-
Remapping coastal areas damaged by Hurricane Sandy

Hurricane Sandy caused wide-scale landscape-altering destruction, resulting in an estimated damage of $50 billion, making Sandy the second-costliest cyclone to hit the United States since 1900. “Sandy’s most fundamental lesson is that storm vulnerability is a direct consequence of the elevation of coastal communities in relation to storm waves,” says USGS Kevin Gallagher. Three federal agencies are using ships, aircraft, and satellites to measure water depth, look for submerged debris, and record altered shorelines in high priority areas from South Carolina to Maine.
-
-
Demolition of building allows study of earthquake along Calif. Hayward Fault
In an effort to track which area of California’s East Bay would suffer the worst shaking in future earthquakes caused by the dangerous Hayward Fault, the U.S Geological Survey (USGS) initiated an artificial earthquake through the densely populated area of valleys and hills across bay from San Francisco.
-
-
Bay Bridge repairs expensive, slow

California’s 8-mile San Francisco-Oakland Bay Bridge was designed and built in the 1930s in about 5.5 years at a cost of $78 million, well under budget and ahead of schedule. Presently, the 2-mile eastern span of the bridge needs to be replaced, and it has taken the state five years just to design the replacement. Construction is taking about three times the expected time, and the $6.4 billion budget is almost five times the estimate provided by engineers.
-
-
Aquifer supplying a third of U.S. irrigated groundwater depleting quickly: study
The High Plains Aquifer of Kansas — also called the Ogallala Aquifer — supplies 30 percent of the U.S. irrigated groundwater. New study finds that if current irrigation trends continue, 69 percent of the groundwater stored in the High Plains Aquifer will be depleted in fifty years.
-
-
Post-Sandy infrastructure must be more resilient: Sandy Task Force
The task force appointed by President Barack Obama, charged with developing a strategy for rebuilding areas damaged by Superstorm Sandy, has urged coastal communities to recognize that owing to climate change, storms are going to be more frequent and more destructive, and that floods are going to occur more frequently. The best way to prepare for the more extreme weather ahead is to build a more robust and resilient infrastructure that can withstand the more demanding challenges.
-
-
New reactor design makes nuclear power competitive with natural gas

San Diego-based General Atomics has applied for funding of several hundred millions from the U.S Department of Energy to commercialize a nuclear reactor which, the firm claims, could cut the cost of nuclear power by as much as 40 percent. The new design replaces water with helium as a coolant, allowing the plant to operate at higher temperatures, thus increasing the efficiency of the power plan and reducing the amount of waste needing storage.
-
-
Long-term radiation effects: Chernobyl’s lessons for Fukushima
The Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster spread significant radioactive contamination over more than 3,500 square miles of the Japanese mainland in the spring of 2011. Now several recently published studies of Chernobyl are bringing a new focus on just how extensive the long-term effects on Japanese wildlife might be.
-
-
Predicting when lightning will strike

When something is unlikely to happen, people often say that there is a greater chance of being struck by lightning. The fact is, however, that lightning does strike, and is one of the leading weather-related causes of death and injury. Furthermore, important infrastructure including airports, hospitals, sports stadiums, and power lines can often be affected by lighting. Electronic components are particularly vulnerable to lightning-induced transient voltages. Lightning is estimated to cause up to 16 percent of forest fires in the EU, costing 70 million euros in mitigation efforts a year. The EU-funded LOLIGHT (Lightning Mapping and Supercell Tracking System) project sought to address this by developing a low-cost system capable of detecting lightning to an accuracy of 100 meters.
-
-
New levee system offers New Orleans better protection
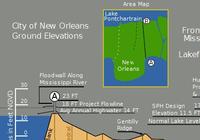
With the busiest period of the 2013 hurricane season approaching metro New Orleans, the area is ready to face the challenge with a flood control system worth about $14.5 billion. The network of levees, floodwalls, and pumps, its designers say, should nearly eliminate the risk of flooding from most hurricanes, and substantially reduces flooding from hurricanes the size of 2005 Hurricane Katrina.
-
-
Ultrathin radios enable flexible structural-health monitoring system
Currently, engineers can use single-point sensors or fiber optic strips to detect structural problems, but the devices can collect data over relatively small spaces. The problem is that many failures develop over large areas and cannot be detect that at an early stage. The 2007 collapse of a highway bridge in Minneapolis, for example, developed over a gusset plate with an area of several square meters, far too large for current monitoring systems to practically survey. Researchers have developed ultrathin radios which can be embedded directly on plastic sheets, which can be applied to walls and other structures. The innovation could be used for new devices ranging from an invisible communications system inside buildings to sophisticated, flexible structural health monitoring system for use on bridges, buildings, roads, pipelines, and other structures.
-
-
Old concrete helps keep water clean
Lakes and streams are often receiving so much phosphorous that it could pose a threat to the local aquatic environment. Now, researchers show that there is an easy and inexpensive way to prevent phosphorus from being discharged to aquatic environments. The solution is crushed concrete from demolition sites.
-
-
Cost of flood losses in major coastal cities to exceed $50 billion by 2050
A new study estimate present and future flood losses — or the global cost of flooding — in 136 of the world’s largest coastal cities, taking into account existing coastal protections. Average global flood losses in 2005, estimated at about $6 billion per year, could increase to $52 billion by 2050 with projected socio-economic change alone. Due to their high wealth and low protection level, three American cities — Miami, New York City, and New Orleans — are responsible for 31 percent of the losses across the 136 cities.
-
-
Investigating earthquake retrofits for “soft” first-floor buildings
A team of researchers has spent the last month shaking a four-story building on the world’s largest outdoor shake table at the University of California, San Diego, to learn how to make structures with first-floor garages better withstand seismic shocks. Since July, the team has successfully tested a variety of earthquake retrofits on a full-scale, 44,000-square-foot building built specifically for the tests at the Englekirk Structural Engineering Center at UCSD. The structure — three stories atop an open first floor — has survived three of four simulated seismic events of increasing strength on the shake table.
-
-
Accessible critical rare Earth deposit confirmed in Montana
U.S. Rare Earths, Inc. (UREE) the other day announced the results of its 2013 exploration in Lemhi Pass, Montana. The company says the results confirmed that its properties have the highest accessible rare earth deposit in North America.
-
-
Sandy shows need for more effective preparedness, resiliency standards
The rebuilding efforts following the devastation wreaked by Superstorm Sandy have triggered a discussion over preparedness and resiliency in America’s commercial and residential buildings.Some experts callfor a presidential appointment of a building resilience “’czar”’ with authority to coordinate and seek synergies between public and private sector initiatives.
-
More headlines
The long view
Water Wars: A Historic Agreement Between Mexico and US Is Ramping Up Border Tension
As climate change drives rising temperatures and changes in rainfall, Mexico and the US are in the middle of a conflict over water, putting an additional strain on their relationship. Partly due to constant droughts, Mexico has struggled to maintain its water deliveries for much of the last 25 years, deliveries to which it is obligated by a 1944 water-sharing agreement between the two countries.
Trump Is Fast-Tracking New Coal Mines — Even When They Don’t Make Economic Sense
In Appalachian Tennessee, mines shut down and couldn’t pay their debts. Now a new one is opening under the guise of an “energy emergency.”
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
