-
Digital privacy services enjoying a surge in demand
Digital privacy services such as encrypted e-mail, secure instant messaging, and services that provide hard-to-track IP addresses are enjoying a surge in demand as individuals and businesses seek to protect information from spies and hackers in the wake of the National Security Agency’s (NSA) surveillance program revelations. These services promise security, but may also slow down computer performance. Moreover, they are not likely to deter those who are determined to hack into a particular computer network.
-
-
Deflecting asteroids to avoid Armageddon

It sounds like the script for a Hollywood film: a giant meteorite from outer space heading straight for the Earth and threatening the destruction of mankind. Yet such a scenario does represent a real threat to our planet, as researchers reckon that we can expect an asteroid to collide with Earth every few hundred years. In real life, though, nobody wants to rely on a rescue plan hastily improvised at the last minute. Scientists with the European-funded research project NEOShield are working to develop concepts designed to help avert these impacts and to alter asteroids’ orbits as they race toward Earth.
-
-
Indian Ocean phenomenon helps in predicting extreme weather
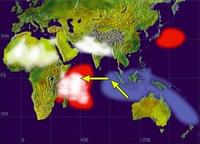
The Indian Ocean Dipole is the difference in sea-surface temperatures between the western and eastern part of the Indian Ocean. A better understanding of the relationship between the Indian Ocean Dipole and extreme weather events will enable farmers, industry, communities, and governments better to anticipate and prepare for droughts and increased bushfire risk, up to six months in advance of the event.
-
-
Developing cyber resilience to meet increasing cyberthreats
Managing resilience for cyber systems requires metrics that reflect the relationships among system components in physical, information, cognitive, and social domains. In a paper, researchers describe a framework for understanding the concept of cyber resilience, and lay out a systematic method by which to generate resilience metrics for cyber systems.
-
-
Modeling earthquakes and explosives reactions
Researchers are developing mathematical models that can help in reducing rock fracturing and soil liquefaction caused by natural or man-made disasters. The outcomes of the research could improve safety levels in the mining and petroleum industries, and play a critical role in the ability of civil infrastructure to withstand disasters such as earthquakes and explosions.
-
-
Methane emissions in the U.S. exceed government estimates
Along with carbon dioxide, methane is one of the most important greenhouse gases in terms of its potential to raise global temperatures. It also encourages the formation of surface ozone in cities and affects other aspects of atmospheric chemistry. A new study finds that emissions of methane from fossil fuel extraction and refining activities in the South Central United States are nearly five times higher than previous estimates. The collaborative study indicates that in addition to fossil fuel extraction, animal husbandry is also a major contributor to the higher-than-expected methane emissions.
-
-
New catalyst for cleanup of nitrites
Nitrites and their more abundant cousins, nitrates, are inorganic compounds that are often found in both groundwater and surface water — a big problem, particularly for agricultural communities. The compounds are a health hazard, and the EPA places strict limits on the amount of nitrates and nitrites in drinking water. While it is possible to remove nitrates and nitrites from water with filters and resins, the process can be prohibitively expensive. Chemical engineers at Rice University have found a new catalyst that can rapidly break down nitrites.
-
-
Cybersecurity paradigm shift: from reaction to prediction and prevention
The intensification of cyberattacks on corporations and government agencies has led to a surge of new companies offering cybersecurity solutions, and Israel boasts some of the world’s top cybersecurity firms.Until recently, investment dollars generally supported startups with a focus on defensive cyber solutions, but now firms like Israel’s CyberArk, providers of proactive and full-service cyber solutions, are of growing interest of tech investors.
-
-
NSA, DHS partner with academia to train next generation cyber specialists
Universities across the United States have partnered with the NSA and DHS to prepare the next generation of cybersecurity professionals in anticipation of growing and more serious cyberattacks on the United States. Nearly 200 schools are designing new academic programs to attract more students to the growing field of cybersecurity, and with NSA and DHS as partners, the universities are preparing students for important roles in securing the nation’s digital infrastructure.
-
-
NIST: Joplin tornado highlights need for building design, construction standards
Nationally accepted standards for building design and construction, public shelters, and emergency communications can significantly reduce deaths and the steep economic costs of property damage caused by tornadoes. That is the key conclusion of a two-year technical NIST investigation into the impacts of the 22 May 2011 tornado that struck Joplin, Missouri. Report and recommendations released for public comment.
-
-
The interim agreement between the P5+1 and Iran: the details
The P5+1 countries (the United States, United Kingdom, Germany, France, Russia, and China, facilitated by the European Union) have been engaged in negotiations with Iran in an effort to reach a verifiable diplomatic resolution which would prevent Iran from obtaining a nuclear weapon. On Sunday, the P5+1 and Iran reached a set of initial understandings which halts, at least temporarily, the progress of Iran’s nuclear program and rolls it back in key respects. In return, for Iran’s concessions, and as part of this initial step, the P5+1 will provide what the agreement describes as “limited, temporary, targeted, and reversible” relief to Iran.
-
-
List of most-at-risk L.A. buildings to be released
Scientists have compiled a list of concrete buildings in Los Angeles which could be at risk of collapsing in a major earthquake. The list identifies about 1,500 concrete structures built before 1980 which need further study to determine their risk level. Structural engineers insist that hundreds could die if any of the buildings collapsed.
-
-
Sea-level rise could exceed one meter in this century: experts
Sea-level rise in this century is likely to be 70-120 centimeters by 2100 if greenhouse-gas emissions are not mitigated, a broad assessment of the most active scientists who research in the area, and who are the most prolific publishers on that topic, has revealed. In contrast, for a scenario with strong emissions reductions, experts expect a sea-level rise of 40-60 centimeters by 2100. Ninety international experts, all of whom published at least six peer-reviewed papers on the topic of sea-level during the past five years, provided their probabilistic assessment.
-
-
Understanding Greenland Ice Sheet melting helps sea-level forecasts
New insight into how glacier movement is affected by melting ice in summer could help predictions of sea level rise. In 2012, an exceptionally warm summer caused the Greenland Ice Sheet to undergo unprecedented rates of melting. Researchers have found, however, that fast summer ice flow caused by significant melting is cancelled out by slower motion the following winter.
-
-
Winners announced in NY, NJ coastal protection ideas competition
Ten of the ideas submitted to the Rebuild by Designcompetition, launched by the Hurricane Sandy Rebuilding Task Force, were selected as the most promising concepts for sustainable ways to protect Sandy-affected regions from future catastrophes.
-
More headlines
The long view
Water Wars: A Historic Agreement Between Mexico and US Is Ramping Up Border Tension
As climate change drives rising temperatures and changes in rainfall, Mexico and the US are in the middle of a conflict over water, putting an additional strain on their relationship. Partly due to constant droughts, Mexico has struggled to maintain its water deliveries for much of the last 25 years, deliveries to which it is obligated by a 1944 water-sharing agreement between the two countries.
Trump Is Fast-Tracking New Coal Mines — Even When They Don’t Make Economic Sense
In Appalachian Tennessee, mines shut down and couldn’t pay their debts. Now a new one is opening under the guise of an “energy emergency.”
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
