-
British PM apologizes for British “collusion” in 1989 killing of Irish lawyer
British Prime Minister David Cameron offered an apology to the family of Patrick Finucane, a lawyer who represented IRA activists, saying that there was “a shocking level of state collusion” when it came to his killing in 1989; Cameron offered the apology after a 500-page report on the killing was completed, implicating British Army intelligence unit, as well as MI5 and MI6, of facilitating the killing through both action and inaction; Finucane’s widow, demanding a public inquiry, said this report, like earlier ones, aims to protect senior officials close to then-Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher
-
-
Sandy exposes weaknesses of antiquated sewage systems in N.Y., N.J.

Hurricane Sandy destroyed homes, apartments, and entire communities, and it also exposed the outdated sewage systems in New York and New Jersey; since Hurricane Sandy, millions of gallons of raw sewage have infiltrated waterways in both states, and it could take several years and billions of dollars to fix the systems; New York governor Andrew Cuomo estimated that it will cost about $1.1 billion to repair treatment plants; officials in the field say that much more will have to be done
-
-
U.S. formally to recognize rebel coalition as Syria’s legitimate rulers
The end of the Assad family rule over Syria, which begun in 1970, has been moved that much closer yesterday (Tuesday) when President Barack Obama said the United States would formally recognize a coalition of Syrian rebel groups as Syria’s legitimate rulers; other countries, notably France, the United Kingdom, and Turkey have already recognized the opposition as Syria’s legitimate government, but the U.S. move is a game changer; the big question is whether the armed groups inside Syria would feel compelled to accept what members of the coalition agree upon
-
-
Technique used to nab serial killers helps in controlling pests and disease and in counter-terrorism
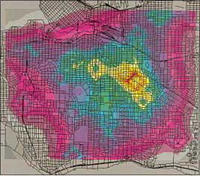
A technique designed to help criminologists catch serial killers is being used by scientists to locate sources of disease, control pests, and study animal behavior; locating a serial killer’s home is similar to finding the nests of animals or centers of disease outbreaks; ecological approaches have applications in counter-terrorism work, as terrorist cells tend to have more than one anchor point within the area in which they operate, exactly so they can avoid detection
-
-
Modeling terrorism risk to the air transportation system
RAND recently evaluated a terrorism risk modeling tool developed by the Transportation Security Administration (TSA) and Boeing to help guide program planning for aviation security; the Risk Management Analysis Tool, or RMAT, simulates terrorist behavior and success in attacking vulnerabilities in the domestic commercial air transportation system, drawing on estimates of terrorist resources, capabilities, preferences, decision processes, intelligence collection, and operational planning
-
-
Israel accused of stealing, revealing IAEA Iran-related documents
Sources within the IAEA complained that Israel, in its zeal to expose Iran’s nuclear-weapons related activities — and, by implication, its attempt to paint the IAEA as slow and indecisive in its scrutiny of Iran’s nuclear activities – has stolen IAEA secret documents about Iran’s nuclear program and, after editing, gave them to the Associated Press
-
-
Sudan says Israel using electronically equipped vultures as spies
Sudanese security forces have captures what they describe as an electronically tagged vulture which was dispatched by the Israeli military on a surveillance mission over Sudan; the Sudanese claimed the vulture was equipped with a camera, a solar-powered satellite uplink, and a GPS device; the Sudanese also claimed that the surveillance gear was produced by the Hebrew University in Jerusalem, and that it was stamped with the university’s logo
-
-
Terrorism on decline in U.S.
From 2002 to 2011, the United States has experienced a noticeable decline in terrorism, and North America was the region least likely to suffer from terrorism: there were only twenty-three deaths as a result of terrorism in the United States from 2002 to 2011; the three most active perpetrators of terrorist acts in the United States have been the Earth Liberation Front, Animal Liberation Front, and various anti-abortion activists; al Qaeda and affiliates, the Taliban and affiliates, the KKK and affiliates – combined — accounted for less than 3 percent of terrorist attacks in the United States in the past decade
-
-
IAEA: Iran finished removing evidence of illicit nuclear work at Parchin

Iran, implausibly, may explain away its uranium enrichment activities by saying it needs the enriched material for civilian reactors and medical research (although the sheer quantities of uranium it enriches bear no relationship to either need); warhead design is done by a few engineers at secret locations; there is one activity – testing of the triggering mechanism for a nuclear bomb – that cannot be explained away (because these triggers do not have any other use) or hidden (because the testing leaves unmistakable traces); Iran has been conducting tests on a triggering mechanism for nuclear warheads at a military base called Parchin, south of Tehran, and has blocked access of UN inspectors to the site; detailed satellite imagery shows that Iran has been engaged in a frantic effort to scrub all evidence related to nuclear weapons testing activity at the military base by demolishing buildings and removing large quantities of soil that might hold traces of illicit nuclear work; the IAEA says that Iran has succeeded in its clean-up effort
-
-
First responders drill response to a “Night of the Walking Dead” scenario

