-
2002 Alaska earthquake helped set standards for buildings, bridges
The Denali 7.9 earthquake that hit Alaska in 2002 was the largest to hit the United States in more than 150 years, and the strongest ever recorded in Alaska; no one was killed and only a few people were injured; the only severe damage the earthquake caused was to a few highways, but the damage was not significant enough to close them; the earthquake set new national standards for building bridges as well as giving seismologists a better understanding of how earthquakes affect frozen ground
-
-
Cooler pavement materials could increase energy consumption in surrounding buildings
A push to replace old, heat-trapping paving materials with new, cooler materials could actually lead to higher electricity bills for surrounding buildings; the new paving materials are designed to lower the overall temperature of the areas where they are used
-
-
Future warming likely to be on high side of climate projections: analysis
Climate model projections showing a greater rise in global temperature are likely to prove more accurate than those showing a lesser rise, according to a new analysis by scientists at the U.S. National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR); NCAR says that the findings could provide a breakthrough in the longstanding quest to narrow the range of global warming expected in coming decades and beyond
-
-
Nor'easter batters NYC, New Jersey
A nor’easter battered New York and New Jersey on Wednesday with rain and wet snow, plunging homes back into darkness, stopping commuter trains, and inflicting yet more misery on thousands of people still trying to recover from Superstorm Sandy; ordinarily, the nor’easter would not pose major problems, but this was not the case yesterday, as the storm hit an area where electrical systems were still fragile and many of Sandy’s victims still busy cleaning their homes and coping with deepening cold
-
-
MIT researchers develop method to help communities plan for climate risk
As the devastation left by Sandy continues to reverberate, decision-makers at every level are asking: How can we be better prepared? MIT researchers developed a tool to assess regional risks of climate change and potential impacts on local infrastructure and planning; the tool helps policymakers, city planners, and others see the possible local effects of climate change, such as long-term temperature and precipitation changes, allowing local planners to evaluate risks, and how these risks could shape crops, roads, and energy infrastructure
-
-
Dealing with power outages more efficiently
When there is a power failure, the utility companies, public officials and emergency services must work together quickly; researchers have created a new planning software product that enables all participants to be better prepared for emergency situations
-
-
Building material of millennium: Autoclave Aerated Concrete

Although widespread rebuilding in the hard-hit New York metro region from Hurricane Sandy has not yet begun, New Jersey Institute of Technology (NJIT) scientists say when the hammers start swinging, it is time to look at autoclaved aerated concrete; the material, best known as AAC, has been heralded as the building material of the new millennium
-
-
The limitations of climate models

How accurate is the latest generation of climate models? Climate physicists have compared them with old models and draws a differentiated conclusion: while climate modeling has made substantial progress in recent years, we also need to be aware of its limitations
-
-
Scientists resurrect process to convert sugar directly to diesel

A long-abandoned fermentation process once used to turn starch into explosives can be used to produce renewable diesel fuel to replace the fossil fuels now used in transportation; the retooled process produces a mix of products that contain more energy per gallon than ethanol that is used today in transportation fuels and could be commercialized within 5-10 years
-
-
Inflatable giant plugs could have saved NYC subway system

Inflatable plugs being developed with funding from DHS, could have saved some of New York’s subway and highway tunnels from flooding during Hurricane Sandy, according to the developers of the plugs; DHS successfully tested a plug earlier this year, using a 16-foot diameter prototype to hold back pressurized water at a test tunnel in Morgantown, West Virginia; the idea was originally intended to protect tunnels from terrorist attacks
-
-
Dutch flood-protection may be suitable for New York, other East Coast cities

Megastorms and disasters are not going to continue to be once in a lifetime storms, but instead become more of an annual occurrence; experts say that the combination of more frequent megastorms and rising sea levels across the east coast would forcemany cities to get serious about flood protection
-
-
Long-term sea level rise could cost Washington, D.C. billions
New study projects that the city of Washington, D.C., and federal property in the city, could suffer billions of dollars in damage if sea level rise as a result of global warming increases over the next century. Potential for significant damage will be even greater in the event of extreme weather like Hurricane Sandy
-
-
2011 Virginia quake triggered landslides very far away
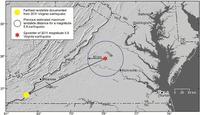
The 2011 Mineral, Virginia M-5.8 earthquake was felt over an extraordinarily large area; a new study details landslides triggered by the earthquake at distances four times greater and over an area twenty times larger than previously documented for M-5.8 earthquakes worldwide
-
-
Many NYC buildings to remain closed for weeks, months for clean-up, repairs
Water and winds produced by Hurricane Sandy destroyed mechanical and electrical systems in many commercial and residential buildings in Lower Manhattan; as a result, many buildings in the area are weeks or months away from being repaired and fully operational
-
-
Protecting New York City from storms, surges
Almost a week after Hurricane Sandy hit New York City; people are still picking up the pieces of their former lives; for New York officials, the next step is decide how best to protect New York City from a similar disaster in the future; there are many ideas and proposals, ranging from moveable sea gates, to expanding protective marshlands and wetlands, to creating a system of artificial reefs in the channel along the Red Hook and Gowanus neighborhoods of Brooklyn, made out of rocks, shells, and fuzzy rope that will promote the growth of oysters
-
More headlines
The long view
Water Wars: A Historic Agreement Between Mexico and US Is Ramping Up Border Tension
As climate change drives rising temperatures and changes in rainfall, Mexico and the US are in the middle of a conflict over water, putting an additional strain on their relationship. Partly due to constant droughts, Mexico has struggled to maintain its water deliveries for much of the last 25 years, deliveries to which it is obligated by a 1944 water-sharing agreement between the two countries.
Trump Is Fast-Tracking New Coal Mines — Even When They Don’t Make Economic Sense
In Appalachian Tennessee, mines shut down and couldn’t pay their debts. Now a new one is opening under the guise of an “energy emergency.”
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
