-
Some citizens of low-lying Pacific island nations seeking climate-change refugee status
More and more resident of Pacific island nations and territories are trying to claim refugee status in Australia and New Zealand, arguing that rising sea levels, caused by climate change, are forcing them out of their homes and destroying their livelihood. The New Zealand High Court has rejected the refugee status petition of Loane Teitota and his family, citizens of Kiribati, a low-lying Pacific Island nation near the equator, saying that Teitota’s argument was “novel” and “optimistic.” The court cautioned that if the argument were adopted, then millions of people suffering from the effects of climate change would seek refugee status in New Zealand or any other country.
-
-
The 9 January chemical leak in West Virginia is the latest in a long history of industrial accidents
The chemical spill that affected the water source in nine West Virginia counties in early January is part of a long history of industrial accidents resulting from the concentration of chemical and coal-mining operations in the region. The 9 January spill, which saw coal-cleansing chemical which leaked from Freedom Industries’ storage tank into the Elk River, leaving more than 300,000 residents without access to clean tap water for days, is the latest in a history of pollution which has poisoned groundwater, spewed toxic gas emissions, and caused fires and explosions.
-
-
Increase in wildfires may significantly degrade air quality, health in the future

As the American West, parched by prolonged drought, braces for a season of potentially record-breaking wildfires, new research suggests these events not only pose an immediate threat to people’s safety and their homes, but also could take a toll on human health, agriculture, and ecosystems.
-
-
The combination of drought and warming climate places severe strain on California’s water supply

As stores of water in the West are reduced — whether by usage in drought, evapotranspiration in heat, or both — warming temperatures also see the snowpack on the wane. The two phenomena together could put severe strain on water supplies, with implications for ecosystems, industries, and people alike. Even at their most severe, the droughts of decades and centuries past did not occur in tandem with today’s degree of temperature change or have to contend with the demands of a population that in California alone now numbers above thirty-eight million residents. As needs for water grow ever greater, so, too, do the potential threats to its supply.
-
-
The world likely to face more frequent, and more severe, blackouts
U.S. household electricity usage increased by 1,300 percent between 1940 and 2001. In the last few decades, air conditioning has been the greatest factor in increased electrical consumption, and one of the greatest sources of systematic strain, with considerably more blackouts occurring in the summer months than during winter. The electricity used to fuel America’s air conditioning is currently of a similar volume to the U.S. entire energy consumption in the 1950s. A new study reveals that today’s occasional blackouts are dress rehearsals for the future, when they will occur with greater frequency and increased severity. Power cuts will become more regular around the globe as electrical supply becomes increasingly vulnerable and demand for technology continues to grow at an unprecedented rate.
-
-
Natural flood management as a solution against future flooding

Natural Flood Management (NFM) aims to reduce the downstream maximum water height of a flood — the peak — or delay the arrival of the flood peak downstream, increasing the time available to prepare. Back-to-nature flood schemes which use the land’s natural defenses to slow river flow and reduce flooding could be a cost-effective way of tackling one of the biggest problems facing the United Kingdom today.
-
-
Deepwater Horizon: Identifying harmful elements of persisting oil

