-
Japan hopes off-shore wind turbines can replace shut-down nukes

Japan inaugurated a floating offshore wind turbine on Monday, symbolizing the country’s effort to reduce its dependency on nuclear energy and fossil fuels and shift to renewable energy sources. The floating platform is anchored thirteen miles offshore from the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant, which has been out of commission since the reactor’s meltdown disasterof March 2011. The platform is anchored to the seabed 400 feet below surface. It is the first project of its kind in Japan, and it aims to show that the country can exploit the country’s powerful offshore winds to create a sustainable energy source.
-
-
National grid in mock power emergency drill today and tomorrow
North American power companies will participate in a mock power emergency scenario today and tomorrow (13-14 November) to test their ability to respond to physical or cyberattacks that may lead to widespread power outages and long term blackouts. The exercise, known as GridEx II, is the second emergency response exercise conducted by North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) intended to task North American electric utility companies with reviewing their security and crisis response strategies.
-
-
Climate scientists say renewables are not enough
Some of the world’s top climatologists have declared their support for nuclear energy as a complementary energy source, alongside wind and solar as energy, which would cut fossil fuel pollution and reduce the growth of global warming. The scientists say that opposing fossil fuels and promoting renewable energy sources offer but a limited solution.
-
-
U.S. mix of fuels used for power generation is changing

The mix of fuels used to generate the electricity in homes, factories, and businesses across the United States has changed in the past few years as coal, still the largest single fuel used for electricity, has lost some of its share of the generation market to natural gas and non-hydroelectric renewables.
-
-
Philippines prepares for worse disasters to come
On average, the Philippines experiences about twenty typhoons a year, including three super-typhoons and many incidents of flooding, drought, earthquakes, tremors, and occasional volcanic eruptions, making the country one of the most naturally disaster-prone areas in the world. Filipino government agencies, with the help of international disaster and relief agencies, have created new strategies for disaster preparedness, response, and mitigation which may well have potential applications in other parts of the world. As the impact of climate change grows more pronounced, the Philippines is becoming a hothouse for developing new methods and systems in the growing business of disaster relief.
-
-
Sunlight-activated nanogrid breaks down pollutants in water
Oil spills do untold damage to the environment — to the waters they pollute and to marine and other wildlife. The Deepwater Horizon spill in the Gulf of Mexico in 2010, for example, the largest accidental marine oil spill in the history of the petroleum industry, flowed unabated for three months. Typically, such oil spills are extraordinarily difficult to clean up. Soon, however, the process may become infinitely easier and ecologically friendly, the result of a new invention — “nanogrid” — a large net consisting of metal grids made of a copper tungsten oxide, that, when activated by sunlight, can break down oil from a spill, leaving only biodegradable compounds behind.
-
-
Chelyabinsk meteor explosion a "wake-up call," scientists warn
Three new studies have revealed details of the meteor that exploded above Russian city, Chelyabinsk, in February this year. Their findings provide information about the meteor’s origin, trajectory, power and damage by the airburst (the shock wave that travelled through the air from the explosion). These findings may help to refine theoretical models about the likely frequency of such events, the potential damage they could cause and hazard mitigation strategies needed for planetary protection.
-
-
Wildfire science returns to California’s Rim Fire

The challenging job of managing wildfires rests with other agencies, but the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) provides the underlying science for sound land management decisions, before, during, and after wildfires. The USGS role studying natural hazards such as floods, landslides, earthquakes, and volcanoes is well known, but fewer people are aware of the USGS scientific work in major wildfire events, which are one of the most regular and sometimes most devastating natural hazards in the West.
-
-
Safe long-term CO2 storage possible
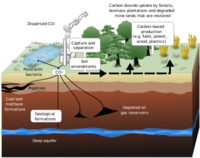
Since 2004, the German Research Centre for Geosciences (GFZ) has led an international research network to investigate the geological storage of the greenhouse gas (CCS, for carbon capture and storage). GFZ’s scientists say that their work at the Ketzin site, 40 km west of Berlin, has shown that geological CO2 storage on a pilot scale can be done safely and reliably.
-
-
Wireless device converts wasted energy into electric power
Using inexpensive materials configured and tuned to capture microwave signals, researchers have designed a power-harvesting device with efficiency similar to that of modern solar panels. The device wirelessly converts the microwave signal to direct current voltage capable of recharging a cell phone battery or other small electronic device.
-
-
Weakening cybersecurity to facilitate NSA surveillance is dangerous: experts
In the wake of revelations about the NSA surveillance programs, an expert on surveillance and cybersecurity recommended a re-evaluation of those surveillance practices that weaken commercial products and services. These practices include weakening standards and placing “back doors” into products that are accessible to U.S. government agencies. The expert – Jon Peha, former chief technology officer of the FCC and assistant director of the White House’s Office of Science and Technology — said deliberately weakening commercial products and services may make it easier for U.S. intelligence agencies to conduct surveillance, but “this strategy also inevitably makes it easier for criminals, terrorists and foreign powers to infiltrate these systems for their own purposes.”
-
-
DHS struggling to respond to cybersecurity threats: IG
A recent reportby DHS inspector general (IG) has documented the agency’s struggle to respond to cybersecurity threats and its inability to disseminate information about threats because of technical, funding, and staffing challenges.
-
-
Developing robots for bridge inspection, mine rescue with NSF grants

In 2011, at Carnegie Mellon University, President Barack Obama announced the National Robotics Initiative. The National Science Foundation announced it has awarded a total of more than $7 million to Carnegie Mellon researchers in the latest round of grants for the initiative — a multi-agency effort to develop robots that can work with humans to extend and augment human skills. Researchers are developing robots for bridge inspection, mine rescue, and aid for the blind.
-
-
Scientists: we should prepare for hell and high water

An international team of climate and social scientists say a new approach to climate preparedness is essential to help people adjust to coming changes. As climate-driven changes get more pronounced, people everywhere will have to adjust. In this week’s issue of the journal Science, an international group of researchers urge the development of science needed to manage climate risks and capitalize on unexpected opportunities.
-
-
Making cybersecurity a political issue
U.S. federal agencies have reported a dramatic rise in the number of cyberattacks over the past few years, with reported cyber incidents rising from 5,503 in 2006 to 48,562 in 2012. Since cyber incidents pose such a threat to national security and infrastructure, could cybersecurity become a political campaign issue? Experts say that if politicians were to focus their attention, and their constituents’ attention, on cybersecurity, the United States could be made safer from cyberattacks before a “cyber Pearl Harbor” – or a “cyber 9/11” – occurs.
-
More headlines
The long view
Water Wars: A Historic Agreement Between Mexico and US Is Ramping Up Border Tension
By Natasha Lindstaedt
As climate change drives rising temperatures and changes in rainfall, Mexico and the US are in the middle of a conflict over water, putting an additional strain on their relationship. Partly due to constant droughts, Mexico has struggled to maintain its water deliveries for much of the last 25 years, deliveries to which it is obligated by a 1944 water-sharing agreement between the two countries.
Trump Is Fast-Tracking New Coal Mines — Even When They Don’t Make Economic Sense
By Katie Myers
In Appalachian Tennessee, mines shut down and couldn’t pay their debts. Now a new one is opening under the guise of an “energy emergency.”
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
By David Montgomery
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
By John Domol
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
By Zach Winn
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
