-
DHS focus on suspicious activity at critical infrastructure facilities
Federal, state, and local law enforcement let people know that if theytake pictures or notes around monuments and critical infrastructure facilities, theycould be subject to an interrogation or an arrest; in addition to the See Something, Say Something awareness campaign, DHS also has broader initiatives such as the Buffer Zone Protection Program, which teach local police and security how to spot potential terrorist activities
-
-
Chile relies on new technologies to cope with frequent earthquakes
Citizens of Chile are used to the ground shaking beneath their feet; in the past two years alone Chile has experienced more than forty earthquakes with magnitudes of six or higher; with so many earthquakes and the potential of thousands dying yearly, Chilean authorities are using new methods to protect their citizens from death and buildings from damage
-
-
Hurricane Irene polluted Catskills watershed

The water quality of lakes and coastal systems will be altered if hurricanes intensify in a warming world, according to a Yale study; researchers found that last summer during Hurricane Irene — the worst storm in the New York area in 200 years — record amounts of dissolved organic matter darkened Catskill waters and affected the Ashokan Reservoir that supplies New York City with drinking water
-
-
Debate over causes of levee failure during Katrina intensifies

A court case in which residents of two sections of New Orleans are suing a construction group has put millions of dollars at stake; residents of the Lower 9th Ward and St. Bernard Parish residents claim that Washington Group International (WGI), an Amy Corps of Engineers contractor, removed several buildings and pilings from land along the Industrial Canal as part of a construction plan to expand the canal’s shipping lock, then failed adequately to plug the holes left behind; the holes allowed rainwater from Hurricane Katrina to seep underneath the 14-foot wall, essentially lifting the wall and allowing the areas to be flooded
-
-
Repair bill for Miami-Dade water and sewage system: $12 billion
Repairing, replacing, and rebuilding 13,000 miles of old water and sewage pipes and the treatment plants they connect to could cost Miami-Dade County, Florida more than $12 billion dollars over the next fifteen years; this is a staggering amount – made even more so in light of the fact that this is considerably more than the original estimate of $1 billion
-
-
Dutch test-levee experiment helps strengthen U.S. levees, dams
In the United States, the national flood-control infrastructure is aging and its structural health is deteriorating; the system comprises more than 5,600 km of levees, and 43 percent of the U.S. population lives in counties with levees designed to provide some level of protection from flooding; some of these levees are as old as 150 years; in 2009, the American Society of Civil Engineers Report Card for America’s Infrastructure gave the condition of the nation’s dams a grade of D, and levees a grade of D-minus; an dam-strength experiment in the Netherland helps engineers collect data to validate new suite of technologies for assessing the health of levees and dams
-
-
New FERC office to focus on cyber security
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) has created a new FERC office — Office of Energy Infrastructure Security (OEIS) — which will help the Commission focus on potential cyber and physical security risks to energy facilities under its jurisdiction
-
-
Rare Earth metals: Will we have enough?
Life in the twenty-first century would not be the same without rare Earth metals; cell phones, iPads, laptops, televisions, hybrid cars, wind turbines, solar cells, and many more products depend on rare Earth metals to function; will there be enough for us to continue our high-tech lifestyle and transition to a renewable energy economy? Do we need to turn to deep seabed or asteroid mining to meet future demand?
-
-
Specialty metals recycling policy needed: experts
An international policy is needed for recycling scarce specialty metals that are critical in the production of consumer goods; because they are used in small amounts for very precise technological purposes, such as red phosphors, high-strength magnets, thin-film solar cells, and computer chips, recovery can be so technologically and economically challenging that the attempt is seldom made
-
-
New York unprepared for flooding, sea level rise
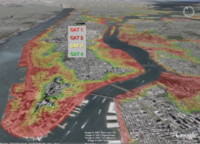
New York City may be a fast paced city of bright lights, sleek attitudes, fashion trends, and some of the best sports teams in the country, but underneath the glitz and glamour is a city which is not prepared for an act of God and which is being threatened by rising sea levels and severe storm flooding; “It’s a million small changes that need to happen,” one expert says
-
-
Limiting world trade unlikely to reduce CO2 emissions
The United States emits less CO2 in the production of its exports than is contained in its imports, simply because it imports more than it exports; only about 20 percent of CO2 transfers from China into the United States can be traced back to the fact that China is in effect relatively more specialized in the production of dirty goods; interventions in world trade, like CO2 tariffs, would probably have only a small impact on global emissions
-
-
Lessons learned: Cheech and Chong at the Y-12 security breach
On 28 July 2012, an 82-year old nun and her two confederates — both senior citizens themselves – breached the vaunted and supposedly impregnable perimeter protection system at the Y-12 National Security Complex at Oak Ridge, where uranium for nuclear weapons is processed and stored (the Y-12 complex is not affiliated with the Oak Ridge National Laboratory [ORNL]); a report on the incident by the Inspector General of the Department of Energy is couched in bureaucratic jargon, but it reveals that the Y-12 security system and practices were much worse than Cheech and Chong could have ever portrayed in their wildest stand-up comedy routines or loopy films
-
-
New law aims to make Istanbul earthquake-safe, but it has its critics

Estimates of Istanbul’s population range from twelve and nineteen million people, a significant increase from two million people fiftyyears ago; during the waves of migration to Istanbul during the 1960s,1970s, and 1980s, the government gave citizens free permitsto add to their homes, which resulted in single-story residents becoming 4-or 5-story buildings on unstable foundations; Istanbul sits only thirteen miles north of the North Anatolian Fault, the intersection of the Eurasian and Anatolian plates, and has been subject to devastating earthquakes; new, controversial law aims to make Istanbul’s buildings earthquake-safe
-
-
Boeing to pursue cybersecurity opportunities in Japan
Boeing and Japanese trading company Sojitz are teaming up to offer advanced cybersecurity solutions in Japan to help protect critical government, civil, and commercial information technology infrastructure
-
-
Nexans shows its anti-theft cable solutions

Nexans is showing its new anti-theft cable solutions at InnoTrans, which opened yesterday in Berlin; the solution promises to help network operators reduce the high volume of copper cables theft along their railway networks
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