Scientists are unraveling the composition of persisting oil residues collected from Gulf of Mexico beaches following the Deepwater Horizon disaster, insisting on further assessment of the toxic impact of these chemical remnants on the marine ecosystem. A new study targeted the most abundant compounds in the residual oil, dissecting their composition with unprecedented accuracy. This is important for understanding the environmental impact of persisting oil remnants, because ecotoxicologists have demonstrated that all three chemical groups can be harmful to living organisms. More worrisome, relatively little is known about the broader toxicity of saturates and oxygenated hydrocarbons in the marine ecosystem, like the Gulf of Mexico —where there are 223 offshore oil rigs — even though these compounds constitute most of the persisting oil.
-
-
ExxonMobil to pay fines for violations at its Baton Rouge chemical facilities
In a settlement with Louisiana’s Department of Environmental Quality (DEQ), ExxonMobil is ordered to pay $2.329 million to address violations from 2008 to 2013 at its greater Baton Rouge facilities. ExxonMobil was cited for a series of problems at its refinery and resin-finishing and chemical plants in East Baton Rouge Parish, and its tank-farm facility in West Baton Rouge.
-
-
Halting bugs’ crop destruction in India saves up to $309 million
Researchers who first discovered a devastating pest in India and devised a natural way to combat it have now put an economic value on their counterattack: up to $309 million the first year and more than $1 billion over five years. This is the amount of damage the papaya mealybug would have wreaked on farmers and consumers in India without scientists’ intervention. The winning intervention centered on three natural enemies of the mealybug — three parasitic wasps from Mexico— which the U.S. government first employed in Florida after the pest spread there in the late 1990s.
-
-
Israel considering earthquake-proofing important Biblical-period structures
Israel is located in one of the world’s earthquake-prone areas, along the friction point of the African and Arabian tectonic plates.Officials in Israel are taking preventative measures to protect the country’s most important ancient sites from earthquake damage. Engineers from the University of Padua in Italy have installed sensors throughout the Tower of David, one of Jerusalem most important historical sites, to determine what sort of earthquake-proofing may be needed. Some experts opined that in the event of an earthquake, Jerusalem’s most ancient structures might actually be the city’s most dependable. “If they still stand after so many earthquakes during the last 2,000 years, they must be good structures,” one of them said.
-
-
Thumbnail-sized quantum cascade laser, tuning forks detect greenhouse gases
Human activities such as agriculture, fossil fuel combustion, wastewater management, and industrial processes are increasing the amount of nitrous oxide in the atmosphere. The warming impact of methane and nitrous oxide is more than 20 and 300 times, respectively, greater compared to the most prevalent greenhouse gas, carbon dioxide, over a 100-year period. Methane and nitrous oxide detection is crucial to environmental considerations. Scientists use a thumbnail-sized quantum cascade laser (QCL) as well as tuning forks that cost no more than a dime to detect very small amounts of nitrous oxide and methane.
-
-
“Virtual earthquakes” used to forecast Los Angeles quake risk
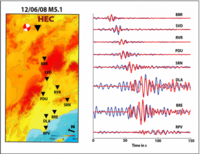
Stanford scientists have developed a new “virtual earthquake” technique and used it to confirm a prediction that Los Angeles would experience stronger-than-expected ground motion if a major quake occurred along the southern San Andreas Fault. The new technique capitalizes on the fact that earthquakes are not the only sources of seismic waves – rather, there is also an ambient seismic field consisting of much weaker seismic waves. The scientists devised a way to make these ambient seismic waves function as proxies for seismic waves generated by real earthquakes. By studying how the ambient waves moved underground, the researchers were able to predict the actions of much stronger waves from powerful earthquakes.
-
-
Texas wants to know whether fracking causes earthquakes
Texas has about 35,000 active injection wells. About 7,000 of Texas’s injection wells are used for disposing wastewater deep underground, and some experts say these wells can cause earthquakes. In response to the several minor earthquakes which occurred in late 2013 around the Azle, Texas area, local officials are investigating whether oil and gas drilling in North Texas and the injection wells that follow after, are responsible for the quakes.
-
-
U.S. power plant emissions down

Power plants that use natural gas and a new technology to squeeze more energy from the fuel release far less of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide than coal-fired power plants do, according to a new analysis. The so-called “combined cycle” natural gas power plants also release significantly less nitrogen oxides and sulfur dioxide, which can worsen air quality.
-
-
Nearby Georgia basin may amplify ground shaking from quakes in Vancouver
In Greater Vancouver, there are more than 700 12-story and taller commercial and residential buildings, and large structures — high-rise buildings, bridges, and pipelines — which are more affected by long period seismic waves, or long wavelength shaking. Researchers find that tall buildings, bridges, and other long-period structures in Greater Vancouver may experience greater shaking from large (M 6.8 +) earthquakes than previously thought due to the amplification of surface waves passing through the Georgia basin.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
