-
Philippines prepares for worse disasters to come
On average, the Philippines experiences about twenty typhoons a year, including three super-typhoons and many incidents of flooding, drought, earthquakes, tremors, and occasional volcanic eruptions, making the country one of the most naturally disaster-prone areas in the world. Filipino government agencies, with the help of international disaster and relief agencies, have created new strategies for disaster preparedness, response, and mitigation which may well have potential applications in other parts of the world. As the impact of climate change grows more pronounced, the Philippines is becoming a hothouse for developing new methods and systems in the growing business of disaster relief.
-
-
Sunlight-activated nanogrid breaks down pollutants in water
Oil spills do untold damage to the environment — to the waters they pollute and to marine and other wildlife. The Deepwater Horizon spill in the Gulf of Mexico in 2010, for example, the largest accidental marine oil spill in the history of the petroleum industry, flowed unabated for three months. Typically, such oil spills are extraordinarily difficult to clean up. Soon, however, the process may become infinitely easier and ecologically friendly, the result of a new invention — “nanogrid” — a large net consisting of metal grids made of a copper tungsten oxide, that, when activated by sunlight, can break down oil from a spill, leaving only biodegradable compounds behind.
-
-
Chelyabinsk meteor explosion a "wake-up call," scientists warn
Three new studies have revealed details of the meteor that exploded above Russian city, Chelyabinsk, in February this year. Their findings provide information about the meteor’s origin, trajectory, power and damage by the airburst (the shock wave that travelled through the air from the explosion). These findings may help to refine theoretical models about the likely frequency of such events, the potential damage they could cause and hazard mitigation strategies needed for planetary protection.
-
-
Wildfire science returns to California’s Rim Fire

The challenging job of managing wildfires rests with other agencies, but the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) provides the underlying science for sound land management decisions, before, during, and after wildfires. The USGS role studying natural hazards such as floods, landslides, earthquakes, and volcanoes is well known, but fewer people are aware of the USGS scientific work in major wildfire events, which are one of the most regular and sometimes most devastating natural hazards in the West.
-
-
Safe long-term CO2 storage possible
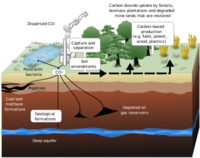
Since 2004, the German Research Centre for Geosciences (GFZ) has led an international research network to investigate the geological storage of the greenhouse gas (CCS, for carbon capture and storage). GFZ’s scientists say that their work at the Ketzin site, 40 km west of Berlin, has shown that geological CO2 storage on a pilot scale can be done safely and reliably.
-
-
Weakening cybersecurity to facilitate NSA surveillance is dangerous: experts
In the wake of revelations about the NSA surveillance programs, an expert on surveillance and cybersecurity recommended a re-evaluation of those surveillance practices that weaken commercial products and services. These practices include weakening standards and placing “back doors” into products that are accessible to U.S. government agencies. The expert – Jon Peha, former chief technology officer of the FCC and assistant director of the White House’s Office of Science and Technology — said deliberately weakening commercial products and services may make it easier for U.S. intelligence agencies to conduct surveillance, but “this strategy also inevitably makes it easier for criminals, terrorists and foreign powers to infiltrate these systems for their own purposes.”
-
-
DHS struggling to respond to cybersecurity threats: IG
A recent reportby DHS inspector general (IG) has documented the agency’s struggle to respond to cybersecurity threats and its inability to disseminate information about threats because of technical, funding, and staffing challenges.
-
-
Developing robots for bridge inspection, mine rescue with NSF grants

In 2011, at Carnegie Mellon University, President Barack Obama announced the National Robotics Initiative. The National Science Foundation announced it has awarded a total of more than $7 million to Carnegie Mellon researchers in the latest round of grants for the initiative — a multi-agency effort to develop robots that can work with humans to extend and augment human skills. Researchers are developing robots for bridge inspection, mine rescue, and aid for the blind.
-
-
Scientists: we should prepare for hell and high water

An international team of climate and social scientists say a new approach to climate preparedness is essential to help people adjust to coming changes. As climate-driven changes get more pronounced, people everywhere will have to adjust. In this week’s issue of the journal Science, an international group of researchers urge the development of science needed to manage climate risks and capitalize on unexpected opportunities.
-
-
Making cybersecurity a political issue
U.S. federal agencies have reported a dramatic rise in the number of cyberattacks over the past few years, with reported cyber incidents rising from 5,503 in 2006 to 48,562 in 2012. Since cyber incidents pose such a threat to national security and infrastructure, could cybersecurity become a political campaign issue? Experts say that if politicians were to focus their attention, and their constituents’ attention, on cybersecurity, the United States could be made safer from cyberattacks before a “cyber Pearl Harbor” – or a “cyber 9/11” – occurs.
-
-
IID raises $8 million to scale shared cyberintelligence offering
Despite the growing danger posed by cybercrime, information vital to stemming the tide is fragmented across the Internet today. Pockets of data about threat activity are siloed within the repositories of individual enterprises, government organizations, vendor networks, and research institutions. IID’s ActiveTrust enables enterprises and government agencies to combat the rising frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks by sharing cyber incident data in real time. IID has raised $8 million in Series A funding from Bessemer Venture Partners (BVP), and said it will use the investment to accommodate growing demand for ActiveTrust.
-
-
Detecting threats in a crowd
Around a military camp situated close to a built-up area there are always people moving about. Scientists at FOI, the Swedish Defense Research Agency, have created a multi-sensor system designed to be able to detect threats by identifying unusual patterns of movement involving individuals or groups.
-
-
Resources on disaster preparedness, resilience

One year after Superstorm Sandy hit the eastern United States, local, state, and federal agencies as well as community groups and businesses are working to strengthen the U.S.s resilience to future disasters. A National Research Council (NRC) has issues a series of studies and reports, and has put together workshops and study groups, which should advance the national conversation on preparedness and resilience.
-
-
Rising temperatures threaten Salt Lake City’s water supply
In an example of the challenges water-strapped Western cities will face in a warming world, new research shows that every degree Fahrenheit of warming in the Salt Lake City region could mean a 1.8 to 6.5 percent drop in the annual flow of streams that provide water to the city. By midcentury, warming Western temperatures may mean that some of the creeks and streams that help slake Salt Lake City’s thirst will dry up several weeks earlier in the summer and fall.
-
-
2012 sees slowdown in the increase in global CO2 emissions
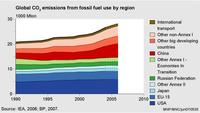
Actual global emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2) reached a new record of 34.5 billion tons in 2012. Yet, the increase in global CO2 emissions in that year slowed down to 1.1 percent, which was less than half the average annual increase of 2.9 percent over the last decade. This is remarkable, as the global economy grew by 3.5 percent. This development signals a shift toward less fossil-fuel-intensive activities, more use of renewable energy, and increased energy saving. Increases in fossil-fuel consumption in 2012 were 2.2 percent for natural gas, 0.9 percent for oil products, and 0.6 percent for coal.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
