-
NASA engineers building sturdy blue-collar mining robot

After decades of designing and operating robots full of scientific gear to study other worlds, NASA is working on a prototype that leaves the delicate instruments at home in exchange for a sturdy pair of diggers and the reliability and strength to work all day, every day for years.
-
-
Extreme rainfall linked to global warming
A worldwide review of global rainfall data has found that the intensity of the most extreme rainfall events is increasing across the globe as temperatures rise. In the most comprehensive review of changes to extreme rainfall ever undertaken, researchers evaluated the association between extreme rainfall and atmospheric temperatures at more than 8,000 weather gauging stations around the world.
-
-
Why some immigrants get citizenship

For immigrants, the path to citizenship in many countries is filled with hurdles: finding a job, learning the language, passing exams. For some people, however, the biggest obstacle of all may be one they cannot help: their country of origin.
-
-
Conflicting cultural identities foster political radicalism
New research suggests that dual-identity immigrants — first-generation immigrants and their descendants who identify with both their cultural minority group and the society they now live in — may be more prone to political radicalism if they perceive their two cultural identities to be incompatible.
-
-
The historical probability of drought

Droughts can severely limit crop growth, causing yearly losses of around $8 billion in the United States. It may be possible, however, to minimize those losses if farmers can synchronize the growth of crops with periods of time when drought is less likely to occur. Researchers are working to create a reliable “calendar” of seasonal drought patterns that could help farmers optimize crop production by avoiding days prone to drought.
-
-
Military electronic devices disappear into the surroundings after use

Electronic devices have become necessary for military operations, but it is almost impossible to track and recover every device. At the end of operations, these devices are often found scattered across the battlefield and might be captured by the enemy and repurposed or studied to compromise DoD’s strategic technological advantage. New DARPA program — Vanishing Programmable Resources (VAPR) program — seeks transient electronics, that is, devices which would maintain the current functionality and ruggedness of conventional electronics, but, when triggered, be able to degrade partially or completely into their surroundings.
-
-
Biometric workshop studied voice, dental, oral standards
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) hosted a workshop to discuss proposed supplements to the biometric data format standard that support voice recognition, dental and oral data, disaster victim identification, and special data needs for mobile ID applications.
-
-
Projected U.S. water use to increase as climate warms
Despite increases in efficiency, water demand in the United States is likely to increase substantially in the future if climate continues to warm, new projections indicate.
-
-
Laser scanner documents crimes scenes quickly, accurately
The Carlsbad, California police is using a new laser scanner to capture what happened at crime scene. Thenew technology cuts the time it takes to document a crime scene, from the size of the room to the bullet holes in the wall, by up to 80 percent.
-
-
Maryland counties debate funding stormwater drainage management
A new tax aimed at property owners could finance the first set of improvements of the drainage works in Salisbury, Maryland since the original system was laid almost a century ago. City leaders have been arguing since 2009 over dedicating a source of funding to stormwater management, when an environmental panel recommended it. In the past, funding for projects like this has been hard to find as other priorities were deemed more important.
-
-
Developing educational materials, courses on standards
So called “documentary standards,” generally developed by industry-based committees, significantly influence industry, commerce and even daily life, but their role is often unrecognized save by those people who are immediately concerned.
-
-
Using silicon to produce hydrogen on demand
Super-small particles of silicon react with water to produce hydrogen almost instantaneously, according to researchers. In a series of experiments, the scientists created spherical silicon particles about ten nanometers in diameter. When combined with water, these particles reacted to form silicic acid (a nontoxic byproduct) and hydrogen — a potential source of energy for fuel cells.
-
-
NIST seeking partners for graduate fellowship programs in science, engineering, math
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is seeking one or more qualified institutions or organizations to work with it in developing and implementing a fellowship program to afford doctoral-level graduate students opportunities to work at NIST laboratories on research topics in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics.
-
-
Improving cities by using the notion of “urban metabolism”
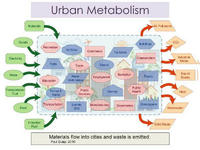
As is the case with organisms, cities need energy, water, and nutrients, and they need to dispose of wastes and byproducts in ways which are viable and sustainable over the long run. This concept of “urban metabolism” is a model for looking systematically at the resources that flow into cities and the wastes and emissions that flow out from them in order better to understand the environmental impacts of cities and to highlight opportunities for efficiencies, improvements, and transformation.
-
-
“Rebound” effect of energy-efficient technology exaggerated
The argument that those who have fuel-efficient cars drive them more and hence use more energy is overplayed and inaccurate. Researchers find evidence that, indeed, if a technology is cheaper to run – for example, a fuel-efficient car — people may use it more, but the effects of an increased use of the technology are too small to erase energy savings from energy efficiency standards and energy-efficient technologies.
-
More headlines
The long view
A Shining Star in a Contentious Legacy: Could Marty Makary Be the Saving Grace of a Divisive Presidency?
While much of the Trump administration has sparked controversy, the FDA’s consumer-first reforms may be remembered as its brightest legacy. From AI-driven drug reviews to bans on artificial dyes, the FDA’s agenda resonates with the public in ways few Trump-era policies have.
Risk Assessment with Machine Learning
Researchers utilize geological survey data and machine learning algorithms for accurately predicting liquefaction risk in earthquake-prone areas.
Foundation for U.S. Breakthroughs Feels Shakier to Researchers
With each dollar of its grants, the National Institutes of Health —the world’s largest funder of biomedical research —generates, on average, $2.56 worth of economic activity across all 50 states. NIH grants also support more than 400,000 U.S. jobs, and have been a central force in establishing the country’s dominance in medical research. Waves of funding cuts and grant terminations under the second Trump administration are a threat to the U.S. status as driver of scientific progress, and to the nation’s economy.
The True Cost of Abandoning Science
“We now face a choice: to remain at the vanguard of scientific inquiry through sound investment, or to cede our leadership and watch others answer the big questions that have confounded humanity for millennia —and reap the rewards.”
Bookshelf: Smartphones Shape War in Hyperconnected World
The smartphone is helping to shape the conduct and representation of contemporary war. A new book argues that as an operative device, the smartphone is now “being used as a central weapon of war.”
New Approach Detects Adversarial Attacks in Multimodal AI Systems
New vulnerabilities have emerged with the rapid advancement and adoption of multimodal foundational AI models, significantly expanding the potential for cybersecurity attacks. Topological signatures key to revealing attacks, identifying origins of threats.
