-
High performance concrete to rescue Brittany's lighthouses

Lighthouses in Brittany, France, have stood at the intersection of violent currents, blinding storms, and breaking surf for over a century. A lighthouse turret off the coast of Lorient in Brittany has been enhanced with technology developed for bridges. This trial run will test the application of Ultra-High Performance Concrete (UHPC).
-
-
Bay Bridge repairs expensive, slow

California’s 8-mile San Francisco-Oakland Bay Bridge was designed and built in the 1930s in about 5.5 years at a cost of $78 million, well under budget and ahead of schedule. Presently, the 2-mile eastern span of the bridge needs to be replaced, and it has taken the state five years just to design the replacement. Construction is taking about three times the expected time, and the $6.4 billion budget is almost five times the estimate provided by engineers.
-
-
Ultrathin radios enable flexible structural-health monitoring system
Currently, engineers can use single-point sensors or fiber optic strips to detect structural problems, but the devices can collect data over relatively small spaces. The problem is that many failures develop over large areas and cannot be detect that at an early stage. The 2007 collapse of a highway bridge in Minneapolis, for example, developed over a gusset plate with an area of several square meters, far too large for current monitoring systems to practically survey. Researchers have developed ultrathin radios which can be embedded directly on plastic sheets, which can be applied to walls and other structures. The innovation could be used for new devices ranging from an invisible communications system inside buildings to sophisticated, flexible structural health monitoring system for use on bridges, buildings, roads, pipelines, and other structures.
-
-
Sandy shows need for more effective preparedness, resiliency standards
The rebuilding efforts following the devastation wreaked by Superstorm Sandy have triggered a discussion over preparedness and resiliency in America’s commercial and residential buildings.Some experts callfor a presidential appointment of a building resilience “’czar”’ with authority to coordinate and seek synergies between public and private sector initiatives.
-
-
A 34-story wooden skyscraper to be built in Stockholm
A Swedish architectural form is building a 34-story wood skyscraper in downtown Stockholm. Solid wood will be the predominant material in the building’s pillars and beams, while inside the apartments, walls, ceilings, fittings and window frames will be also constructed of wood.The firm says that wood is not only cheaper than either steel or concrete, but is also more fire resistant than both. This is due to 15 percent of wood mass being water, which will evaporate before the wood actually burns. In addition, logs get charred which protects the core.
-
-
Eighty-six collegiate teams compete for the best car design and build
Eighty-six teams competed in the Baja Society of Automotive Engineers competition in Bellingham, Washington to determine the Baja car with the best design and build. Every year, collegiate automotive clubs enter to compete in any of the three national competitions that test the design, speed, maneuverability, and endurance of a student-manufactured Baja car — a frame-only vehicle used for off-roading and high adventure activity. Arizona State University’s Sun Devil Motorsports Team improved its ranking from 37th last year to 17th this year.
-
-
Man-induced quakes to help in building safer, sturdier buildings
A team led by Johns Hopkins structural engineers is shaking up a building in the name of science and safety. Using massive moving platforms and an array of sensors and cameras, the researchers are trying to find out how well a two-story building made of cold-formed steel can stand up to a lab-generated Southern California quake.
-
-
New internally cured concrete increases bridge life span
Concrete is normally made by mixing portland cement with water, sand, and stone. In the curing or hardening process, water helps the concrete mixture gain strength by reacting with the cement. Traditionally, curing is promoted by adding water on top of the bridge deck surface. The new technology for internal curing provides additional water pockets inside the concrete, enhancing the reaction between the cement and water, which adds to strength and durability. This new technology is enabling Indiana to improve bridges in the state with a new “internally cured” high-performance concrete.
-
-
Developing educational materials, courses on standards
So called “documentary standards,” generally developed by industry-based committees, significantly influence industry, commerce and even daily life, but their role is often unrecognized save by those people who are immediately concerned.
-
-
Engineers to build Australia’s first bushfire resistant straw house
With Australia’s bushfire season fast approaching, construction of the first bushfire resistant straw bale house tested by engineers from CSIRO has begun in rural Victoria; the house is based on design principles that minimize environmental impact and it is set to withstand temperatures equal to that of a worst case bushfire scenario
-
-
Tunnel disaster shows age of Japan’s infrastructure, but there is no money to fix it

The collapse of hundreds of concrete ceiling slabs in a tunnel just outside Tokyo has focused the attention of the Japanese on the country’s has citizens calling for Japan to fix its aging infrastructure; the amounts of money needed for this refurbishing are large, and , but signs indicate that Japan may not have the money, as the public debt is already more than 200 percent of its Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
-
-
Building material of millennium: Autoclave Aerated Concrete

Although widespread rebuilding in the hard-hit New York metro region from Hurricane Sandy has not yet begun, New Jersey Institute of Technology (NJIT) scientists say when the hammers start swinging, it is time to look at autoclaved aerated concrete; the material, best known as AAC, has been heralded as the building material of the new millennium
-
-
Microstructural improvements enhance material properties
DARPA merges structural engineering principles with new fabrication technologies to demonstrate microstructural control of materials at the micron level; the ultimate objective of the agency’s Materials with Controlled Microstructural Architecture (MCMA) program is to be able to develop materials in the future with properties tailored to meet specific mission requirements
-
-
Serious limitations make boost-phase missile interception impractical
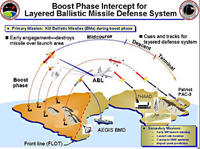
One of the central elements of President Reagan’s 1983 “Star Wars” ballistic missile defense initiative was boost-phase defense: boost-phase defense systems are intended to shoot down enemy missiles immediately following launch while the rocket engine is still firing; a new congressionally mandated study by the National Research Council study says that to defend against ballistic missile attacks more effectively, the United States should concentrate on defense systems that intercept enemy missiles in midcourse and stop spending money on boost-phase defense systems of any kind
-
-
Raytheon opens STEM teacher award program
Raytheon has opened the 2012 application process for its Raytheon-Engineering is Elementary (EiE) Teacher Scholarship Program; during the 2012-13 school year, Raytheon will grant awards of $3,000 each for selected elementary school teachers nation-wide whose applications best demonstrate innovative methods of generating student enthusiasm about engineering concepts
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
