-
Radiation problems on San Francisco’s Treasure Island persist

The Army Corps of Engineers created San Francisco’s Treasure Island for the 1939 Golden Gate International Exposition, with plans to turn the island into a civilian airport after the exposition. When the United States entered the Second World War in 1941, the Navy used the island for the Treasure Island Naval Station, where nuclear war training exercises were conducted. The Naval Station was decommissioned in 1993, and parts of the island were transferred to SF for civilian use. Radiation levels on the island are still high, however, and critics charge that the Navy did not do enough to clean the island while downplaying the risks of radiation that still remain.
-
-
Employees exposed to radiation at nuclear waste disposal site
Thirteen employees at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant(WIPP),a nuclear waste burial site in New Mexico, have been exposed to radioactive radiation after a leak in one of WIPP’s underground tunnels. Energy Department officials say it is too soon to determine the scope of health risks the employees will deal with. The employees inhaled plutonium and americium, both of which can irradiate the body’s internal organs with subatomic particles for a lifetime.
-
-
Islanders’ radiation worries 60 years after Bikini Atoll atomic test

Sixty years ago, On 1 March 1954 the United States tested a 15-megaton hydrogen bomb – a thousand times more powerful than the bomb dropped on Hsroshima —- at Bikini Atoll, part of the Marshall Islands. The explosion vaporized one island, and exposed inhabitants on neighboring islands to radioactive fallout. The United States relocated many of the islanders and spent years – and more than $45 million – to clean up and decontaminate the islands, before allowing the relocated inhabitants to return. Many were forced to leave again, however, after they were found to be exposed to residual radiation. From 30 June 1946 to 18 August 1958, the United States conducted 67 atmospheric nuclear tests in the Marshall Islands.
-
-
Operator of Hanford nuclear disposal site fires scientists who voice safety concerns
The Hanford project in Washington State is the Department of Energy’s (DoE) largest nuclear cleanup project. DoE plans to transform fifty-six million gallons of radioactive sludge, currently stored in underground tanks, into solid glass. Scientists and engineers who work at Hanford have questioned the effectiveness of the required technology, and have voiced serious concerns about safety issues. Two of those who were the most persistent in voicing their concerns about safety have been fired, and a third one has left his job voluntarily.
-
-
Cost of plutonium disposal facility skyrockets
The Mixed Oxide (MOX) nuclear fuel factory at the Savannah River Site in South Carolina, being built to help dispose of cold war-era weapon-grade plutonium, would cost up to $30 billion in addition to the $4 billion spent on construction so far. The staggering cost overruns have led many to call for a new, less expensive solution. Matthew Bunn, a former Clinton White House official who helped develop the plutonium disposal program, agrees that the cost of the MOX factory is excessive. “The things we’re trying to accomplish aren’t worth that amount of money,” he said.
-
-
IAEA: Iran's stockpile of 20% enriched uranium shrunk under interim nuclear agreement
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) reports in its quarterly inspections assessment that the quantity of 20 percent enriched uranium in Iran’s hands has been reduced since last November, when the world’s six powers (P5+1) and Iran have reached an interim agreement on Iran’s nuclear activities. Iran now has 354 pounds of the material — or about one-fifth less than what it had in November. With the right type of centrifuges, it is quicker to enrich uranium from 20 percent to weapon-grade 90 percent than it is to enrich uranium from 1 or 2 percent to 20 percent, so that the smaller the amount of 20 percent uranium a country has, the longer the “breakout” time — the time it would take a country to assemble a nuclear bomb once a decision to do so has been made.
-
-
Operations at a New Mexico nuclear waste repository suspended because of leaks
Operations at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant, or WIPP, a New Mexico burial site for military nuclear waste, were suspended for the fourth day, the Department of Energy said, after sensors picked up radiation leaks inside salt tunnels where the radioactive material is entombed.Officials said no radiation escaped to the surface.This is the second time this month the facility had to suspend operations. Earlier this month operations were halted after a truck caught fire in an underground tunnel.
-
-
33 A.D. Old Jerusalem earthquake helps determine age of Shroud of Turin
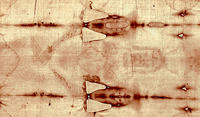
The Shroud of Turin has been at the center of scientific controversy and questions ever since Secondo Pia took the first photograph of it in 1898: whether it is Jesus’s purported burial cloth, how old it might be, and how the image was created. Scientists who conducted radiocarbon dating of the cloth in 1988 determined that the shroud was only 728 years old at the time, and thus that it could not have been in existence during Jesus’s life. Other scientists have since suggested that the shroud is much older, and thus that it could have been produced during Jesus’s time, and that the dating process was incorrect because of neutron radiation — a process which is the result of nuclear fusion or nuclear fission during which free neutrons are released from atoms — and its interaction with the nuclei of other atoms to form new carbon isotopes. No plausible physical reason, however, had been proposed to explain the origin of this neutron radiation – until now: Italian scientists say the source of the neutron emission is a historical earthquake in 33 A.D. in Old Jerusalem, which measured 8.2 on the Richter scale.
