-
Jellyfish-like robot for underwater surveillance

Researchers at the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Virginia Tech built an unmanned underwater vehicle (UUV) inspired by jellyfish morphology and propulsion mechanism
-
-
The navigational skills of bacteria inspire robotics researchers
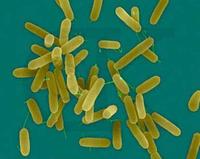
Humans may regret this, but bacteria have superior survival skills; bacteria are not the only organisms that travel in swarms — fish, bees, and birds also exhibit collective navigation; bacteria, however, have superior survival tactics and such tactics may be inspire better robot design
-
-
Double whammy: dinosaurs killed by massive volcanoes, meteorite impacts

The mass extinction of the dinosaurs, which occurred at the end of the Cretaceous period sixty-five million years ago, was the result not of one catastrophic event (meteorite strike) but rather the result of a catastrophic one-two punch: colossal volcanic eruptions and meteorite strikes
-
-
Game to improve defense, homeland security decision making
Raytheon BBN Technologies has been awarded a $10.5 million multi-year contract to develop serious games that result in better decision-making by teaching participants to recognize and mitigate the effects of their own biases when analyzing information used to make decisions
-
-
Europe faces rare Earth metal shortages
The EU’s ambitious low-carbon energy production goal depends on five technologies: nuclear, solar, wind, bio-energy, and carbon capture; these technologies, in turn, depend on rare Earth metals; the EU estimates that a large-scale deployment of only one of these technologies — solar energy — will require half the current world supply of tellurium and 25 percent of the supply of indium
-
-
Ionized plasmas as cheap sterilizer in tough places
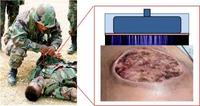
Scientists show that ionized plasmas like those in neon lights and plasma TVs not only can sterilize water, but make it antimicrobial; these plasma devices could be life-savers in developing countries, disaster areas, or on the battlefield where sterile water for medical use is in short supply and expensive to produce
-
-
Terahertz helps detection
Terahertz waves make collecting meteorological data from space, searching for flaws on an aircraft fuselage, or using certain medical diagnostics easier and more accurate
-
-
Mother-of-pearl inspires design of stronger materials
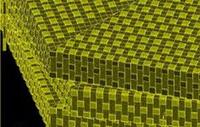
In nature, the strength of mother-of-pearl is a key to survival for some shellfish; researchers have offered an explanation for the unusual resilience – and they believes the findings could serve as a blueprint for engineering tough new materials in the laboratory
-
-
Nature inspires advances in ultrasound technology
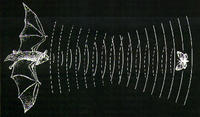
Sonar and ultrasound, which use sound as a navigational device and to paint accurate pictures of an environment, are the basis of many technologies, including medical ultrasound machines and submarine navigation systems; when it comes to more accurate sonar and ultrasound, however, animals’ “biosonar” capabilities still have the human race beat – but not for long
-
-
DARPA to boost cyber research spending by 50 percent
Last week, the head of the Department of Defense’s advanced research arm announced that the agency would increase cyber research spending by 50 percent over the next five years to develop both defensive and offensive capabilities
-
-
Brazilian fern inspires waterproof coating
A floating weed that clogs waterways around the world has at least one redeeming feature: it has inspired a high-tech waterproof coating intended for boats and submarines
-
-
Innovative ultrasonic nozzle changes the way water cleans
Scientists have developed a revolutionary ultrasonic attachment for taps, which massively enhances the ability of water to clean; currently, industry uses excessive water, power, and additives for cleaning
-
-
Rebuilding dried-up swamps to protect New Orleans from hurricanes
During the past four decades, swamps and wetlands which used to offer New Orleans a natural defense against hurricane, were dried and paved over. The city has launched a new project to restore a key area of cypress swampland near the Lower 9th Ward, an effort they called essential to protecting the metro area in the event of another major hurricane.
-
-
White House: no evidence of, contact with extra terrestrials

Two petitions, signed by 17,000, were submitted to the White house; the first demanded immediate disclosure of the U.S. government’s knowledge of and communications with extraterrestrial beings, the second a formal acknowledgement from the White House that extraterrestrials have been engaging the human race; in response, the White House Office of Science & Technology Policy wrote that the U.S. government has no evidence that any life exists outside our planet, or that an extraterrestrial presence has contacted or engaged any member of the human race
-
-
Making counter-hacking cool

NYU-Poly will, for the first time, open cyber security awareness week events on 11-12 November to student guests interested in digital privacy and security — not just the so-called “cyber ninjas” who qualified as national finalists in feats of digital forensics, ethical hacking, and research; the event is expected to attract up to 400 student finalists, professionals, academics, and guests
-
More headlines
The long view
New Technology is Keeping the Skies Safe
DHS S&T Baggage, Cargo, and People Screening (BCP) Program develops state-of-the-art screening solutions to help secure airspace, communities, and borders
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
How Artificial General Intelligence Could Affect the Rise and Fall of Nations
Visions for potential AGI futures: A new report from RAND aims to stimulate thinking among policymakers about possible impacts of the development of artificial general intelligence (AGI) on geopolitics and the world order.
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
