-
Osaka Basin quake map identifies high-rise buildings at risk

The Osaka Basin, Japan is home to many high-rise buildings which sit atop its thick soft sediments, vulnerable to long-period strong ground motions that last minutes. A new map created by Japanese researchers is intends to guide engineers and city planners in new construction and identifies existing buildings with the potential of resonance vibration.
-
-
New bridge construction technologies to shore up U.S. infrastructure
Experts agree that there is an urgent need to construct and repair bridges across the United States. Around 70,000 bridges in the country are considered “structurally deficient” by government standards. New technology could help the United States manage its growing, and aging, infrastructure without breaking the bank or levying high taxes on citizens.
-
-
Extreme rainfall linked to global warming
A worldwide review of global rainfall data has found that the intensity of the most extreme rainfall events is increasing across the globe as temperatures rise. In the most comprehensive review of changes to extreme rainfall ever undertaken, researchers evaluated the association between extreme rainfall and atmospheric temperatures at more than 8,000 weather gauging stations around the world.
-
-
Pentagon to bolster U.S cyberwar capabilities
The Department of Defense is planning an expansion of the U.S. Cyber Command, and the Pentagon plans on recruiting thousands of code crackers, online security professionals, and hackers in order to assemble the nation’s largest cyber army ever.
-
-
Maryland counties debate funding stormwater drainage management
A new tax aimed at property owners could finance the first set of improvements of the drainage works in Salisbury, Maryland since the original system was laid almost a century ago. City leaders have been arguing since 2009 over dedicating a source of funding to stormwater management, when an environmental panel recommended it. In the past, funding for projects like this has been hard to find as other priorities were deemed more important.
-
-
Grammar rules undermine security of long computer passwords
When writing or speaking, good grammar helps people make themselves understood. When used to concoct a long computer password, however, grammar — good or bad — provides important hints that can help someone crack that password, researchers at Carnegie Mellon University have demonstrated by devising grammar-aware password cracker.
-
-
Improving cities by using the notion of “urban metabolism”
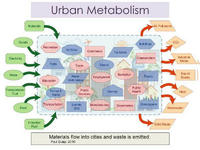
As is the case with organisms, cities need energy, water, and nutrients, and they need to dispose of wastes and byproducts in ways which are viable and sustainable over the long run. This concept of “urban metabolism” is a model for looking systematically at the resources that flow into cities and the wastes and emissions that flow out from them in order better to understand the environmental impacts of cities and to highlight opportunities for efficiencies, improvements, and transformation.
-
-
Exploring asteroids for commercial metal harvesting

Deep Space says that in a decade, it will be harvesting asteroids for metals and other building materials, to construct large communications platforms to replace communications satellites, and later solar power stations to beam carbon-free energy to consumers on Earth. “More than 900 new asteroids that pass near Earth are discovered every year. They can be like the Iron Range of Minnesota was for the Detroit car industry last century,” says the company’s CEO.
-
-
DOE addresses rare earth, critical materials shortage
The U.S. Department of Energy announced earlier this month that a team led by Ames Laboratory in Ames, Iowa, has been selected for an award of up to $120 million over five years to establish an Energy Innovation Hub which will develop solutions to the domestic shortages of rare earth metals and other materials critical for U.S. energy security.
-
-
Black carbon’s contribution to climate change underestimated
Black carbon is the second largest man-made contributor to global warming and its influence on climate has been greatly underestimated, according to the first quantitative and comprehensive analysis of this issue; black carbon is believed to have a warming effect of about 1.1 Watts per square meter (W/m²), approximately two thirds of the effect of the largest man made contributor to global warming, carbon dioxide.
-
-
Black carbon’s contribution to climate change underestimated

Black carbon is the second largest man-made contributor to global warming and its influence on climate has been greatly underestimated, according to the first quantitative and comprehensive analysis of this issue; black carbon is believed to have a warming effect of about 1.1 Watts per square meter (W/m²), approximately two thirds of the effect of the largest man made contributor to global warming, carbon dioxide.
-
-
NASA: 2012 sustained long-term climate warming trend
NASA scientists say 2012 was the ninth warmest of any year since 1880, continuing a long-term trend of rising global temperatures. With the exception of 1998, the nine warmest years in the 132-year record all have occurred since 2000, with 2010 and 2005 ranking as the hottest years on record. Scientists emphasize that weather patterns always will cause fluctuations in average temperature from year to year, but the continued increase in greenhouse gas levels in Earth’s atmosphere assures a long-term rise in global temperatures. Each successive year will not necessarily be warmer than the year before, but on the current course of greenhouse gas increases, scientists expect each successive decade to be warmer than the previous decade.
-
-
The humble jute serves as a sustainable reinforcement for concrete
Fashionable people may turn up their noses at jute, the cheap fiber used to make burlap, gunny sacks, twine, and other common products, but new research is enhancing jute’s appeal as an inexpensive, sustainable reinforcement for mortar and concrete.
-
-
DHS: Industrial control systems subject to 200 attacks in 2012
A DHS report released last week revealed that industrial control systems, which are used to monitor and control critical infrastructure facilities, were hit with 198 documented cyberattacks in 2012, and that many of these attacks were serious.
-
-
Shoring up Long Island’s natural shore defenses against future storms

Sand and other coarse-grained sediments are vital to the naturally occurring barrier systems which dissipate storm surges, protect coastal residences, and shelter biologically diverse estuaries and ecosystems; a team of researchers is conducting marine geophysical surveys of the seafloor and shallow subsurface to assess the health of the offshore barrier system which protects the New York Harbor and southwestern Long Island region against damage from future storms
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
