-
Oil-devouring microbe communities a mile deep in the Gulf
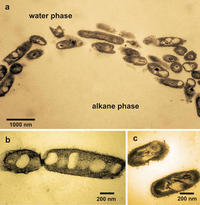
The Deepwater Horizon explosion on 20 April 2010, caused the largest marine oil spill in history, with several million barrels of crude oil released into the Gulf of Mexico over the course of three months. Soon after the spill began, a massive oil slick was visible from orbiting satellites, yet once the underwater gusher was sealed, obvious traces of the crude oil disappeared much sooner than nearly all observers predicted. Some of the oil evaporated; some was skimmed off. Microbes “ate” much of the oil as well.
-
-
U.S. geological carbon dioxide storage potential
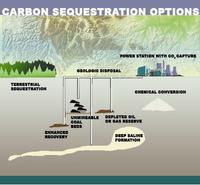
The United States has the potential to store a mean of 3,000 metric gigatons of carbon dioxide (CO2) in geologic basins throughout the country. Technically accessible storage resources are those that can be accessed using today’s technology and pressurization and injection techniques. The most common method of geologic carbon storage involves pressurizing CO2 gas into a liquid, and then injecting it into subsurface rock layers for long-term storage.
-
-
U.S. ports vulnerable to cyberattacks
New study says that the U.S. largest ports are vulnerable to cyberattacks.The study argues that the level of cyber security awareness and culture in U.S. port facilities is relatively low, and that a cyberattack at a major U.S. port would quickly cause significant damage to the economy.
-
-
Improving the reliability, resiliency of post-Sandy N.J. electric grid
According to NOAA, prolonged electrical outages, largely because of storms, have been steadily increasing in frequency since 1995. Sandia Lab will help East Coast communities devastated by Hurricane Sandy boost the resiliency of their electric grids, so they can be better prepared to deal with natural disasters in the future.
-
-
Research network to search for extraterrestrial intelligence launched in U.K.
A network has been launched to promote academic research in the United Kingdom relating to the search for extraterrestrial intelligence. The network brings together academics from eleven institutions across the country, and it covers a broad spectrum of research topics, including potential methods for detecting signals, the linguistic challenge of deciphering messages, the probability of an extraterrestrial civilization interacting with Earth, and the longevity of civilizations.
-
-
Protecting drinking water systems from deliberate contamination

The importance of water and of water infrastructures to human health and to the running of the economy makes water systems likely targets for terrorism and CBRN (chemical, biological, and radionuclide) contamination. Reducing the vulnerability of drinking water systems to deliberate attacks is one of the major security challenges. An international project has developed a response program for rapidly restoring the use of drinking water networks following a deliberate contamination event.
-
-
Earthquake-proofing precast buildings
Precast or ready-made building structures offer a number of advantages when compared to more traditional construction techniques in terms of time and cost savings. The vulnerability of joints and connections between assembled precast elements, however, is widely recognized as a potential safety issue, especially in earthquake-prone areas. An EU-funded project has set out to develop new procedures and guidelines for designing precast structure joints and connections that can stand up to seismic forces.
-
-
U.S. tax code has minimal effect on CO2, other greenhouse gas emissions
Current federal tax provisions have minimal net effect on greenhouse gas emissions, according to a new report from the National Research Council. The report found that several existing tax subsidies have unexpected effects, and others yield little reduction in greenhouse gas emissions per dollar of revenue loss.
-
-
Cuomo: New York infrastructure must be made more resilient in face of climate challenge
New York governor Andrew Cuomo says global warming l is a serious threat and that all levels of government must work together to design a more resilient infrastructure to deal with the changing weather.
-
-
Former Pentagon No. 2 suspected of being source of Stuxnet leaks
The Justice Department has informed Gen. (Ret.) James E. “Hoss” Cartwright that he is the target of an investigation into the leaking of a secret U.S.-Israeli cyber campaign to slow down Iran nuclear weapons program. The four-star Marine Corps general served as deputy chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff and was part of President Obama’s inner circle on many important national security issues before retiring in 2011.
-
-
Renewables to surpass gas by 2016 in the global power mix: IEA

An International Energy Agency (IEA) report says power generation from hydro, wind, solar, and other renewable sources worldwide will exceed that from gas and be twice that from nuclear by 2016.
-
-
Improved water purification technology reduces logistics burden
The logistics burden of supplying water to deployed troops is comparable to that of fuel and the economic cost is high. The Department of Defense (DoD) currently relies on a number of water desalination systems to produce clean water from local sources, but all of these systems have size, weight, and power (SWaP) constraints that affect their suitability for some missions. DARPA initiated the Materials with Novel Transport Properties (MANTRA) program to improve water desalination technologies and reduce their SWaP requirements.
-
-
Maryland shorelines facing sea level rise threatening state’s infrastructure: report
Maryland has 3,100 miles of tidal shoreline and low-lying rural and urban lands that will be impacted. A new report on sea level rise recommends that the State of Maryland should plan for a rise in sea level of as much as two feet by 2050. Governor Martin O’Malley said that “[we must] ensure that we have a sound understanding of our vulnerability and are making informed decisions about how best to protect our land, infrastructure, and most importantly, the citizens of Maryland.”
-
-
Transporting diluted bitumen through pipelines does not increase likelihood of release
Scientific study has found that the thick Canadian crude oil, known asdiluted bitumen, whichwould be shipped to the U.S. through the Keystone XL pipleline is no more dangerous than transporting other types of crude oil.
-
-
Environmentalists begin a summer of protest against Keystone project
A coalition of environmentalist groups calling itself “fearless summer” launched what it said would be a series of protests against the Keystone XLL pipeline project. Near the city of Seminole, Oklahoma, members of the group shackled themselves to industrial equipment and disruoted work at Keystone-related construction site. Ten were arrested.
-
More headlines
The long view
Water Wars: A Historic Agreement Between Mexico and US Is Ramping Up Border Tension
As climate change drives rising temperatures and changes in rainfall, Mexico and the US are in the middle of a conflict over water, putting an additional strain on their relationship. Partly due to constant droughts, Mexico has struggled to maintain its water deliveries for much of the last 25 years, deliveries to which it is obligated by a 1944 water-sharing agreement between the two countries.
Trump Is Fast-Tracking New Coal Mines — Even When They Don’t Make Economic Sense
In Appalachian Tennessee, mines shut down and couldn’t pay their debts. Now a new one is opening under the guise of an “energy emergency.”
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
