-
App-enabled robocopters to bring supplies to Marines

Marines running low on ammo may one day use an app on their digital handhelds to summon a robotic helicopter to deliver supplies within minutes; the Navy officials in charge of the program are seeking researchers who will develop threat- and obstacle-detection and avoidance systems, as well as autonomous landing capabilities that can operate across different types of aircraft
-
-
Military seeking high-pressure materials without high-pressure processes
Military missions place tremendous stress on the materials used for defense weapons, vehicles, and other applications; applications range from stronger armor, to lighter weights which allow for faster propulsion, to greater resiliency in aerospace, ground, and naval platforms
-
-
U.S. Army to deploy VTOL UAV
The U.S. Army is developing a helicopter-like, VTOL (vertical-take-off-and-landing) UAS (unmanned aircraft system) with a DARPA-sponsored ARGUS wide-area surveillance sensor suite designed to beam back information and images of the surrounding terrain
-
-
NORAD is ready to track Santa's flight
The North American Aerospace Defense Command is getting ready to track Santa’s yuletide journey. The NORAD Tracks Santa Web site went live the other day featuring a Countdown Calendar, a Kid’s Countdown Village complete with holiday games and activities that change daily, and video messages from students and troops from around the world
-
-
The Israeli military prepares for a new type of war
The Israel Defense Force (IDF) has created a new military command – the Strategic Depth Command; this new command, and the new, commando-heavy, look of the IDF’s higher echelon, should tell us that Israel is preparing for a new type of war; adversaries of Israel who have been entertaining the thought that sheer distance from Israel would offer them some protection, may want to think again
-
-
Research may yield more compact antennas for military use
Researchers say that the tall, bulky antennas the U.S. military uses could be scrapped for low-profile, broadband antennas — thanks to a different approach to antenna design that replaces large dipole antennas with a more compact and conformal multi-mode radiator
-
-
New material increases weapons' explosive force
A new material, called High-Density Reactive Material (HDRM), is designed to replace steel in warhead casings with little or no compromise in strength or design
-
-
Research centre to combat devastating effects of roadside bombs

Gaining a better understanding of the injuries caused by roadside bombs and improving both treatment and the means of protection are key aims of a new £8 million research center launched the other day; designing “intelligent” combat boots to deflect the impact of a roadside bomb and diagnosing damage more quickly in the injured to reduce future medical problems are two potential benefits
-
-
U.S. Marines train in collect biometrics, evidence
U.S. Marines train in an “Afghan” city built inside a California Marines base; they train in foot-patrols, room clearing, and search operations where they collected biometric data and other evidence on citizens displaying suspicious behavior or possessing contraband
-
-
Dogs of war: the role of canines in the Second World War
A new book examines how dogs were used by the U.S. and Japanese militaries during the Second World War; the book goes beyond the battlefield duties of these four-legged soldiers and captures how dogs like New York City’s “Skippy” and Tokyo’s “Aren” mobilized their people to their nations’ causes
-
-
Autonomous deployment vehicles in flight tests
The Autonomous Deployment Demonstration (ADD) program has successfully completed flight tests; the ADD concept is to enable small unmanned air vehicles (UAV) equipped with sensor payloads to be launched from aircraft (manned or unmanned), balloons, or precision guided munitions, and dispersed in selectable patterns around designated areas
-
-
Raytheon tests smallest air-launched weapon in its portfolio

Unmanned vehicles continue to evolve, and defense contractors build munitions form them; Raytheon has completed captive carry tests of its Small Tactical Munition Phase II configuration, paving the way for flight tests
-
-
Nature inspires advances in ultrasound technology
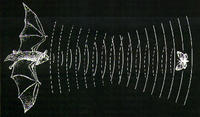
Sonar and ultrasound, which use sound as a navigational device and to paint accurate pictures of an environment, are the basis of many technologies, including medical ultrasound machines and submarine navigation systems; when it comes to more accurate sonar and ultrasound, however, animals’ “biosonar” capabilities still have the human race beat – but not for long
-
-
Brazilian fern inspires waterproof coating
A floating weed that clogs waterways around the world has at least one redeeming feature: it has inspired a high-tech waterproof coating intended for boats and submarines
-
-
Researchers fire 1,000th shot on laboratory railgun
Scientists reached a milestone in the Electromagnetic Railgun program when they fired a laboratory-scale system for the 1,000th time on 31 October, the raygun is a long-range weapon that launches projectiles using electricity instead of chemical propellants
-
More headlines
The long view
Bookshelf: Smartphones Shape War in Hyperconnected World
The smartphone is helping to shape the conduct and representation of contemporary war. A new book argues that as an operative device, the smartphone is now “being used as a central weapon of war.”
