-
U.S. infrastructure drops in world infrastructure ranking

The U.S. infrastructure has slipped badly in the world’s infrastructure ranking, both in absolute and relative terms, according to the Global Competitiveness Report for 2012-13, published earlier this month by the World Economic Forum.
-
-
Wind energy in cold-climate countries showing significant potential
Wind energy capacity is growing rapidly in the cold climates of the world. According to the latest forecasts, between 45 and 50 gigawatts of wind energy will be built in cold climates by 2017, which would mean an increase of as much as 72 per cent since the end of 2012 and investments amounting to approximately 75 billion euro.
-
-
A majority on Earth will soon face severe, self-inflicted water shortage: scientists

A conference of 500 leading water scientists from around the world, held last week in Bonn, issued a stark warning that, without major reforms, “in the short span of one or two generations, the majority of the nine billion people on Earth will be living under the handicap of severe pressure on fresh water, an absolutely essential natural resource for which there is no substitute. This handicap will be self-inflicted and is, we believe, entirely avoidable.”
-
-
New filtration material to make petroleum refining cheaper, more efficient
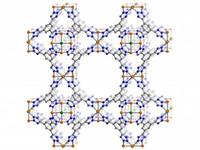
A newly synthesized material might provide a dramatically improved method for separating the highest-octane components of gasoline. The material is a metal-organic framework, or MOF, which can be imagined as a sponge with microscopic holes.
-
-
Report: U.S. companies should consider counter-hacking Chinese hackers
A group studying how the United States should respond to the sustained campaign of cyberattacks conducted by Chinese government hackers against U.S. companies, said the United States should seriously consider a campaign of retaliatory cyberattacks against the hackers.
-
-
GOP lawmakers urge Obama not to link Keystone decision to climate policies
Democrats who are uncomfortable with the Keystone XL pipeline have urged President Obama to consider attaching policies requiring cuts in greenhouse gases emissions to his approval of the project. Republican lawmakers are urging the president not to link approval of Keystone to climate change policies.
-
-
Administration more actively to support expansion of fracking
The Obama administration is leaning toward offering more active support for the expansion hydraulic fracturing, or fracking, despite the opposition of environmental groups.
-
-
House will see floor battle today over Keystone XL pipeline
Republican and Democrats lawmakers are set to engage in a fierce battle on the House floor over the fate of the Keystone XL project. Representative Lee Terry’s (R-Nebraska) proposed legislation to allow TransCanada to start construction of the Keystone XL pipeline, which runs from Hardisty, Canada through seven states to Houston, Texas. The bill will come to the House floor today.
-
-
Algae could become an important source of fuel in U.S.

A new analysis shows that the U.S. land and water resources could likely support the growth of enough algae to produce up to twenty-five billion gallons of algae-based fuel a year in the United States, one-twelfth of the country’s yearly needs.
-
-
U.S. to help protect private companies from malicious cyberattacks
The U.S. government said it will help protect private companies from cyber attacks. DHS secretary Janet Napolitano said a system is being developed which will monitor Internet traffic directed to critical infrastructure businesses and block attacks on software programs.
-
-
Senate passes water resources bill, funding flood control projects
Several projects for the Army Corps of Engineers will now be expedited under a bi-partisan Senate legislation passed last Wednesday. The authors of the bill hope the legislation will move the Morganza-to-the-Gulf hurricane protection project forward. The project goal is to install a series of levees, locks, and other systems through the Terrebonne and Lafourche parishes, which will protect about 200,000 people from storm surges like the ones Hurricane Katrina caused.
-
-
Compressing air for renewable energy storage
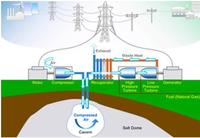
Enough Northwest wind energy to power about 85,000 homes each month could be stored in porous rocks deep underground for later use, according to a new, comprehensive study. Researchers identified two unique methods for this energy storage approach and two eastern Washington locations to put them into practice.
-
-
Panel's draft bill shields DHS funds
A house panel introduced a bill last week that will protect DHS from budget cuts facing other domestic agencies under the house’s budget plan. This will allow the department to hire 1,600 new agents at Customs and Border Patrol agency, replace cuts to local and state governments, boost spending on cybersecurity, and abandon cuts to the Coast Guard.
-
-
Cybersecurity framework for critical infrastructure: analysis of initial comments
On 12 February 2013 President Obama issued the “Improving Critical Infrastructure Cybersecurity” executive order, which called for the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) to work with industry to develop a voluntary framework to reduce cybersecurity risks to the nation’s critical infrastructure, which includes power, water, communication, and other critical systems.
-
-
GPS technology offers 3-minute tsunami alerts
Researchers show that by using global positioning systems (GPS) to measure ground deformation caused by a large underwater earthquake, they can provide accurate warning of the resulting tsunami in just a few minutes after the earthquake onset.
-
More headlines
The long view
Water Wars: A Historic Agreement Between Mexico and US Is Ramping Up Border Tension
As climate change drives rising temperatures and changes in rainfall, Mexico and the US are in the middle of a conflict over water, putting an additional strain on their relationship. Partly due to constant droughts, Mexico has struggled to maintain its water deliveries for much of the last 25 years, deliveries to which it is obligated by a 1944 water-sharing agreement between the two countries.
Trump Is Fast-Tracking New Coal Mines — Even When They Don’t Make Economic Sense
In Appalachian Tennessee, mines shut down and couldn’t pay their debts. Now a new one is opening under the guise of an “energy emergency.”
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