-
-
Security of dirty bomb materials in U.S. inadequate: experts
There are more than 5,000 medical and research devices in the United States containing high-activity radiation sources, including 700 with category-1 sources. Category-1 radiation material could be used by terrorists in dirty bombs. The security measures developed by the industry were written with accident prevention in mind, not in order to thwart a deliberate, forcible effort by terrorists or criminals to gain control of the toxic material. In addition, radioactive materials were considered to be “self-protecting,” because it was assumed that the powerful radiation would deter anyone thinking of tampering with these devices. Terrorist bomb-makers, however, showed themselves to be more technologically-savvy than earlier thought, and, in any event, suicide bombers would not be deterred by the risk of radiation poisoning.
-
-
Nuclear physicists prove a Peggy Guggenheim Collection painting is a fake
For more than forty years now, art experts and researchers have been trying to determine whether a painting in the Peggy Guggenheim Collection in Venice was a genuine painting which the French artist Fernand Leger produced between 1913 and 1914 as part of his “Contraste de Formes” series. Scientists from the Instituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare (INFN) in Florence have used, for the first time in the art world, a brand new carbon 14 dating method — the so-called “bomb peak” curve, which measures the presence of C-14 in the atmosphere — to establish that the canvas used in the painting was produced in 1959, and thus could not have been used by Leger, who died in 1955.
-
-
Chemical, physical traits of post-nuclear detonation fallout identified
Post-detonation nuclear forensics relies on advanced analytical techniques and an understanding of the physio-chemical processes associated with a nuclear detonation to identify the device type and the source of the nuclear material in the device. Researchers have begun to develop a technique that provides a practical approach for looking into the complex physical and chemical processes that occur during fallout formation following a nuclear detonation.
-
-
The basis for a permanent deal: deep, verifiable changes to Iran’s nuclear program
A new study says that only broad and verifiable changes to Iran’s current nuclear program could serve as a basis for a permanent nuclear deal between Iran and the international community. Among the changes: reducing the number of Iran’s uranium-enrichment centrifuges from the current 19,500 to no more than 4,000, and limiting Iran to one enrichment site; converting the heavy-water reactor being built in Araq to a light-water reactor fueled by low-enriched uranium; and imposing a tight, intrusive inspection regime for at least twenty years.
-
-
Service lives of European nuclear power stations to be extended
Germany has decided to abandon nuclear energy – in what the Germans call Energiewende (energy turnaround) – but new nuclear power stations are being built on all sides of Germany and service lives for existing facilities on the territory of Germany’s neighbors are being extended. German nuclear scientists should thus continue to be involved in assessing the safety of the nuclear power stations in neighboring countries, especially so since the EU has launched its LONGLIFE project, which aims to extend the service life of existing reactors from forty to sixty or even eighty years.
-
-
NRC: storing spent nuclear fuel in cooling pools is safe
The nuclear reactors now in service in the United States were built with the assumption that the spent fuel would be removed from nuclear the facilities after a few years, but because the government has failed to provide a centralized place to store the spent fuel, utility companies have had to store an ever-growing quantity of it in spent fuel pools on the grounds of the facilities. Scientists argue that it would be safer to move some of the spent fuel into giant steel and concrete casks, where it can be stored dry, with no reliance on water, pumps, or filters to keep them cool. The nuclear industry and the NRC do not agree.
-
-
Surviving a nuclear explosion in your city

During the cold war, scientists modeled every imaginable consequence of a nuclear explosion. Michael Dillon, a Lawrence Livermore Lab mathematician, found a gap in the sheltering strategies for people far enough from ground zero to survive the initial blast but close enough to face deadly radioactive fallout. Dillon’s model’s addresses the most vulnerable people, those who found shelter from the blast in lightweight buildings, or buildings lacking a basement (these buildings are more easily penetrated by deadly radioactive dust). His recommendations: if adequate shelter is fifteen minutes away, people should remain in their initial, poor-quality shelter no longer than thirty minutes after detonation. If the better shelter is only five minutes away, however, individuals should move there immediately, leaving the closer but unsafe buildings altogether.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
