-
New bridge construction technologies to shore up U.S. infrastructure
Experts agree that there is an urgent need to construct and repair bridges across the United States. Around 70,000 bridges in the country are considered “structurally deficient” by government standards. New technology could help the United States manage its growing, and aging, infrastructure without breaking the bank or levying high taxes on citizens.
-
-
NASA engineers building sturdy blue-collar mining robot

After decades of designing and operating robots full of scientific gear to study other worlds, NASA is working on a prototype that leaves the delicate instruments at home in exchange for a sturdy pair of diggers and the reliability and strength to work all day, every day for years.
-
-
Extreme rainfall linked to global warming
A worldwide review of global rainfall data has found that the intensity of the most extreme rainfall events is increasing across the globe as temperatures rise. In the most comprehensive review of changes to extreme rainfall ever undertaken, researchers evaluated the association between extreme rainfall and atmospheric temperatures at more than 8,000 weather gauging stations around the world.
-
-
Why some immigrants get citizenship

For immigrants, the path to citizenship in many countries is filled with hurdles: finding a job, learning the language, passing exams. For some people, however, the biggest obstacle of all may be one they cannot help: their country of origin.
-
-
Conflicting cultural identities foster political radicalism
New research suggests that dual-identity immigrants — first-generation immigrants and their descendants who identify with both their cultural minority group and the society they now live in — may be more prone to political radicalism if they perceive their two cultural identities to be incompatible.
-
-
The historical probability of drought

Droughts can severely limit crop growth, causing yearly losses of around $8 billion in the United States. It may be possible, however, to minimize those losses if farmers can synchronize the growth of crops with periods of time when drought is less likely to occur. Researchers are working to create a reliable “calendar” of seasonal drought patterns that could help farmers optimize crop production by avoiding days prone to drought.
-
-
Military electronic devices disappear into the surroundings after use

Electronic devices have become necessary for military operations, but it is almost impossible to track and recover every device. At the end of operations, these devices are often found scattered across the battlefield and might be captured by the enemy and repurposed or studied to compromise DoD’s strategic technological advantage. New DARPA program — Vanishing Programmable Resources (VAPR) program — seeks transient electronics, that is, devices which would maintain the current functionality and ruggedness of conventional electronics, but, when triggered, be able to degrade partially or completely into their surroundings.
-
-
Biometric workshop studied voice, dental, oral standards
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) hosted a workshop to discuss proposed supplements to the biometric data format standard that support voice recognition, dental and oral data, disaster victim identification, and special data needs for mobile ID applications.
-
-
Projected U.S. water use to increase as climate warms
Despite increases in efficiency, water demand in the United States is likely to increase substantially in the future if climate continues to warm, new projections indicate.
-
-
Laser scanner documents crimes scenes quickly, accurately
The Carlsbad, California police is using a new laser scanner to capture what happened at crime scene. Thenew technology cuts the time it takes to document a crime scene, from the size of the room to the bullet holes in the wall, by up to 80 percent.
-
-
Maryland counties debate funding stormwater drainage management
A new tax aimed at property owners could finance the first set of improvements of the drainage works in Salisbury, Maryland since the original system was laid almost a century ago. City leaders have been arguing since 2009 over dedicating a source of funding to stormwater management, when an environmental panel recommended it. In the past, funding for projects like this has been hard to find as other priorities were deemed more important.
-
-
Developing educational materials, courses on standards
So called “documentary standards,” generally developed by industry-based committees, significantly influence industry, commerce and even daily life, but their role is often unrecognized save by those people who are immediately concerned.
-
-
Using silicon to produce hydrogen on demand
Super-small particles of silicon react with water to produce hydrogen almost instantaneously, according to researchers. In a series of experiments, the scientists created spherical silicon particles about ten nanometers in diameter. When combined with water, these particles reacted to form silicic acid (a nontoxic byproduct) and hydrogen — a potential source of energy for fuel cells.
-
-
NIST seeking partners for graduate fellowship programs in science, engineering, math
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is seeking one or more qualified institutions or organizations to work with it in developing and implementing a fellowship program to afford doctoral-level graduate students opportunities to work at NIST laboratories on research topics in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics.
-
-
Improving cities by using the notion of “urban metabolism”
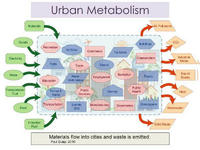
As is the case with organisms, cities need energy, water, and nutrients, and they need to dispose of wastes and byproducts in ways which are viable and sustainable over the long run. This concept of “urban metabolism” is a model for looking systematically at the resources that flow into cities and the wastes and emissions that flow out from them in order better to understand the environmental impacts of cities and to highlight opportunities for efficiencies, improvements, and transformation.
-
More headlines
The long view
Are We Ready for a ‘DeepSeek for Bioweapons’?
Anthropic’s Claude 4 is a warning sign: AI that can help build bioweapons is coming, and could be widely available soon. Steven Adler writes that we need to be prepared for the consequences: “like a freely downloadable ‘DeepSeek for bioweapons,’ available across the internet, loadable to the computer of any amateur scientist who wishes to cause mass harm. With Anthropic’s Claude Opus 4 having finally triggered this level of safety risk, the clock is now ticking.”
A Brief History of Federal Funding for Basic Science
Biomedical science in the United States is at a crossroads. For 75 years, the federal government has partnered with academic institutions, fueling discoveries that have transformed medicine and saved lives. Recent moves by the Trump administration — including funding cuts and proposed changes to how research support is allocated — now threaten this legacy.
Bookshelf: Preserving the U.S. Technological Republic
The United States since its founding has always been a technological republic, one whose place in the world has been made possible and advanced by its capacity for innovation. But our present advantage cannot be taken for granted.
Autonomous Weapon Systems: No Human-in-the-Loop Required, and Other Myths Dispelled
“The United States has a strong policy on autonomy in weapon systems that simultaneously enables their development and deployment and ensures they could be used in an effective manner, meaning the systems work as intended, with the same minimal risk of accidents or errors that all weapon systems have,” Michael Horowitz writes.
Ukraine Drone Strikes on Russian Airbase Reveal Any Country Is Vulnerable to the Same Kind of Attack
Air defense systems are built on the assumption that threats come from above and from beyond national borders. But Ukraine’s coordinated drone strike on 1 June on five airbases deep inside Russian territory exposed what happens when states are attacked from below and from within. In low-level airspace, visibility drops, responsibility fragments, and detection tools lose their edge. Drones arrive unannounced, response times lag, coordination breaks.
Shots to the Dome—Why We Can’t Model US Missile Defense on Israel’s “Iron Dome”
Starting an arms race where the costs are stacked against you at a time when debt-to-GDP is approaching an all-time high seems reckless. All in all, the idea behind Golden Dome is still quite undercooked.