DHS funds were approved to pay the $1,000 fee for a week-long conference at Paradise Point Resort and Spa in San Diego; the marquee event of the summit was its highly-promoted “zombie apocalypse” demonstration; Strategic Operations, a tactical training firm, was hired to put on a “zombie-driven show” designed to simulate a real-life terrorism event; the firm performed two shows on Halloween, which featured forty actors dressed as zombies getting gunned down by a military tactical unit
-
-
TVA considering raising height of dams to prevent future floods
The dams located on the upper Tennessee River never had flood waters top them, and government officials want to keep it that way, saying that due to recent disasters such as the 2010 Nashville flood and the 2011Fukushima tsunami, they need to prepare the worst possible situation
-
-
Huawei rejects U.S. “threat to national security” claims
In October the United States House Intelligence Committee issued a report warning U.S. companies against using two Chinese companies, Huawei and ZTE, for their telecommunication technology needs; the report said that the firms may be too close to China’s Communist Party and its military’ the report also suggested their products and services could pose a threat to the security of the United .States; Huawei vigorously disputes both claims
-
-
Nuclear wonder fuel poses serious weapons proliferation risk

Thorium is being touted as an ideal fuel for a new generation of nuclear power plants, but new study shows that it may pose a serious weapons proliferation risk; experiments to separate protactinium-233 show that it is feasible that just 1.6 tons of thorium metal would be enough to produce eight kilograms of uranium-233, which is the minimum amount required for a nuclear weapon; a nuclear reactor using thorium for fuel could produce that amount of thorium metal in less than a year
-
-
Critics: post-Fukushima nuclear power may be safer, but it is still not cost effective
The Southern Company wants to show its customers that it has learned from the Fukushima disaster in Japan and has protected its nuclear reactors to make sure the same thing does not happen in the United .States’ critics of nuclear power are not convinced – and also, they say, alternative energy sources, such as natural gas, are much cheaper to produce
-
-
Israel to test advanced Arrow 3 anti-missile missile
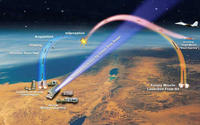
The official in charge of developing Israel’s missile defense system said yesterday that in the coming days Israel would conduct a test of the advanced Arrow 3 missile; the Arrow 3 has been developed to shoot down Iranian ballistic missiles on their way to Israel; the Arrow 3 has been designed to intercept missiles carrying nuclear warheads – and intercept them outside the atmosphere
-
More headlines
The long view
What Does Netflix’s Drama “Adolescence” Tell Us About Incels and the Manosphere?
While Netflix’s psychological crime drama ‘Adolescence’ is a work of fiction, its themes offer insight into the very real and troubling rise of the incel and manosphere culture online.
A Shining Star in a Contentious Legacy: Could Marty Makary Be the Saving Grace of a Divisive Presidency?
While much of the Trump administration has sparked controversy, the FDA’s consumer-first reforms may be remembered as its brightest legacy. From AI-driven drug reviews to bans on artificial dyes, the FDA’s agenda resonates with the public in ways few Trump-era policies have.
The Center Can Hold — States’ Rights and Local Privilege in a Climate of Federal Overreach
As American institutions weather the storms of executive disruption, legal ambiguity, and polarized governance, we must reexamine what it means for “the center” to hold.
How to Reverse Nation’s Declining Birth Rate
Health experts urge policies that buoy families: lower living costs, affordable childcare, help for older parents who want more kids
Foundation for U.S. Breakthroughs Feels Shakier to Researchers
With each dollar of its grants, the National Institutes of Health —the world’s largest funder of biomedical research —generates, on average, $2.56 worth of economic activity across all 50 states. NIH grants also support more than 400,000 U.S. jobs, and have been a central force in establishing the country’s dominance in medical research. Waves of funding cuts and grant terminations under the second Trump administration are a threat to the U.S. status as driver of scientific progress, and to the nation’s economy.
The True Cost of Abandoning Science
“We now face a choice: to remain at the vanguard of scientific inquiry through sound investment, or to cede our leadership and watch others answer the big questions that have confounded humanity for millennia —and reap the rewards.”
