-
U.S. electric power grid “inherently vulnerable” to terrorist attacks: report
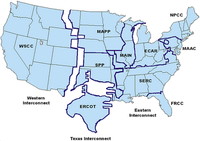
The U.S. electric power delivery system is vulnerable to terrorist attacks which could cause much more damage to the system than natural disasters such as Hurricane Sandy, blacking out large regions of the country for weeks or months, and costing many billions of dollars, says a newly released report by the National Research Council
-
-
Con Ed overcame many obstacles to restore power to NYC
On 29 October Hurricane Sandy slammed into New York City and took out the power in most of Lower Manhattan, even knocking out power to the headquarters of Consolidated Edison’s (Con Ed), the electricity supplier for NYC; due to the flooding in Lower Manhattan, employees had to use rafts to rescue coworkers trapped in the company’s East 13th Street power station; in the days after the storm, as with many other New Yorkers, Con Ed almost ran out of gas, but that did not stop the company from restoring power back to Lower Manhattan less than four days after the storm
-
-
Hurricane Sandy caused dramatic changes to hundreds of miles of East Coast shoreline

The United States Geological Survey (USGS) has released a series of aerial photographs showing before-and-after images of Hurricane Sandy’s impacts on the Atlantic Coast; the photos, part of a USGS assessment of coastal change from as far south as the Outer Banks of North Carolina to as far north as Massachusetts, show that the storm caused dramatic changes to portions of shoreline extending hundreds of miles
-
-
Plants, soils could exacerbate climate change as global climate warms

Scientists have demonstrated that plants and soils could release large amounts of carbon dioxide as global climate warms; this finding contrasts with the expectation that plants and soils will absorb carbon dioxide and is important because that additional carbon release from land surface could be a potent positive feedback that exacerbates climate warming
-
-
Sea-level records reveal tight correlation between ice volume and polar temperature

During the last few million years, global ice-volume variability has been one of the main feedback mechanisms in climate change, because of the strong reflective properties of large ice sheets. Ice volume changes in ancient times can be reconstructed from sea-level records; a new study has revealed a rapid response between global temperature and ice volume/sea-level, which could lead to sea-levels rising by over one meter
-
-
In 2009, engineers predicted surge threats to N.Y.-N.J. and offered detailed mitigation measures
The leaders of the U.S. top engineering association, reflecting on the destruction inflicted by Superstorm Sandy, say that more than three years ago the association presented studies showing that a devastating storm surge in the region was all but inevitable; participants in the 30-31 March 2009 American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE) conference called on NYC officials seriously to consider whether to install surge barriers or tide gates in New York Harbor to protect the city
-
-
New book discusses storm surge protection for New York City

A new book from American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE), to be published on 3 December, includes sixteen papers exploring the development of storm surge barriers to protect New York City and nearby New Jersey from the effects of a future deluge
-
-
Increasing the efficiency of wireless networks
A “spectrum crunch” is quickly being accelerated as customers convert from traditional cell phones to smartphones and tablets; new method, which doubles the efficiency of wireless networks, was developed by researchers; it could have broad impacts on the mobile Internet and wireless industries
-
-
“Groundwater inundation” doubles previous predictions of flooding with future sea level rise

Scientists published a study today showing that besides marine inundation (flooding), low-lying coastal areas may also be vulnerable to “groundwater inundation,” a factor largely unrecognized in earlier predictions on the effects of sea level rise (SLR)
-
-
Michigan launches Cyber Range – a cutting-edge cybersecurity training program
Michigan has launched the Michigan Cyber Range, a state-of-the-art facility that prepares cybersecurity professionals in the detection and prevention of cyber attacks; the initiative pairs cybersecurity resources with hands-on training opportunities to enhance Michigan’s protection of computer systems and sensitive data
-
-
2002 Alaska earthquake helped set standards for buildings, bridges
The Denali 7.9 earthquake that hit Alaska in 2002 was the largest to hit the United States in more than 150 years, and the strongest ever recorded in Alaska; no one was killed and only a few people were injured; the only severe damage the earthquake caused was to a few highways, but the damage was not significant enough to close them; the earthquake set new national standards for building bridges as well as giving seismologists a better understanding of how earthquakes affect frozen ground
-
-
Future warming likely to be on high side of climate projections: analysis
Climate model projections showing a greater rise in global temperature are likely to prove more accurate than those showing a lesser rise, according to a new analysis by scientists at the U.S. National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR); NCAR says that the findings could provide a breakthrough in the longstanding quest to narrow the range of global warming expected in coming decades and beyond
-
-
Nor'easter batters NYC, New Jersey
A nor’easter battered New York and New Jersey on Wednesday with rain and wet snow, plunging homes back into darkness, stopping commuter trains, and inflicting yet more misery on thousands of people still trying to recover from Superstorm Sandy; ordinarily, the nor’easter would not pose major problems, but this was not the case yesterday, as the storm hit an area where electrical systems were still fragile and many of Sandy’s victims still busy cleaning their homes and coping with deepening cold
-
-
MIT researchers develop method to help communities plan for climate risk
As the devastation left by Sandy continues to reverberate, decision-makers at every level are asking: How can we be better prepared? MIT researchers developed a tool to assess regional risks of climate change and potential impacts on local infrastructure and planning; the tool helps policymakers, city planners, and others see the possible local effects of climate change, such as long-term temperature and precipitation changes, allowing local planners to evaluate risks, and how these risks could shape crops, roads, and energy infrastructure
-
-
Dealing with power outages more efficiently
When there is a power failure, the utility companies, public officials and emergency services must work together quickly; researchers have created a new planning software product that enables all participants to be better prepared for emergency situations
-
More headlines
The long view
Helping Strengthen America’s Critical Infrastructure
Everyday life depends on a robust infrastructure network that provides access to running water, communications technology and electricity, among other basic necessities. The experts who keep our national infrastructure secure and resilient also need a strong network to share their knowledge and train the next generation of professionals capable of solving complex infrastructure challenges.
AI and the Future of the U.S. Electric Grid
Despite its age, the U.S. electric grid remains one of the great workhorses of modern life. Whether it can maintain that performance over the next few years may determine how well the U.S. competes in an AI-driven world.
