-
Hazard of Western Indian Ocean earthquake, tsunami greater than thought
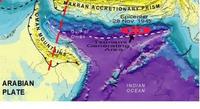
Earthquakes similar in magnitude to the 2004 Sumatra earthquake could occur in an area beneath the Arabian Sea at the Makran subduction zone, according to recent research. The study suggests that the risk from undersea earthquakes and associated tsunami in this area of the Western Indian Ocean — which could threaten the coastlines of Pakistan, Iran, Oman, India, and potentially further afield — has been previously underestimated.
-
-
Quickly identifying chemical, biological warfare agents
For more than fifty years, researchers have been studying exactly how aspirin affects the human body. Despite thousands of publications on the topic, our understanding is still incomplete. Meanwhile, novel chemical and biological weapons have historically been mass produced within a year of discovery. Using current methods and technologies, researchers would require decades of study to gain a robust understanding of how new threat agents exert effects on human biological systems. DARPA wants to close this capability gap, which leaves U.S. forces vulnerable.
-
-
Terahertz technology helps to see more with less
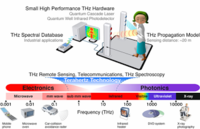
Terahertz technology is an emerging field which promises to improve a host of useful applications, ranging from passenger scanning at airports to huge digital data transfers. Terahertz radiation sits between the frequency bands of microwaves and infrared radiation, and it can easily penetrate many materials, including biological tissue. The energy carried by terahertz radiation is low enough to pose no risk to the subject or object under investigation.
-
-
Assessing asteroid risk to Earth
Of the more than 600 000 known asteroids in our Solar System, almost 10 000 are classified as near-Earth objects, or NEOs, because their orbits bring them relatively close to Earth’s path. A dramatic proof that any of these can strike Earth came on 15 February, when an unknown object thought to be 17-20 meter in diameter arrived at 66 000 km/h and exploded high above Chelyabinsk, Russia, with 20-30 times the energy of the Hiroshima atomic bomb.
-
-
Silica particles purify water by acting as oil magnets
Engineers develop an innovative method designed to purify water through the rapid removal of oily pollutants. The technology involves the deployment of surface engineered silica particles, which act as oil magnets in water, adsorbing oil, yet repelling water.
-
-
New grass hybrid helps reduce runoffs, flooding

Scientists use hybridized forage grass to combine fast root growth and efficient soil water retention. Field experiments show Festulolium cultivar reduces water runoff by up to 51 percent against nationally-recommended cultivar. The hybrid captures more water and reduces runoff and likelihood of flood generation.
-
-
Lower waves' impact on coastal communities uncertain
Coastal impacts of climate change studies have predominantly focused on the influence of sea-level rise and, until now, not focused on how changing wave conditions will impact the coastal zone in a changing climate. Scientists note, though, that waves are dominant drivers of coastal change in these sandy environments, and variability and change in the characteristics of surface ocean waves can far exceed the influences of sea-level rise in such environments. Since warmer oceans will see lower waves, the effect of warming on coastal communities is uncertain.
-
-
N.C. university becomes first in state to offer homeland security degree
There are 380 security-related academic programs in U.S. colleges, most of which are two-year programs. Campbell University, established in 1887, has become the first university in North Carolina to offer a bachelor’s degree program in homeland security, beginning this fall. The school says the new degree is a direct result of a rising interest in the field.
-
-
Sponsors: Immigration bill addresses visa flaws highlighted by the Boston bombing
Lawmakers behind the bipartisan Senate immigration say bill directly addresses some of the security flaws that may have been exploited by the foreign student who helped Dzhokhar Tsarnaev dispose of evidence after the Boston Marathon bombings.
-
-
U.S. may acquire additional land for constructing border fence
A U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) draft plan regarding the final sections of the border fence that separates the United States from Mexico could impact about 100 people, most reside in a nursing home, according to federal documents.
-
-
Schools do not offer students sufficient practical science experience

New evidence shows that a worrying number of students are not experiencing a complete and authentic education in the sciences, due to a lack of resources for practical work. Secondary schools reported not having enough of some of the most commonly used equipment, such as microscopes, eye protection, and connecting leads for circuits. The research also shows that many secondary schools lack essential support from qualified technicians to carry out practical work.
-
-
New technology prevents bridge collapse
Researchers propose a new technology that could divert vibrations away from load-bearing elements of bridges to avoid catastrophic collapses. The researchers propose a “wave bypass” technique that has many similarities to those being used by researchers looking to create Harry Potter-style invisibility cloaks, which exploit man-made materials known as metamaterials to bend light around objects.
-
-
Ash from olive residue biomass leads to more effective, cheaper concrete
Researchers have produced self-compacting concrete with ash from boiler combustion of olive pruning residue pellets. The plasticity and cohesion of this type of concrete mean no compaction is needed when used in construction and, moreover, it has other advantages with respect to conventional concrete.
-
-
NASA high school STEM challenge announces winning team
NASA science challenge asked students in grades 7–12 either to re-design a shield to keep Webb telescope cold enough to “detect infrared light from faint sources such as distant galaxies and extrasolar planets,” or to re-design a mirror assembly “so that Webb telescope may produce images that are “sufficiently bright and sharp to look back in time to when galaxies were young.”
-
-
California braces for out-of-control wildfires

The lack of precipitation over the past two winters has California and federal officials concerned about the impact wildfires could have in the summer months. California has already recorded 845 wildfires this year, a 60 percent increase compared with the average for the previous five years.
-
More headlines
The long view
New Technology is Keeping the Skies Safe
DHS S&T Baggage, Cargo, and People Screening (BCP) Program develops state-of-the-art screening solutions to help secure airspace, communities, and borders
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
How Artificial General Intelligence Could Affect the Rise and Fall of Nations
By Barry Pavel et al.
Visions for potential AGI futures: A new report from RAND aims to stimulate thinking among policymakers about possible impacts of the development of artificial general intelligence (AGI) on geopolitics and the world order.
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
By David Montgomery
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
By John Domol
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
By Zach Winn
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
