-
Climate-induced disasters linked to food security across time and place
Teams of researchers in the American Southwest and North Atlantic Islands have found that historic and prehistoric peoples in these regions who had created vulnerabilities to food shortfall were especially susceptible to impacts from climate challenges. Their “natural” disasters were human made in conjunction with climate challenges.
-
-
Wild bee decline threatens U.S. crop production

About 39 percent of U.S. croplands depend on pollinators — from apple orchards to pumpkin patches. Between 2008 and 2013, the number of bees in the contiguous United States declined in 23 percent, creating a mismatch between rising demand for pollination and a falling supply of wild bees. The first national study to map U.S. wild bees suggests they are disappearing in many of the country’s most important farmlands — including California’s Central Valley, the Midwest’s corn belt, and the Mississippi River valley. If losses of these crucial pollinators continue, the new nationwide assessment indicates that farmers will face increasing costs — and that the problem may even destabilize the nation’s crop production.
-
-
U.S. facing looming grain failures

Across the United States, record quantities of corn and soybeans have been harvested in recent years. However, according to new research, this trend may soon change. “By midcentury,” the interdisciplinary team reports, “temperatures in Illinois will likely be closer to those of today’s mid-South, and precipitation will range somewhere between that of today’s East Texas and that of the Carolinas.” In the face of a rapidly changing climate, the researchers call for a U.S. Midwest field research network to address crucial agricultural challenges.
-
-
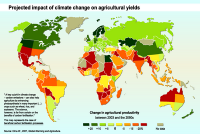
Climate change poses multiple threats to global food system
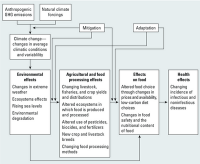
Climate change is likely to have far-reaching impacts on food security throughout the world, especially for the poor and those living in tropical regions, according to a new international report. The report warns that warmer temperatures and altered precipitation patterns can threaten food production, disrupt transportation systems, and degrade food safety, among other impacts. As a result, international progress in the past few decades toward improving food security will be difficult to maintain.
-
-
Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) technology for on-site detection
Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) technology currently is applied using chemical analysis of materials, such as scanning at airports to identify what materials may be inside of glass vials. Researchers want to expand SERS for use in biological applications that could employ antibodies for purposes such as identifying viruses, water toxins, or pathogens in food samples. The researchers work on developing a small hand-held device that allows users to take a sample, put it in a glass vial and insert into the instrument for rapid identification.
-
-
Syria’s civil war, Europe’s refugee crisis the result of spikes in food prices: Experts

The disintegration of Syria and Europe’s refugee crisis are only the latest tragic consequences of two spikes in food prices in 2007-08 and 2010-11 that triggered waves of global unrest, including the Arab Spring. Researchers have traced these spikes and spiraling crises to their root causes: deregulated commodity markets, financial speculation, and a misguided U.S. corn-to-ethanol fuel policy which removes nearly five billion bushels of corn from markets each year.
-
-
Medical research techniques to help food crops withstand climate change

Roughly one in nine people on Earth do not have enough food to eat. And climate change is only making it harder for farmers to meet the global demand for food, according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). By 2030, the IPCC expects climate change to reduce crop and pasture yields by as much as 14 percent in some parts of the world. Adapting crops, livestock, and fisheries will be critical for global food security. A new Center for Research on Plant Transporters (CROPS) at UC San Diego aims to help develop the molecular tools necessary to grow the hardier crop varieties that farmers need now and will increasingly need in coming years — corn, wheat, and rice that are more tolerant to heat, drought, salinity, and other adverse conditions.
-
-
Pediatricians: Food insecurity ongoing health risk to U.S. children
The latest data show that more than fifteen million U.S. children live in households still struggling with hunger. For the first time, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) is recommending that pediatricians screen all children for food insecurity. In a new policy statement identifying the short and long-term adverse health impacts of food insecurity, the AAP also recommends that pediatricians become familiar with and refer families to needed community resources, and advocate for federal and local policies that support access to adequate, nutritious food.
-
-
Hunger levels “serious” or “alarming” in 52 developing countries: Report
Despite progress in reducing hunger worldwide, hunger levels in 52 of 117 countries in the 2015 Global Hunger Index remain “serious” (44 countries) or “alarming” (8 countries). The Central African Republic, Chad, and Zambia had the highest hunger levels in the report, which was released last week. Conflicts can be strongly associated with severe hunger, according to the report, which focused on armed conflict and the challenge of hunger.
-
-
Global marine analysis: Food chain collapse likely
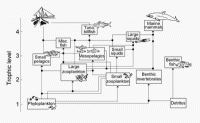
A world-first global analysis of marine responses to climbing human CO2 emissions has painted a grim picture of future fisheries and ocean ecosystems. Marine ecologists say the expected ocean acidification and warming is likely to produce a reduction in diversity and numbers of various key species that underpin marine ecosystems around the world. The researchers found that there would be “limited scope” for acclimation to warmer waters and acidification. Very few species will escape the negative effects of increasing CO2, with an expected large reduction in species diversity and abundance across the globe.
-
-
Former peanut company owner to jail for 28 years for fatal 2009 salmonella outbreak
In a rare instance of a prison sentence in a food contamination case, Stewart Parnell, the former owner of Peanut Corporation of America, was sentenced to twenty-eight years in prison for his role in a 2009 salmonella outbreak which killed nine people and sickened hundreds. Parnell, 61, who once managed the Peanut Corporation of America, and his brother, Michael Parnell, who was a food broker for the company, were convicted on Monday on federal conspiracy charges for knowingly shipping salmonella-tainted peanuts to customers.
-
-
Rather food versus fuel, think in terms of both food and fuel

Whether you have taken a side or a backseat in the discussion, the “food versus fuel” debate affects us all. Some say growing more biofuel crops today will decrease greenhouse gas emissions, but will make it harder to produce food tomorrow, which has prevented the United States from maximizing the potential of environmentally beneficial biofuels. Scientists argue that farmers can sustainably, and affordably, meet humanity’s growing demand for food and fuel.
-
-
2015 drought costs for California agriculture: Loss of $1.84 billion, 10,100 jobs

The drought is tightening its grip on California agriculture, squeezing about 30 percent more workers and cropland out of production than in 2014, according to the latest drought impact report. In 2015, the state’s agricultural economy will lose about $1.84 billion and 10,100 seasonal jobs because of the drought, the report estimated, with the Central Valley hardest hit. The heavy reliance on groundwater comes at ever-increasing energy costs as farmers pump deeper and drill more wells. Some of the heavy pumping is in basins already in severe overdraft — where groundwater use greatly exceeds replenishment of aquifers — inviting further land subsidence, water quality problems, and diminishing reserves needed for future droughts.
-
-
Repurposing wasted food would feed the hungry, create jobs
Roughly one third of all global food gets wasted. In the United States, that number is even higher, with nearly 40 percent of all food going to waste, making it one of the most wasteful countries in the world. Researchers have developed a new model for recovering would-be wasted — or surplus — food and repurposing it to feed hungry people, generate revenue, and even create jobs. The model — Food System-Sensitive Methodology (FSSM) — was recently piloted in West Philadelphia. The researchers say that applying FSSM nationally would likely yield about 1.1 billion pounds of recovered wasted food annually.
-
-
EU-funded research: Climate change and food safety
The global fresh produce supply chain must take into account climate change in order to ensure food safety, warn EU-funded researchers. This was the key recommendation of the EU-funded VEG-I-TRADE project, which was launched in 2010 to assess the safety of fresh produce in a rapidly evolving context of climate change and expanding international trade.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
