetermined (fatalism), have very strong norms and severe punishments for deviation from norms (cultural tightness), and those that privilege masculinity and have very distinct gender roles (low gender egalitarianism) have higher terrorism rates than those that are low on these dimensions.
-
-
Violent hate crimes, lone-wolf terrorism share characteristics
Researchers examined the timing, locations, methods, targets, and geographic distributions of lone-actor terrorist attacks, group-based terrorist attacks, and violent hate crimes that occurred in the United States between 1992 and 2010. They found that locations where the 101 lone-actor terrorism incidents occurred shared more demographic similarities with the locations of the 46,000 violent hate crimes than with the locations of 424 group-based terrorist attacks over the time period.
-
-
Tiny smartphone sensors create an urban seismic network
A tiny chip used in smart phones to adjust the orientation of the screen could serve to create a real-time urban seismic network, easily increasing the amount of strong motion data collected during a large earthquake. This urban seismic network could transmit in real-time ground motion data to a central location for assessment. The rich volume of data could help first responders identify areas of greatest potential damage, allowing them to allocate resources more effectively.
-
-
Harnessing lightning power to charge a mobile phone

Scientists from the University of Southampton have collaborated with Nokia on ground-breaking, proof-of-concept research into harnessing the power of lightning for personal use, an industry first that could potentially see consumers tap one of nature’s significant energy sources to charge their devices in a sustainable manner.
-
-
Parental, administrative support breeds academic success
Researchers used data collected from 180,000 students, 170,000 parents, 14,000 teachers, and 6,000 principals across thirty-four countries to look at the issue of cultural excellence — what parents, schools, and students are doing to improve success in reading, math, and science. It is a long-held belief that parental and administrative support helps breed academic success; and the new study offers data to back that up.
-
-
New technology spots killer waves
Sailors throughout the ages have wished they could predict the strength and size of the next wave. The Environmental and Ship Motion Forecasting (ESMF) system, a Future Naval Capability effort supported by the Office of Naval Research’s (ONR) Sea Warfare and Weapons Department, seeks to provide sea-based forces with new capabilities for difficult operations like ship-to-ship transfer of personnel, vehicles, or materiel — giving operators sea condition information at levels of accuracy never possible before.
-
-
Alabama State launches Nuclear Academy
A new academy at Alabama State University (ASU) will enhance security at nuclear, electric, and green-energy power installations across the United States and abroad. The new academy will provide comprehensive training for current and future security professionals who will offer infrastructure protection services to nuclear, electric and green-energy power installations.
-
-
Arbor Day meets Kyoto: Tree planting promotes carbon capture, green neighborhoods
Schemes which offer economic incentives for growing trees for carbon present an opportunity to reverse trends in land clearing but also to restore ecosystem services — such as pest control, pollination, soil and water conservation. Best practice carbon farming that considers more than just the carbon in trees is thus needed if the full benefits of trees in the landscape are to be realized by farmers, landholders, and the community.
-
-
Innovations help lighten the load for marines
The Office of Naval Research (ONR) was at the Modern Day Marine exposition last week, showcasing some of the newest technologies it has helped develop to give sailors and marines the edge. The Expeditionary Maneuver Warfare and Combating Terrorism Department at ONR highlighted its focused initiatives to lighten the load for marines, including integrated day/night vision sights, scalable body armor, and other research which will help marines out-think, out-maneuver, and out-perform the enemy.
-
More headlines
The long view
New Technology is Keeping the Skies Safe
DHS S&T Baggage, Cargo, and People Screening (BCP) Program develops state-of-the-art screening solutions to help secure airspace, communities, and borders
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
How Artificial General Intelligence Could Affect the Rise and Fall of Nations
Visions for potential AGI futures: A new report from RAND aims to stimulate thinking among policymakers about possible impacts of the development of artificial general intelligence (AGI) on geopolitics and the world order.
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
