-
Improving oil recovery, aiding environmental cleanup
Researchers have taken a new look at an old, but seldom-used technique developed by the petroleum industry to recover oil, and learned more about why it works, how it could be improved, and how it might be able to make a comeback not only in oil recovery but also environmental cleanup
-
-
Earthquake risk looms large in the Pacific Northwest
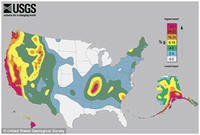
A comprehensive analysis of the Cascadia Subduction Zone off the Pacific Northwest coast confirms that the region has had numerous earthquakes over the past 10,000 years, and suggests that the southern Oregon coast may be most vulnerable based on recurrence frequency
-
-
Researcher wins public interest award for research into water safety
Virginia Tech professor wins prestigious public service award for research work which found that many homes in the nation’s capital were receiving water contaminated with lead leached from city pipes to an extent far exceeding acceptable industry levels; the amount of lead in the water likely put several thousand people, especially children, at risk, yet government agencies, including CDC, used faulty data and analysis to hide the risks
-
-
Earth’s oceans, ecosystems still absorbing about half the greenhouse gases emitted by people
Earth’s oceans, forests, and other ecosystems continue to soak up about half the carbon dioxide emitted into the atmosphere by human activities, even as those emissions have increased, according to a study published yesterday in the journal Nature
-
-
Under industry pressure, DHS drops chemical plant employee screening proposal

Security experts agree that short of a nuclear attack on a U.S. city, the most casualty-heavy disaster would occur as a result of an accident in, or a terrorist attack on, a chemical plant which would release a cloud of toxic fumes; there are about 15,000 plants in the United States which produce, process, use, or store volatile and toxic chemicals; more than 300 of the these plants are so close to large population centers, that a chemical release in any one of them would cause more than 50,000 casualties; DHS wanted to have employees in these plants screened for potential ties terrorism, but the chemical industry objected, saying this would be too costly; last Thursday DHS pulled the proposal
-
-
New, affordable instant warnings of bridge collapse

The Federal Bureau of Transportation lists nearly 70,000 U.S. bridges as “structurally deficient,” requiring extra surveillance; in addition, more than 77,000 others are categorized as “obsolete” — exceeding their intended lifespan and carrying loads greater than they were designed to handle; researchers developed a new technology for monitoring these 150,000 aging U.S. highway bridges
-
-
Examination of Finnish lakes reveals radiation secrets
A new study casts doubt over the validity of models used to assess the impact of radiation on human health; an examination of the affects of radioactive fallout from the 1986 Chernobyl accident on two Finnish lakes sows that the transfer of the radioactive compounds is non-linear, and that the levels of radioactive compounds appear to be three times higher in fish-eating species (piscivores) than in non-fish-eating species
-
-
A second look at off-shore use of vertical-axis wind turbines

Wind energy researchers are re-evaluating vertical axis wind turbines (VAWTs) to help solve some of the problems of generating energy from offshore breezes; though VAWTs have been around since the earliest days of wind energy research, VAWT architecture could transform offshore wind technology
-
-
Radiation detection equipment installed in four Mexican ports
The Megaports Initiative is a U.S. Department of Energy program intended to enhance the ability of ports around the world to detect and interdict illicit shipments of special nuclear and other radioactive materials; Under the initiative, radiation detection gear and protocols were implemented in the Mexican ports of Manzanillo, Altamira, Lazaro Cardenas, and Veracruz, through which 92 percent of Mexico’s containerized cargo pass
-
-
Raytheon's Space Fence technology tracks space debris

Space debris threatens systems the U.S. military and economy depend on every day, including satellites that power navigation, weather and critical infrastructures; the Space Fence program is capable of detecting more and much smaller objects in low earth orbit
-
-
Measuring DHS effectiveness monitoring chemical plant safety standards
The events of 9/11 triggered a national re-examination of the security of facilities that use or store hazardous chemicals in quantities which, in the event of a terrorist attack, could put large numbers of Americans at risk of serious injury or death; the GAO issued a report on how DHS ensures compliance with chemical facilities security standards
-
-
Surface coal mining destroying West Virginia streams, rivers
More than 22 percent of streams and rivers in southern West Virginia have been degraded to the point they may now qualify as impaired under state criteria; the substantial losses in aquatic insect biodiversity and increases in salinity is linked to sulfates and other pollutants in runoff from mines often located miles upstream
-
-
Conflict of interests charges surround two pro-fracking studies
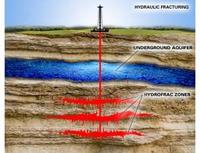
Two recent studies — by research institutes at the University of Buffalo and the University of Texas — on the relationship between fracking and the contamination of groundwater, offered what was claimed to be scientific, peer-reviewed research which concluded that fracking does not contribute to such contamination; an examination of the two reports reveals that they were not properly reviewed according to accepted academic standards, and that their authors, and the research institutes which sponsored them, are heavily involved with companies which conduct fracking operations; the author of the University of Texas report sits on the board of a leading fracking company, where his compensation is more than twice as large as his UT salary; he did not disclose this fact in the study — or inform UT of this connection; UT is investigating
-
-
The five biggest stories at Black Hat
The annual Black Hat Briefings conference, held last week in Las Vegas, is the world’s biggest, and arguably the most important, gathering of security researchers; here are the five biggest stories to take away from last week’s Black Hat meeting in Las Vegas
-
-
Science group: storing spent nuclear fuel in dry casks significantly safer then wet pools storage

An NRC report on the lessons of the Fukushima disaster says that storing spent nuclear fuel in wet pools is “adequate” to protect the public; a science groups says there is a significantly safer way to store the 55,000 tons of radioactive waste currently stored by the 104 nuclear power plants operating in the United States: transferring the spent fuel to dry casks
-
More headlines
The long view
Helping Strengthen America’s Critical Infrastructure
Everyday life depends on a robust infrastructure network that provides access to running water, communications technology and electricity, among other basic necessities. The experts who keep our national infrastructure secure and resilient also need a strong network to share their knowledge and train the next generation of professionals capable of solving complex infrastructure challenges.
AI and the Future of the U.S. Electric Grid
Despite its age, the U.S. electric grid remains one of the great workhorses of modern life. Whether it can maintain that performance over the next few years may determine how well the U.S. competes in an AI-driven world.
Using Liquid Air for Grid-Scale Energy Storage
New research finds liquid air energy storage could be the lowest-cost option for ensuring a continuous power supply on a future grid dominated by carbon-free but intermittent sources of electricity.
Enhanced Geothermal Systems: A Promising Source of Round-the-Clock Energy
With its capacity to provide 24/7 power, many are warming up to the prospect of geothermal energy. Scientists are currently working to advance human-made reservoirs in Earth’s deep subsurface to stimulate the activity that exists within natural geothermal systems.
Experts Discuss Geothermal Potential
Geothermal energy harnesses the heat from within Earth—the term comes from the Greek words geo (earth) and therme (heat). It is an energy source that has the potential to power all our energy needs for billions of years.
