-
Researchers invent safe wireless vehicle charging technology
Researchers have invented a safe, efficient technology wirelessly to charge electric vehicles using “remote magnetic gears” — a rotating base magnet driven by electricity from the grid, and a second located within the car — and successfully tested it on campus service vehicles
-
-
A coal economy has multiple health, social risks, says major review
A major review of evidence on the impact of coal mining has highlighted serious, ongoing health and social problems, and an urgent need for improvements in government coal mining policy
-
-
Hurricanes will test Florida buildings, built under new, post-Wilma building codes
In 2005 Hurricane Wilma was responsible for five deaths and millions of dollars worth of damage in Florida; building codes in the state were updated, and experts predict that these new buildings, most of which were designed with wind-tunnel testing, should perform well in all but the most severe conditions
-
-
Human activity can trigger an earthquake
Earthquakes occur when tectonic plates try to move past each other, and the friction between them holds them in place; the friction creates energy which builds up, and when the plates move past each other, the energy is released, triggering an earthquake; fracturing increases the fluid pressure inside faults; this increased pressure, in turn, lowers the stress threshold for triggering an earthquake enough for one to take place
-
-
Thawing permafrost to release nitrogen, carbon – doubling the amount of carbon in the atmosphere today
As much as forty-four billion tons of nitrogen and 850 billion tons of carbon stored in arctic permafrost, or frozen ground, could be released into the environment as the region begins to thaw over the next century as a result of a warmer planet; for context, this is roughly the amount of carbon stored in the atmosphere today
-
-
Asteroid DA14 will be whizzing by Earth on 15 February -- the closest asteroid fly by in history
On 15 February 2013, asteroid 2012 DA14, the size of a city block, will be whizzing within 14,000 miles of Earth, squeezing between Earth’s atmosphere and the geostationary satellites orbiting the planet; it will be the closest asteroid fly by in history; experts say there is no chance the asteroid will hit Earth — this time; with more than 4,700 asteroids NASA has identified as potential threats to Earth, however, some as big as sixteen football fields, these objects are getting a lot of attention
-
-
Paintballs may deflect an incoming asteroid
With twenty years’ notice, paint pellets could cause an asteroid to veer off course; researchers say that, if timed just right, pellets full of paint powder, launched in two rounds from a spacecraft at relatively close distance, would cover the front and back of an asteroid, more than doubling its reflectivity, or albedo; the initial force from the pellets would bump an asteroid off course; over time, the sun’s photons would deflect the asteroid even more
-
-
U.S. shale gas drives up coal exports – and CO2 emissions
U.S. CO2 emissions from domestic energy have declined by 8.6 percent since a peak in 2005, the equivalent of 1.4 percent per year; researchers warn, however, that more than half of the recent emissions reductions in the power sector may be displaced overseas by the trade in coal
-
-
Making toilets out of waste plastic
Washington Open Object Fabricators (WOOF) has won the 3D4D Challenge, and awarded a prize of $100,000 to help toward implementing the winning project – which will enable waste plastic to be used as filament for 3D printing machines, to create new products; the winning team plans to use the winning technology to address local issues in water and sanitation in Oaxaca, Mexico
-
-
Understanding the effects of Fukushima by studying fish
Japan’s “triple disaster,” as it has become known, began on 11 March 2011, and remains unprecedented in its scope and complexity; to understand the lingering effects and potential public health implications of that chain of events, scientists are turning to a diverse and widespread sentinel in the world’s ocean: fish; the data from Japan fisheries provide a look at how the ocean is faring eighteen months after the worst accidental release of radiation to the ocean in history
-
-
Safety glass – cut to any shape
If an object slams into the glass façade of a high-rise building, the glass must not shatter and fall down, because it could harm pedestrians below; in addition, the window panes must hold if a person were to fall against it from the inside; architects and builders must therefore use something stronger than laminated safety glass on the façades of high rise buildings; scientists develop a method which offers more flexibility with the design and handling of safety glass
-
-
Carbon-negative fuel at projected cost of less than $1.50 per gallon

Cool Planet Energy Systems the other day announced a major breakthrough in the commercialization and affordability of biofuels from non-food biomass that can run in any vehicle on the road today; a successful field testing was conducted at Google Campus
-
-
Scientists improving process to recycle rare-earth materials
Recycling keeps paper, plastics, and even jeans out of landfills. Could recycling rare-earth magnets do the same? Perhaps, if the recycling process can be improved; scientists are working more effectively to remove the neodymium, a rare earth element, from the mix of other materials in a magnet; initial results show recycled materials maintain the properties that make rare-earth magnets useful
-
-
Large-scale production of algae-based biofuels poses sustainability concerns

Scaling up the production of biofuels made from algae to meet at least 5 percent — approximately thirty-nine billion liters — of U.S. transportation fuel needs would place unsustainable demands on energy, water, and nutrients, says a new report from the National Research Council; these concerns, however, are not a definitive barrier for future production, and innovations that would require research and development could help realize algal biofuels’ full potential
-
-
New biorenewables technology about to reach the marketplace
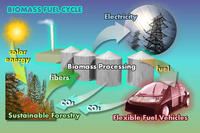
Innovative technology provides a new way to transform cellulosic biomass into renewable fuels and high-value chemicals; ,the technology uses ionic liquids to break down cellulosic or non-food plant biomass without using enzymes or costly pretreatment steps
-
More headlines
The long view
Helping Strengthen America’s Critical Infrastructure
Everyday life depends on a robust infrastructure network that provides access to running water, communications technology and electricity, among other basic necessities. The experts who keep our national infrastructure secure and resilient also need a strong network to share their knowledge and train the next generation of professionals capable of solving complex infrastructure challenges.
AI and the Future of the U.S. Electric Grid
Despite its age, the U.S. electric grid remains one of the great workhorses of modern life. Whether it can maintain that performance over the next few years may determine how well the U.S. competes in an AI-driven world.
Using Liquid Air for Grid-Scale Energy Storage
New research finds liquid air energy storage could be the lowest-cost option for ensuring a continuous power supply on a future grid dominated by carbon-free but intermittent sources of electricity.
Enhanced Geothermal Systems: A Promising Source of Round-the-Clock Energy
With its capacity to provide 24/7 power, many are warming up to the prospect of geothermal energy. Scientists are currently working to advance human-made reservoirs in Earth’s deep subsurface to stimulate the activity that exists within natural geothermal systems.
Experts Discuss Geothermal Potential
Geothermal energy harnesses the heat from within Earth—the term comes from the Greek words geo (earth) and therme (heat). It is an energy source that has the potential to power all our energy needs for billions of years.
