-
Scientists discover new materials to capture methane
Scientists have discovered new materials to capture methane, the second highest concentration greenhouse gas emitted into the atmosphere. Unlike carbon dioxide, the largest emitted greenhouse gas, which can be captured both physically and chemically in a variety of solvents and porous solids, methane is completely non-polar and interacts very weakly with most materials.
-
-
First U.S. commercial enhanced geothermal system connected to the grid
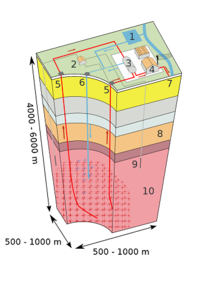
Enhanced geothermal system (EGS) projects capture power from intensely hot rocks, buried thousands of feet below the surface, which lack the permeability or fluid saturation found in naturally occurring geothermal systems. The Energy Department the other day announced the U.S. first commercial EGS project which supplies electricity to the grid.
-
-
Former NRC chairman: all 104 U.S. nuclear reactors suffer from “irreparable” safety issues
According to former U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) chairman Gregory Jaczko, all 104 nuclear reactors in the United States currently have irreparable safety issues and should be shut down and replaced. Jaczko was the NRC chairman from 2009 through 2012.
-
-
Critics: Fukushima-influenced U.S. nuclear accident response procedures are flawed
The U.S. government is using the Fukushima nuclear disaster in Japan two years ago as a model for rewriting its plans on how to respond to radiation contamination — emphasizing long-term cleanup and return of residents to affected areas instead of emergency response. Critics say this is a mistake.
-
-
Giant snails invade Florida

South Florida has found itself in battle with a destructive invasive species known as the giant African land snail. The snail can grow as big as a rat and can eat plaster.
-
-
Direct CO2 removal could lower costs of climate mitigation
Two broad strategies are typically offered to protect infrastructure from the consequences of climate change: reducing to emissions of CO2 into the atmosphere by using less fossil fuels, and mitigation (building sea walls, dams, and levees; changing building codes, etc.). Both approaches are costly. Scientists suggest that directly removing CO2 from the air could alter the costs of climate change mitigation. It could allow prolonging greenhouse-gas emissions from sectors like transport which are difficult, and thus expensive, to turn away from using fossil fuels.
-
-
Population growth a challenge to secure supplies of energy, food, water
Mention great challenges in feeding a soaring world population, and thoughts turn to providing a bare subsistence diet for poverty-stricken people in developing countries. An expert says, however, that there is a parallel and often-overlooked challenge: the global population will rise from seven billion today to almost nine billion people by 2040. Providing enough food to prevent starvation and famine certainly will be a daunting problem.
-
-
Footwear safety reflectors help in detecting bioterror threats

Tiny versions of the reflectors on sneakers and bicycle fenders that help ensure the safety of runners and bikers at night are moving toward another role in detecting bioterrorism threats and diagnosing everyday infectious diseases, scientists said the other day.
-
-
Canada’s crime-rate calculation method significantly underestimates actual crime numbers
The government of Canada is using a method called “capping” to measure crime in Canada. Capping is a common methodological practice used in most victimization surveys. Researchers find, however, that the technique significantly underestimates the number of crimes — especially the violent kinds — that occur in Canada.
-
-
Future computers will identify users by thoughts, not passwords

Instead of typing your password, in the future you may only have to think your password, according to researchers. A new study explores the feasibility of brainwave-based computer authentication as a substitute for passwords.
-
-
Fundamental changes needed in the education of tomorrow’s scientists
Fundamental changes are needed in the education of the scientists whose work impacts medicine, drug discovery, development of sustainable new fuels, and other global challenges society is facing in the twenty-first century. Those changes in graduate education in chemistry were the topic of a special symposium the other day at the 245th National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society.
-
-
More border security means more business opportunities for tech companies

At last month’s Border Security Expo in Phoenix, both start-ups and established companies showed off their inventions in an effort to pitch projects to federal agencies. Two themes emerged in the show: the expo demonstrated that many of the systems and weapons systems that were used in the Iraq and Afghanistan wars are now becoming available to local, state, and federal law enforcement agencies – and companies expressed concern about the impact the federal budget cuts will have on their pockets.
-
-
L.A County to turn rain water into drinking water
Residents of Los Angeles County know that on the rare occasion that it rains, staying away from the beach is a good idea. Runoff from rain typically brings heavy metals, pesticides, cigarette butts, animal waste, and other pollutants into the streams and rivers which go into the Pacific Ocean. Now, local officials are getting together to find a solution to the water pollution and water scarcity, with an ambitious plan to make the runoff water drinkable.
-
-
Finding the right tools to respond to suspicious powder incidents

HazMat teams across the United States respond to hundreds of white powder calls each year in large cities where quick decision-making is critical. DHS makes it easier to buy the right technology for bio-threat incidents.
-
-
Oregon citizens preparing for the Big One

A new study concludes that an earthquake of a magnitude 8.0 or above will strike off the coast of the state within the next fifty years. The Cascadia Fault, which runs from Northern California to British Columbia, Canada, causes a massive earthquake every 300 years or so, and the last time an earthquake hit the region was in the year 1700.
-
More headlines
The long view
New Technology is Keeping the Skies Safe
DHS S&T Baggage, Cargo, and People Screening (BCP) Program develops state-of-the-art screening solutions to help secure airspace, communities, and borders
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
How Artificial General Intelligence Could Affect the Rise and Fall of Nations
Visions for potential AGI futures: A new report from RAND aims to stimulate thinking among policymakers about possible impacts of the development of artificial general intelligence (AGI) on geopolitics and the world order.
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
