-
Arkansas deploys first statewide SmartPrepare system
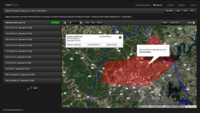
Arkansas uses citizen-supplied data for more efficient emergency planning and response. The service allows citizens to create secure profiles online which contain vital details about their household. Public safety officials can use the data to gain greater insight into their communities and identify potential challenges in order to prepare more effectively for disasters, allocate resources, and expedite emergency response and recovery efforts during events.
-
-
Dolphin-inspired radar system detects hidden surveillance, explosive devices

Scientists, inspired by the way dolphins hunt using bubble nets, have developed a new kind of radar that can detect hidden surveillance equipment and explosives. The twin inverted pulse radar (TWIPR) is able to distinguish true targets, such as certain types of electronic circuits that may be used in explosive or espionage devices, from clutter (for example, other metallic items like pipes, drinks cans, or nails) which may be mistaken for a genuine target by traditional radar and metal detectors.
-
-
New spectrometry standard for handheld chemical detectors
When it comes to detectors for dangerous chemicals, toxins, or nefarious germs, smaller and faster is better. Size and speed, however, must still allow for accuracy, especially when measurements by different instruments must give the same result. The recent publication of a new standard provides confidence that results from handheld chemical detectors can be compared, apples-to-apples.
-
-
Cell phone technology for quicker search-and-rescue operations
Avalanches and earthquakes can be highly unpredictable — and all too often deadly. Search and Rescue (SAR) operations are expensive, and somewhat limited given the current tools at their disposal. Many of these tools are highly complex, and require intense training or the deployment of specialized teams. A new project aims to address this weakness by developing cost-effective, robust, and lightweight technology that can easily be transported to an affected zone.
-
-
Snake robots move quickly in confined spaces, rough terrain

Snakes usually travel by bending their bodies in the familiar S-pattern. When they are stalking prey, however, snakes can move in a straight line by expanding and contracting their bodies. This “rectilinear gait” is slow, but it is quiet and hard to detect—-a perfect way to grab that unsuspecting rodent. This “limbless locomotion” is a highly effective way for a robot to move through cluttered and confined spaces.
-
-
Building disaster-relief phone apps on the fly
Researchers combine powerful new Web standards with the intuitive, graphical MIT App Inventor to aid relief workers with little programming expertise.
-
-
How Sandy has changed storm warning procedures
Superstorm Sandy slammed against the U.S. Eastern Seaboard in October 2012, inundating iconic communities. Those communities have been rebuilding since then and things are almost back to normal for most. Something else, however, has had to be rebuilt as well: the structured procedures for issuing warnings. The goal is to help communities better comprehend what natural disasters will bring their doorsteps.
-
-
Top Five most awesome robots
In the last decade, robots have often been employed on the battlefields of Iraq and Afghanistan, usually to seek out hidden bombs. More and more of these the robots are now being adopted by first response agencies to help in search-and-rescue operations in the wake of disasters. The growing interest in – and usefulness of — robotics have also inspired a series of competitions and challenges, some of which are directed at high-school and college students, to encourage budding scientists to go into the field of robotics.
-
-
Justice Department sues to block release of FirstNet-related information
A federal court in Des Moines, Iowa, accepted arguments by Justice Department lawyers to issue a temporary injunction to block the release by an Iowa Sherriff of e-mails pertaining to a public safety communication network. The Justice Department argued the release of e-mails could seriously impede plans for this single, interoperable network designed to resolve the communications problems that hampered responses to the 9/11 terrorist attacks and other disasters. FirstNet, to whose board Fitzgerald was appointed last year, was authorized by Congress in 2012 to develop and deploy the communications network and is housed in the Department of Commerce.
-
-
World's smallest drone may be a search-and-rescue tool
Researchers have designed, built, and tested the world’s smallest open source autopilot for small unmanned aircraft. A smaller and lighter autopilot — it weighs only 1.9 grams — allows these small flying robots to fly longer, fit into narrower spaces, or carry more payloads such as cameras. This makes them more suitable to be used, for example, rescue operations.
-
-
Rapid response, imaging of injuries aided Boston Marathon bombing victims
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), bombing survivors have the highest incidence of injury to soft tissue and musculoskeletal systems with the most extreme injury being traumatic amputation, which is reported in up to 3 percent of cases. The Boston Marathon bombings resulted in three fatalities and 264 casualties, with the most severe injuries involving lower extremities of those located closest to the blasts. Blast injuries within civilian populations are rare in the United States, so when they do occur they challenge the medical community rapidly to respond to concurrent evaluation and treatment of many victims.
-
-
New camouflage makeup shields soldiers, firefighters from heat of bomb blasts, fire
Camouflage face makeup for warfare is undergoing one of the most fundamental changes in thousands of years, as scientists today described a new face paint that both hides soldiers from the enemy and shields their faces from the searing heat of bomb blasts. Firefighters also could benefit from the new heat-resistant makeup.
-
-
Guaranteeing communication coverage in the event of disaster
An EU-funded project that aims to develop a rapidly deployable wireless communication network for use in the aftermath of an emergency, disaster, or unexpected event, was commended recently at an international event.
-
-
Effective screening of airline passengers arriving from areas of infectious disease outbreaks
New study shows that exit-screening at thirty-six airports would have assessed all air travelers at risk of transporting H1N1 out of Mexico at start of 2009 pandemic. Screening at 99 percent of the world’s international airports could have been forgone with negligible missed opportunities to prevent or delay the spread of disease. Screening at just eight airports worldwide would have led to the assessment of 90 percent of all at-risk air travelers.
-
-
Controlling contagion by restricting mobility
In an epidemic or a bioterrorist attack, the response of government officials could range from a drastic restriction of mobility — imposed isolation or total lockdown of a city — to moderate travel restrictions in some areas or simple suggestions that people remain at home. Deciding to institute any measure would require officials to weigh the costs and benefits of action, but at present there is little data to guide them on the question of how disease spreads through transportation networks. A new MIT study shows that in the face of an epidemic, even moderate government-mandated travel restrictions would slow contagion.
-
More headlines
The long view
The Surprising Reasons Floods and Other Disasters Are Deadlier at Night
It’s not just that it’s dark and people are asleep. Urban sprawl, confirmation bias, and other factors can play a role.
Why Flash Flood Warnings Will Continue to Go Unheeded
Experts say local education and community support are key to conveying risk.
